Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC)
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
EMERGIA post-doctoral research in the Sky Quality Office
Research Professor at the IAA-CSIC (Granada) and co-principal investigator of the SO/PHI instrument on board Solar Orbiter
Astrophysicist at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (IAA-CSIC)
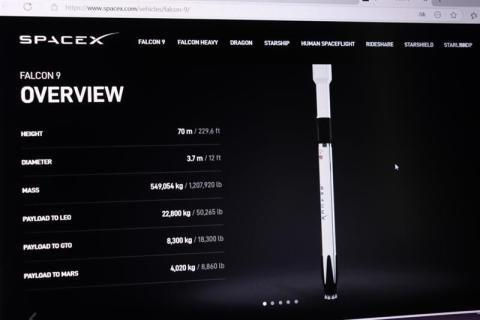
In February 2025, lithium concentrations suddenly increased around 96 km above sea level some 20 hours after a SpaceX Falcon 9 launch vehicle re-entered the atmosphere. This is the first direct detection of pollution in the upper atmosphere due to the re-entry of a spacecraft, according to a study published in Communications Earth & Environment. Lithium is used in spacecraft components, but it is only found naturally at these altitudes in trace amounts, and its accumulation could have consequences on the climate.

The rapid growth of satellite constellations threatens the operation of space telescopes, according to a study published in Nature. If the planned launches are completed, the Hubble Space Telescope could see more than a third of its images affected by light pollution from these satellites, as they share the same orbital space, while other telescopes would have more than 96% of their images damaged, the authors estimate.
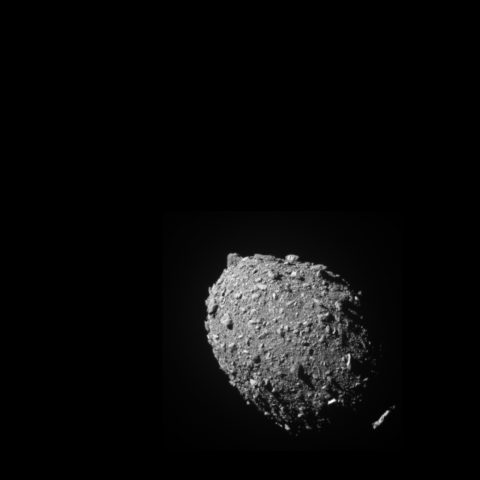

As planned, the DART (Double Asteroid Redirect Test) mission has hit the asteroid Dimorphos, which orbits a larger asteroid, Didymos. Neither is a threat to Earth. This is the first planetary defence test mission designed to change the orbit of an asteroid, launched by NASA and the Johns Hopkins APL laboratory, with Spanish participation. Scientific teams will study with ground-based telescopes how much the orbit of Dimorphos will change around Didymos after the collision.
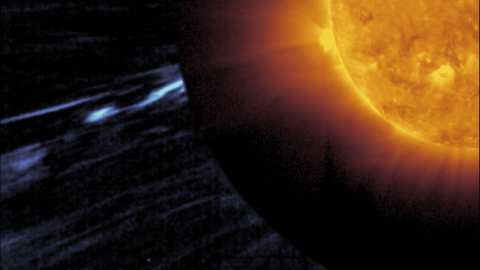
The ESA/NASA Solar Orbiter mission may have made the first direct observation of what are known as magnetic switchbacks on the Sun. The phenomenon, which consists of S-shaped disturbances that cause sudden reversals of its magnetic field, had been identified by different space probes since the 1970s, but its explanation had only been described theoretically. The finding is published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.