Catalan Institute of Human Palaeoecology and Social Evolution (IPHES)
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Researcher at the Catalan Institute of Human Paleoecology and Social Evolution (IPHES-CERCA), associate professor at Rovira i Virgili University, and co-director of the Atapuerca project
Ramón y Cajal researcher at IPHES-CERCA
Researcher at IPHES-CERCA in Tarragona, associate professor at the Universitat Rovira i Virgili and associate researcher at the Muséum National d 'Histoire Naturelle (Paris, France)
Researcher at IPHES-CERCA and associate professor at the Rovira i Virgili University of Tarragona (URV)
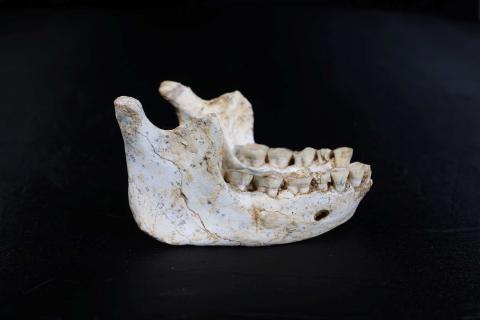
An international team with Spanish participation has analysed hominid remains discovered in Casablanca (Morocco) and concluded that they could be very close ancestors of early modern humans. The fossils date from around the same period as the Homo antecessor found in Atapuerca—some 773,000 years ago—but are morphologically different. According to the authors, who published their findings in Nature, the fossils offer clues about the last common ancestor shared with Neanderthals and Denisovans, and support an African, rather than Eurasian, origin for H. sapiens.

A research team led by the British Museum presents evidence in the journal Nature that humans were making fire – deliberately and not just taking advantage of natural fires – 400,000 years ago in Barnham (United Kingdom). The remains analysed, including burnt sediments, heat-damaged flint axes and pieces of pyrite, are much older than those recorded to date, which dated the deliberate use of fire to around 50,000 years ago in northern France.

An international team of geneticists and archaeologists has analysed more than 50 ancient Iron Age genomes from an area of southern Britain. Their conclusions are that they belonged to a matrilocal society, in which land was inherited through the female line and husbands moved in with the community of their wives. The results are published in the journal Nature and would be the first such finding in prehistoric Europe.
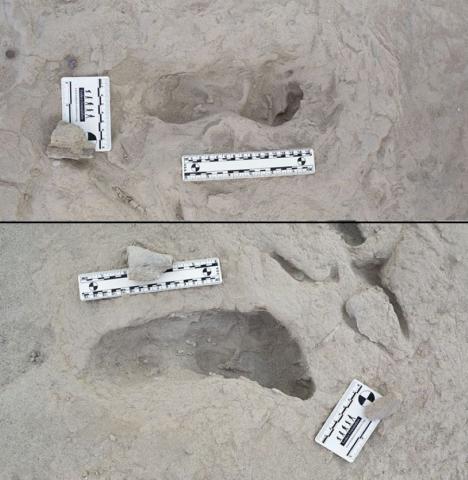

At least two hominin species - Homoerectus and Paranthropus boisei- coexisted in Kenya's Turkana Basin around 1.5 million years ago, a study published in Science confirms. The authors describe the first physical evidence of this coexistence in the form of footprints, found at several sites in the area.

The Karolinska Institute has awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology to Swedish biologist Svante Pääbo, a specialist in evolutionary genetics, for his discoveries on the genomes of extinct hominids and human evolution.