
Institute of Astrophysics of the Canary Islands (IAC)
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Research professor at the Canary Islands Institute of Astrophysics
Support astronomer at the Canary Islands Institute of Astrophysics
In February 2025, lithium concentrations suddenly increased around 96 km above sea level some 20 hours after a SpaceX Falcon 9 launch vehicle re-entered the atmosphere. This is the first direct detection of pollution in the upper atmosphere due to the re-entry of a spacecraft, according to a study published in Communications Earth & Environment. Lithium is used in spacecraft components, but it is only found naturally at these altitudes in trace amounts, and its accumulation could have consequences on the climate.

The rapid growth of satellite constellations threatens the operation of space telescopes, according to a study published in Nature. If the planned launches are completed, the Hubble Space Telescope could see more than a third of its images affected by light pollution from these satellites, as they share the same orbital space, while other telescopes would have more than 96% of their images damaged, the authors estimate.
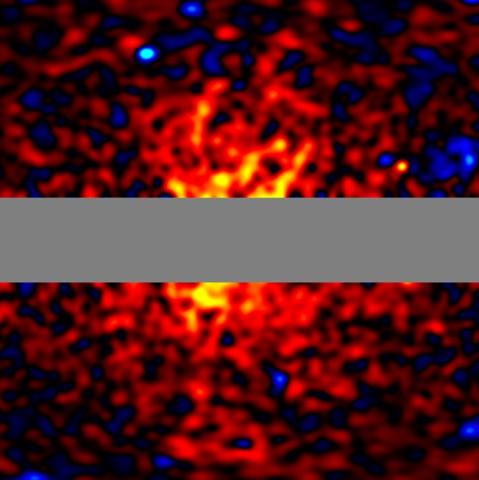
A century ago, astronomer Fritz Zwicky observed that galaxies were moving faster than their mass should allow, leading him to infer the presence of an invisible structure, dark matter. Since the particles that make up dark matter do not interact with electromagnetic force, they cannot be observed directly, as they do not absorb, reflect, or emit light. Now, NASA's Fermi space telescope has found specific gamma rays in the center of the Milky Way that are consistent with the decay of theoretical dark matter particles, although they could also come from other sources. “If this is correct, to my knowledge, it would be the first time that humanity has ‘seen’ dark matter,” said study author Tomonori Totani in a press release. The article is published in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics.

Space-based solar power could provide electricity to support Europe's net-zero emissions target if its cost of supply is reduced sufficiently. This is one of the conclusions of an article published in the journal Joule, by the Cell Press group. Space solar panels would allow continuous capture of solar energy, rather than only when light reaches Earth, reducing the need for wind and solar energy on Earth by 80% in Europe. The researchers estimate that by 2050, space-based solar power could reduce the costs of the European electricity system, although this depends on the development of two NASA space-based solar power designs they have used for their research: the Innovative Heliostat Swarm and the Mature Planar Array.
The maximum number of artificial satellites that can safely orbit the Earth could be reduced due to the increase in greenhouse gas emissions of human origin, according to a modelling study. The increase in these gases may result in a reduction in the density of the planet's orbital space. Between 2000 and 2100, the carrying capacity of satellites between 200 and 1,000 kilometres altitude could be reduced by between 50 and 66%, estimates the study published in Nature Sustainability.

Space debris and satellites orbiting close to Earth have proliferated in recent years. Two articles in Nature Astronomy warn of their impact on light pollution. In the first, a team calculates the increase in the brightness of the night sky and warns of the effect on ecosystems and astronomical observations from Earth. In the second, which is a commentary, the authors call for limiting the production of artificial light and the number of satellites in orbit, calling on the scientific community to take on the big space and big light companies. Both articles are co-signed by Salvador Bará, from the Agrupación Astronómica Coruñesa, and the second by Fabio Falchi, from the University of Santiago de Compostela.