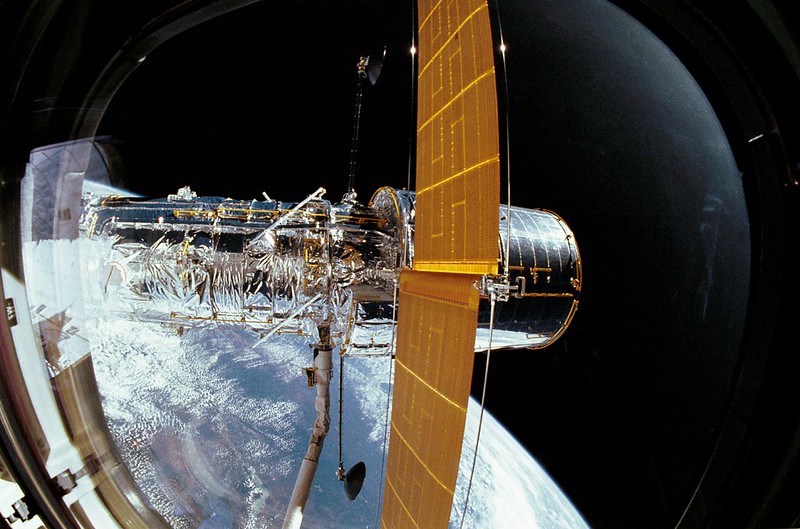
A study warns of the impact that satellite megaconstellations will have on images from space telescopes such as Hubble
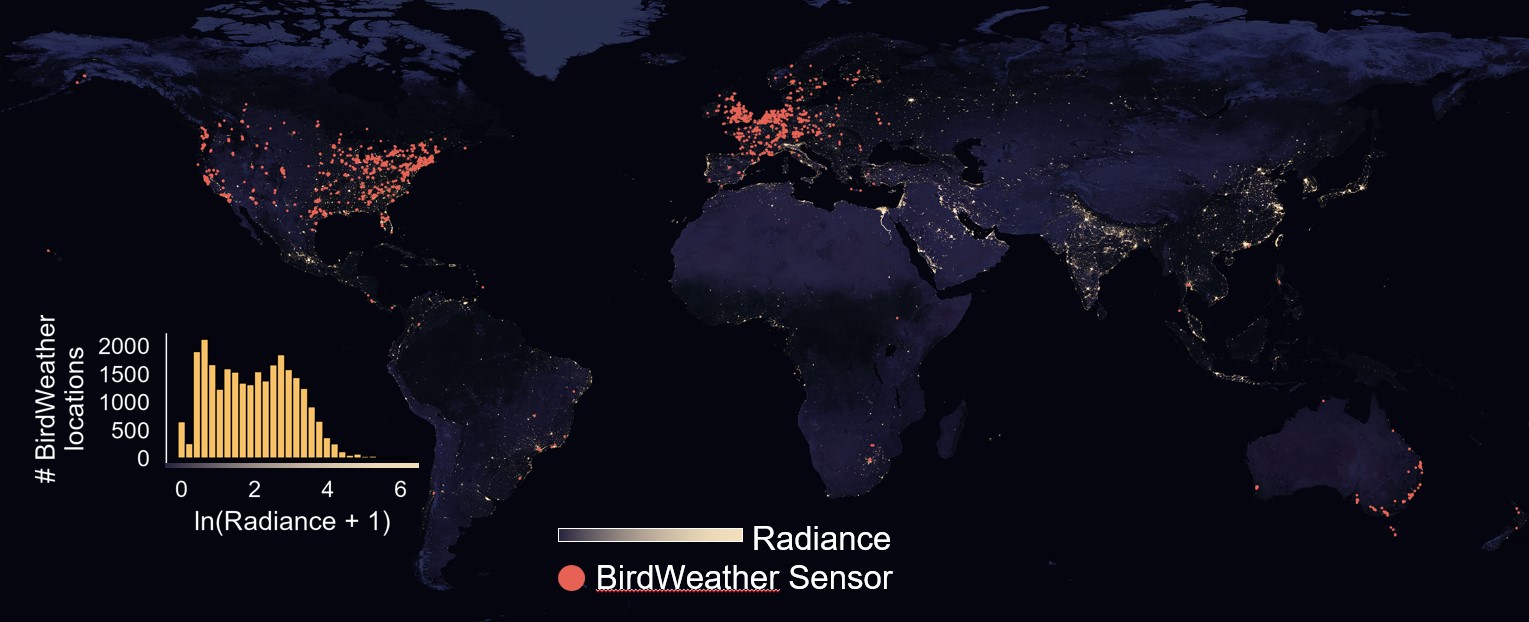
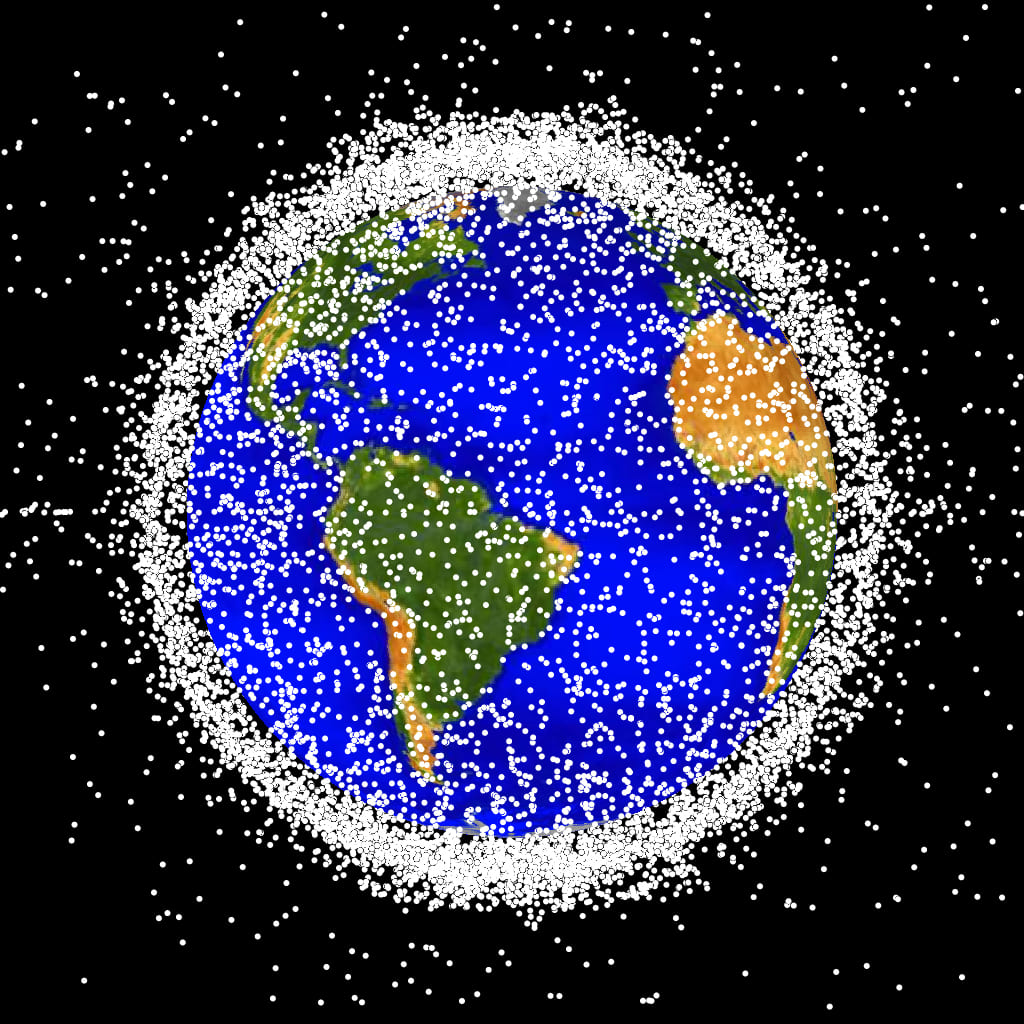
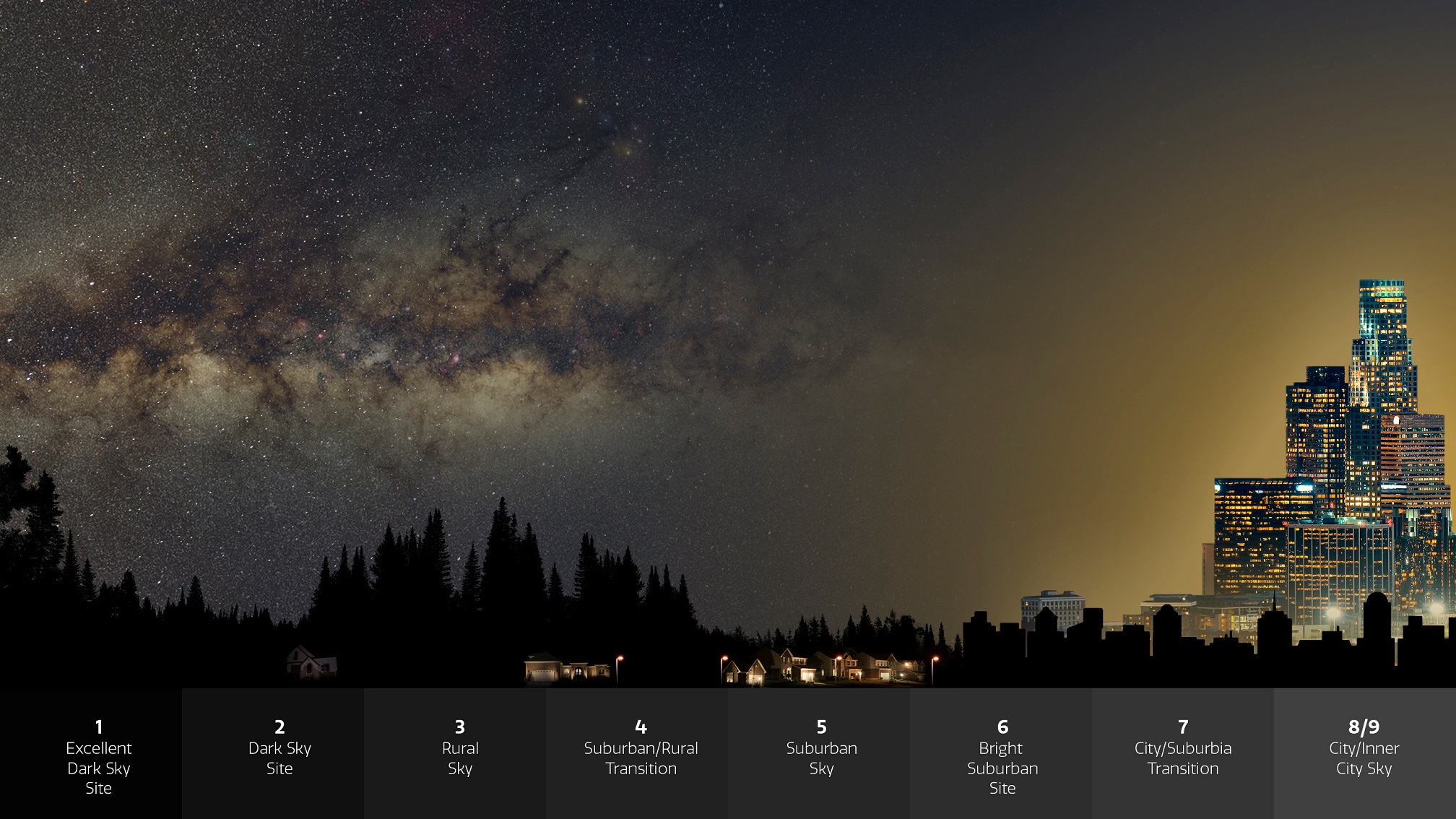
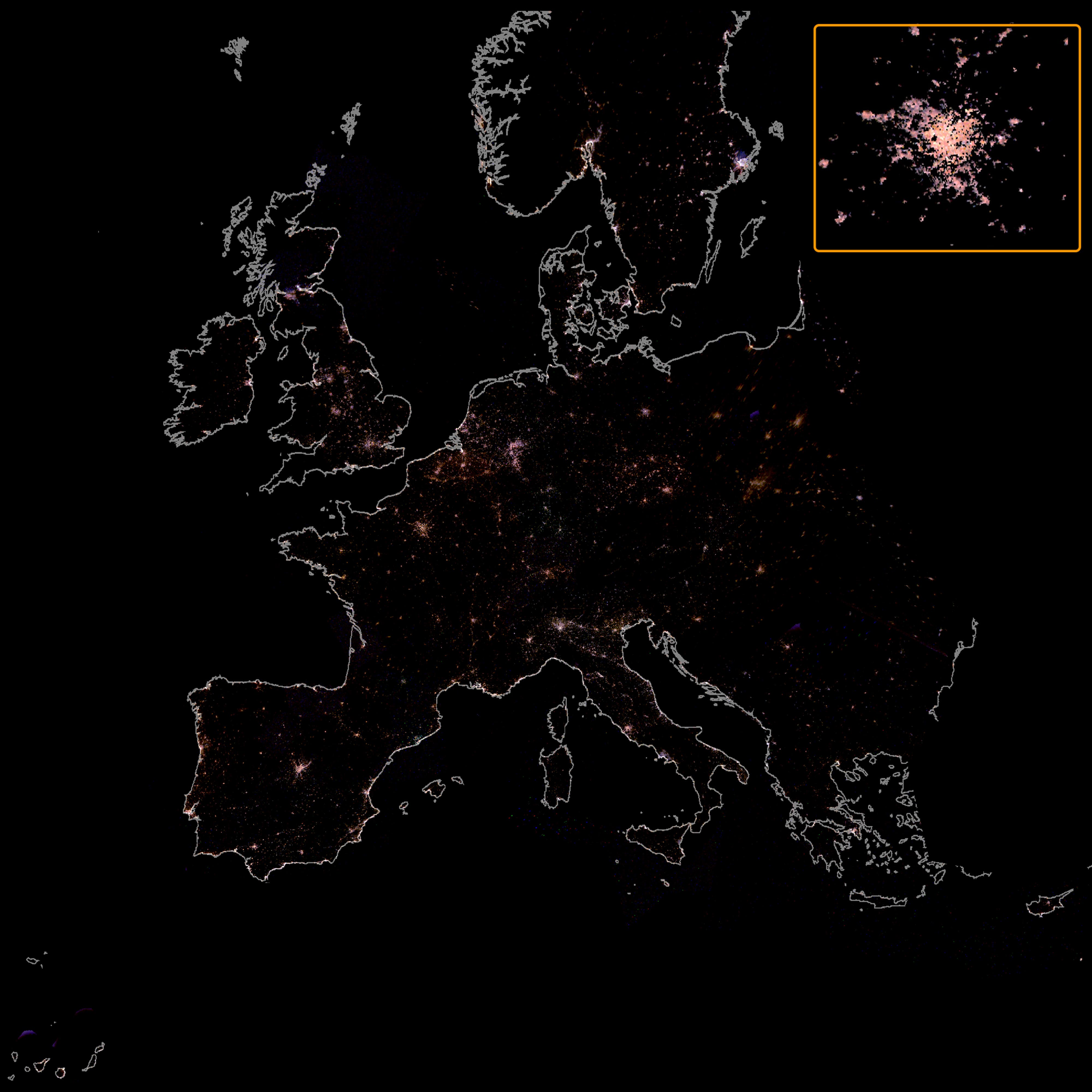
The rapid growth of satellite constellations threatens the operation of space telescopes, according to a study published in Nature. If the planned launches are completed, the Hubble Space Telescope could see more than a third of its images affected by light pollution from these satellites, as they share the same orbital space, while other telescopes would have more than 96% of their images damaged, the authors estimate.