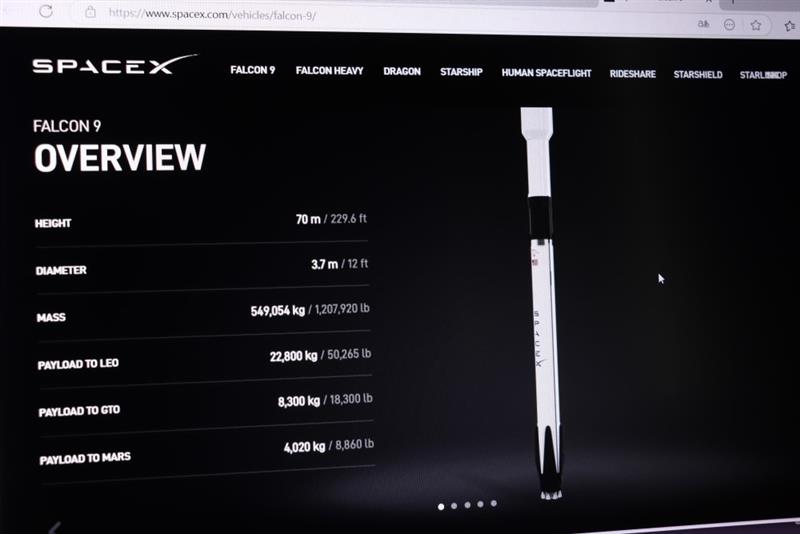
Lithium pollution from Falcon 9 re-entry into the atmosphere measured for the first time
In February 2025, lithium concentrations suddenly increased around 96 km above sea level some 20 hours after a SpaceX Falcon 9 launch vehicle re-entered the atmosphere. This is the first direct detection of pollution in the upper atmosphere due to the re-entry of a spacecraft, according to a study published in Communications Earth & Environment. Lithium is used in spacecraft components, but it is only found naturally at these altitudes in trace amounts, and its accumulation could have consequences on the climate.