Institute of Geosciences , IGEO (UCM-CSIC)
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Research professor at the Institute of Geosciences, IGEO (CSIC-UCM)
Planetary geologist and astrobiologist at the IGEO (CSIC-UCM). Academician of the Royal Academies of Sciences and Doctors of Spain. President of the Planetary Geology Commission of the Geological Society of Spain and of the Spanish Network of Planetology and Astrobiology.
CSIC geologist and paleontologist at the Institute of Geosciences (CSIC-UCM)
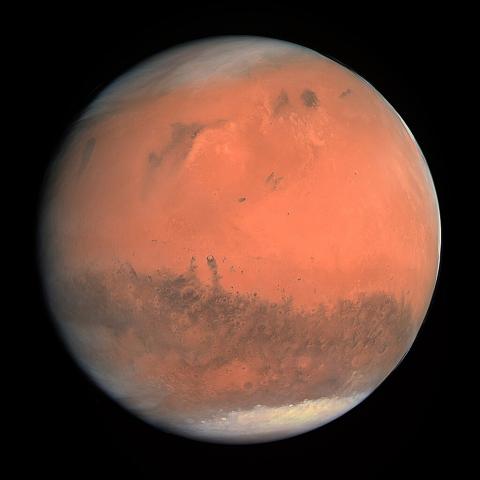

Previous studies had confirmed the presence of liquid in Mars' core. However, there was conflicting information about the possible existence of a solid component. Now, data from NASA's InSight mission show that there is indeed a solid component in the planet's core, whose radius is estimated at about 600 kilometers. The data, published in the journal Nature, may increase our understanding of the formation and evolution of Mars, as well as its potential habitability.
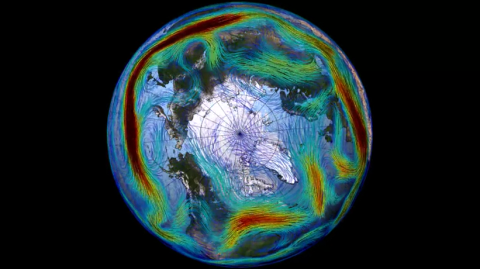
Over the last seven decades, the frequency of planetary wave resonance phenomena has tripled, according to a study published in PNAS. The authors argue that the risk of extreme weather events related to this phenomenon during the northern hemisphere summer could be higher than current model estimates.

The red colour of Mars corresponds to a type of ferrihydrite that is the dominant form of iron oxide in Martian dust, although previous studies have attributed it to anhydrous haematite. The persistence of ferrihydrite, whose formation requires water, suggests that it formed during a cold, wet period, followed by a transition to the planet's current arid environment. The result, based on ESA and NASA space data and new laboratory experiments, is published in Nature Communications.

US researchers have published a model showing that ice in the mid-latitudes of Mars could allow photosynthetic life to develop. Its thickness and composition would attenuate harmful ultraviolet radiation, but allow sufficient visible light to pass through. The work is published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment.

A study has analyzed changes in the Earth's average global surface temperature over the past 485 million years and has discovered oscillations ranging from 11°C to 36°C, representing a variation of up to 25°C. The research concludes that temperatures during the Phanerozoic underwent more fluctuations than previously thought and shows a correlation between CO2 and changes in Earth's temperature. The article, published in the journal Science, combines thousands of data points with a modeling method used for weather forecasting.

ESA's ExoMars and Mars Express missions have for the first time detected ice near the equator of Mars, specifically in the Tharsis volcanoes, an area of the planet where it was thought impossible to exist. According to the researchers, who publish the results in the journal Nature Geoscience, such findings are important for habitability and future human exploration.

According to a report published yesterday in The New York Times, most of the members of the Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy had rejected the proposal to declare the beginning of the Anthropocene, thus showing their opposition to the idea that this is a new geological epoch. Other sources told El País that the result of the vote was not formally confirmed. If this proposal is defeated, the process could be restarted from scratch at a later date.

Fifteen years ago, the European Space Agency's (ESA) Mars Express probe revealed the presence of large deep deposits on Mars, in an area called the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF), located at its equator. Now, new data from the probe's MARSIS radar indicate that the deposits are deeper than previously thought - up to 3.7 kilometers thick - and include both ice-rich and dusty layers. The results are published in Geophysical Research Letters.

The Anthropocene Working Group of the International Commission on Stratigraphy has proposed Crawford Lake in Canada as a reference site for studying the Anthropocene as a possible geological epoch. This proposal for a Global boundary and Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) was presented today at the International Congress of Stratigraphy in Lille, France. It is a necessary, but not sufficient step for the Anthropocene to enter the International Chronostratigraphic Table, the worldwide reference for geological units. Once approved by the AWG, this proposal has to go through three more votes in international geological bodies.

The term Anthropocene describes the profound changes on Earth due to human activities in the past decades. The concept comes from geology but has spread to other areas and has sparked controversy within science. In this article, we provide some keys to understand what the Anthropocene is, and why there has been debate in recent days surrounding its possible declaration.