Forest fires and pest outbreaks could double in Europe before the end of this century
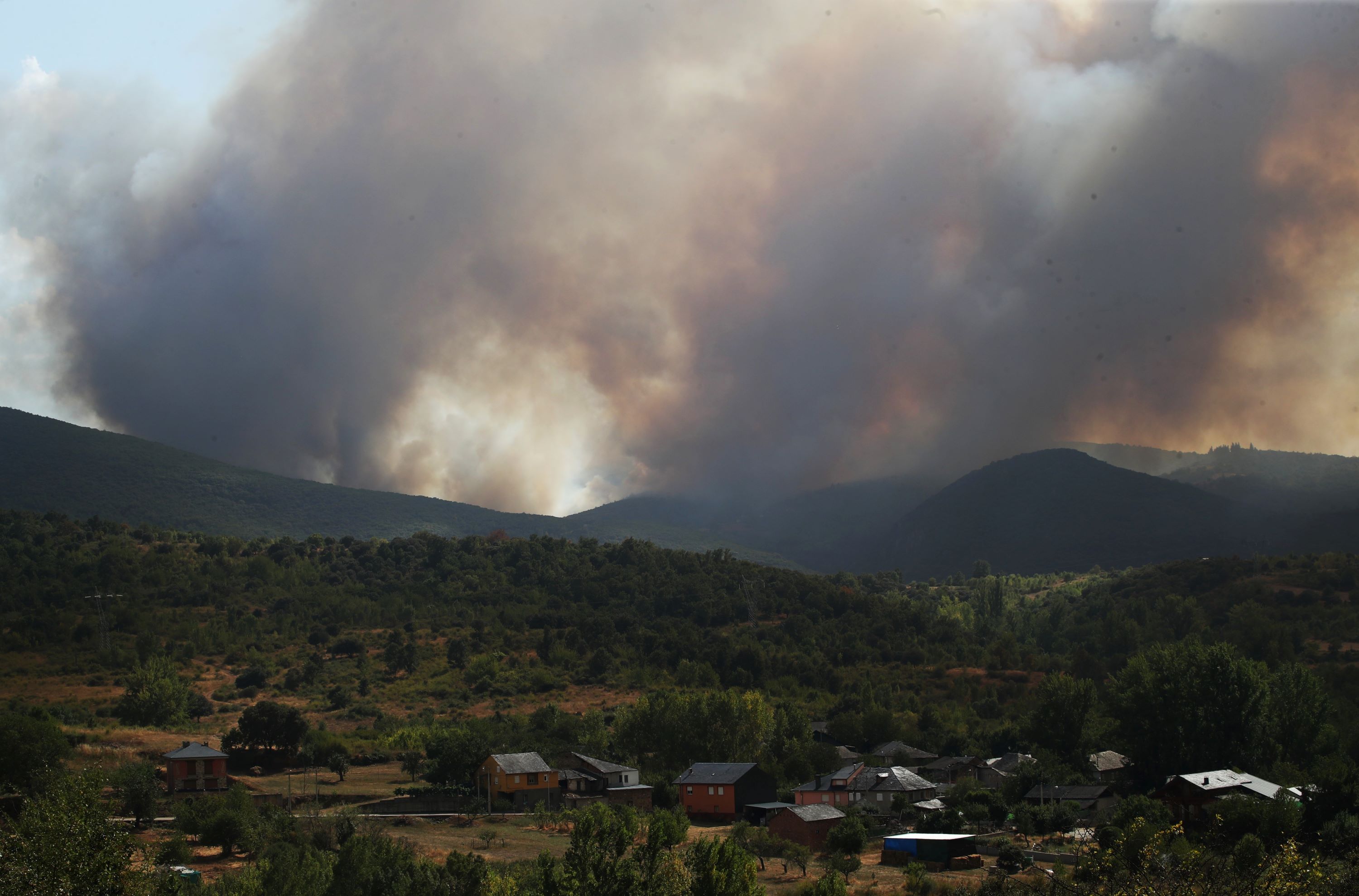
Forest disturbances in Europe—including fires, insect pest outbreaks, and windstorms—could double by the end of the 21st century compared with the 2001–2020 period if emissions are not reduced. In the case of wildfires, the annual area burned could nearly triple. The Mediterranean region ranks among the most vulnerable, and almost 90% of Mediterranean forests could be affected by increased fires and pest outbreaks under higher warming scenarios. The findings are published in a study in the journal Science involving Spanish research centers such as CREAF, the CTFC and the University of Girona.