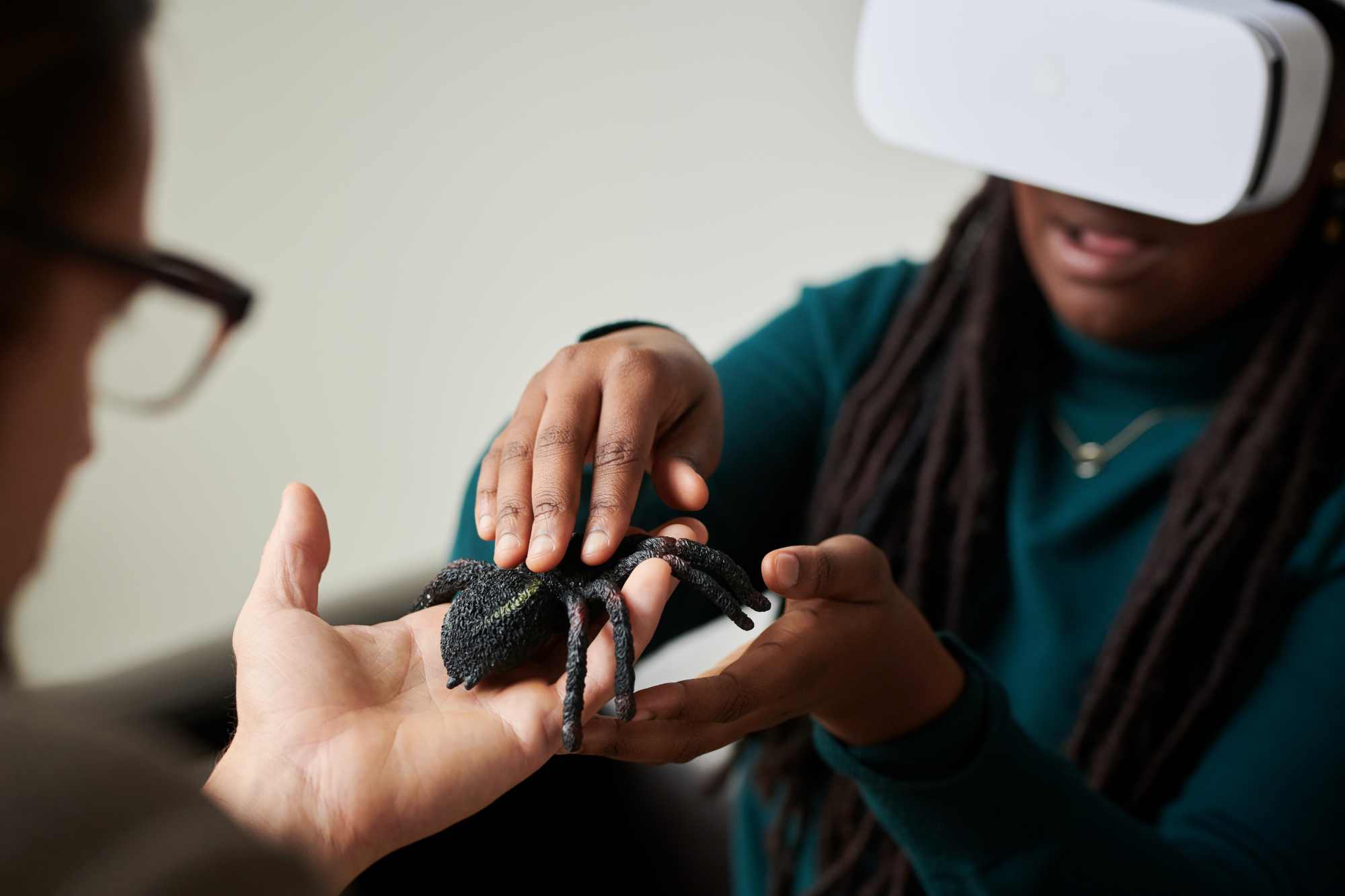
Psychedelics and mental health: questions and answers about research
The study of psychedelic drugs in pharmacological treatments had its eureka moment with chemist Albert Hofmann's famous bike ride under the influence of LSD in 1938 and then developed over decades, but with Richard Nixon it was shelved. In recent years, it has resurfaced in hospitals and laboratories around the world. Last week, the Congress of Deputies hosted a conference on these substances. We explain what they are, what they are used for, the current state of research, and their risks, with the help of expert sources.