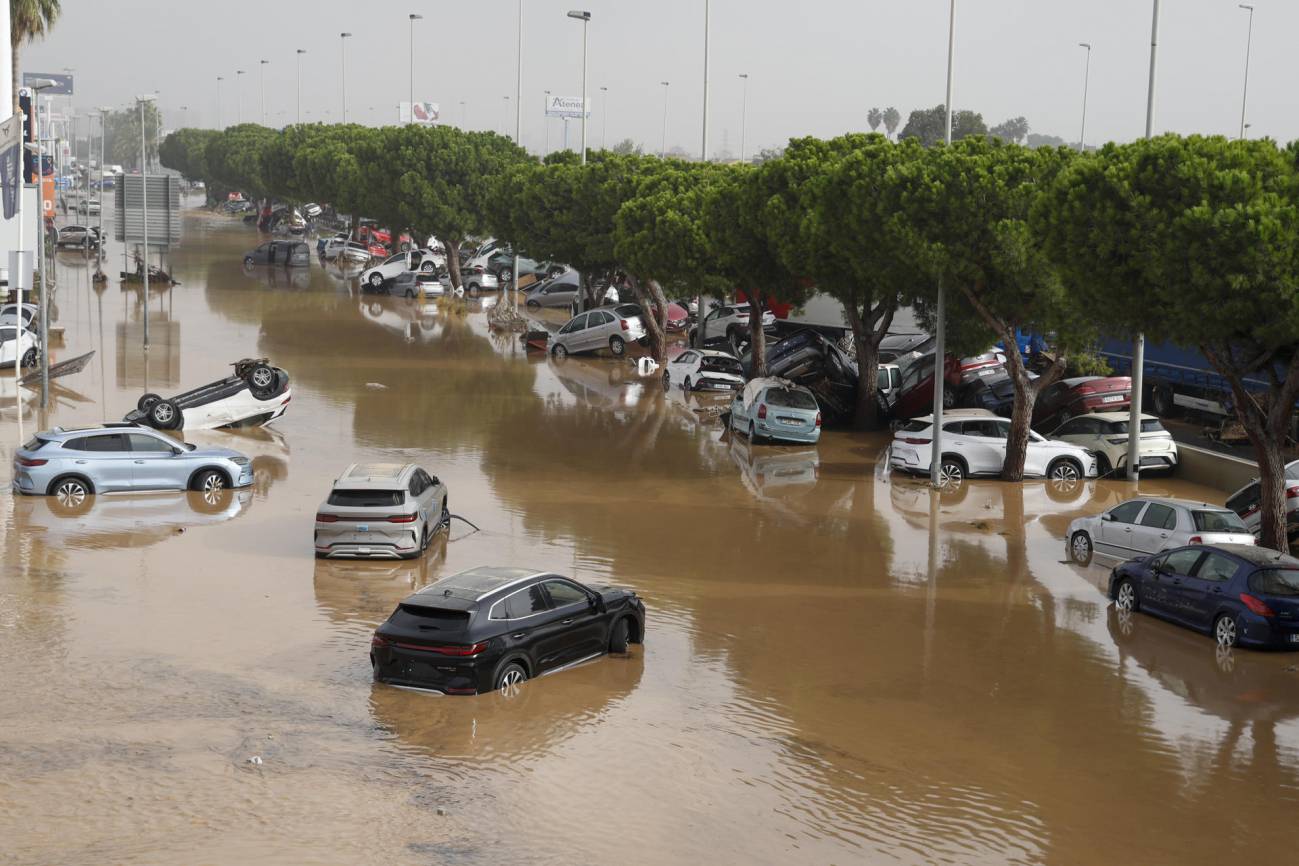
The frequency of planetary wave resonances has tripled in the last 70 years, according to a study
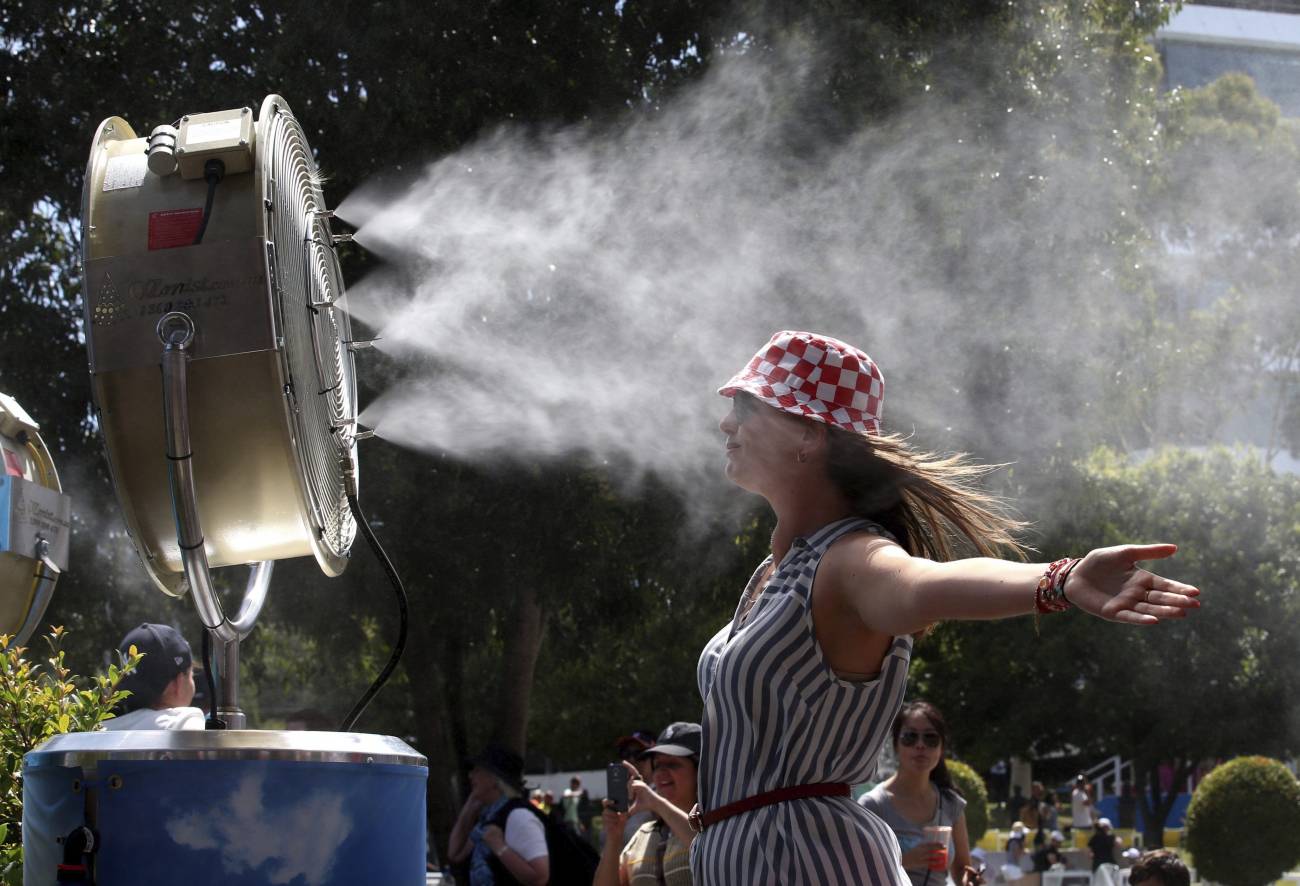
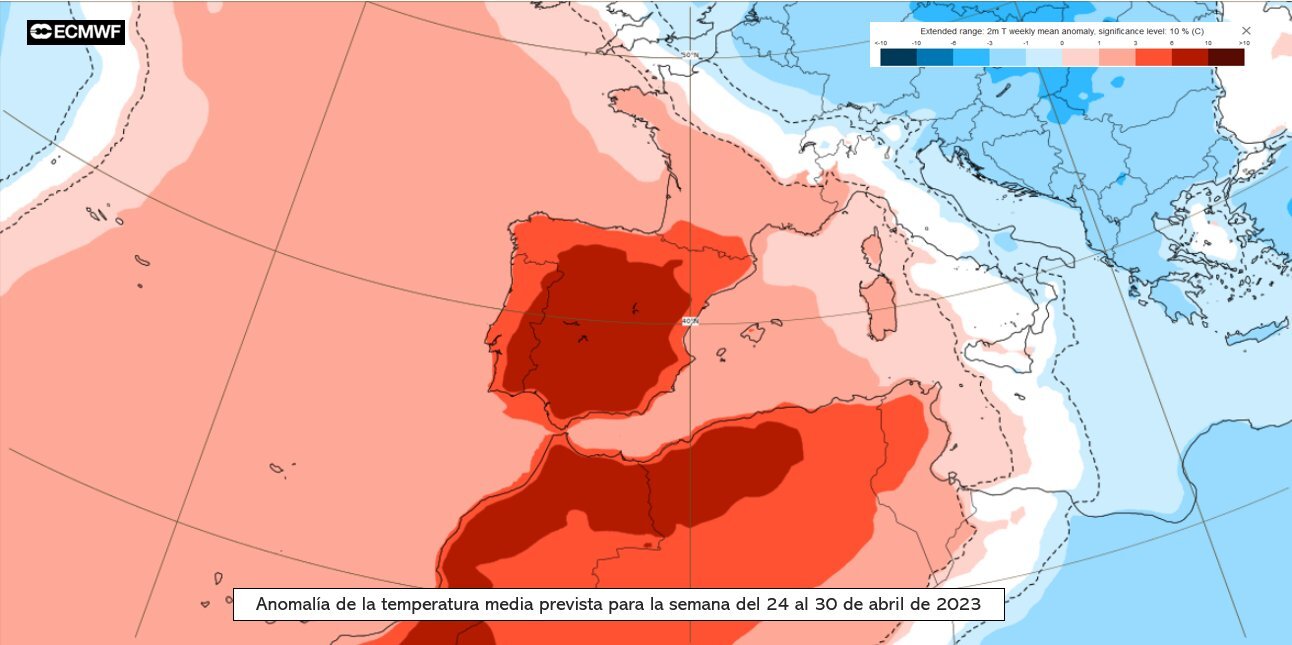
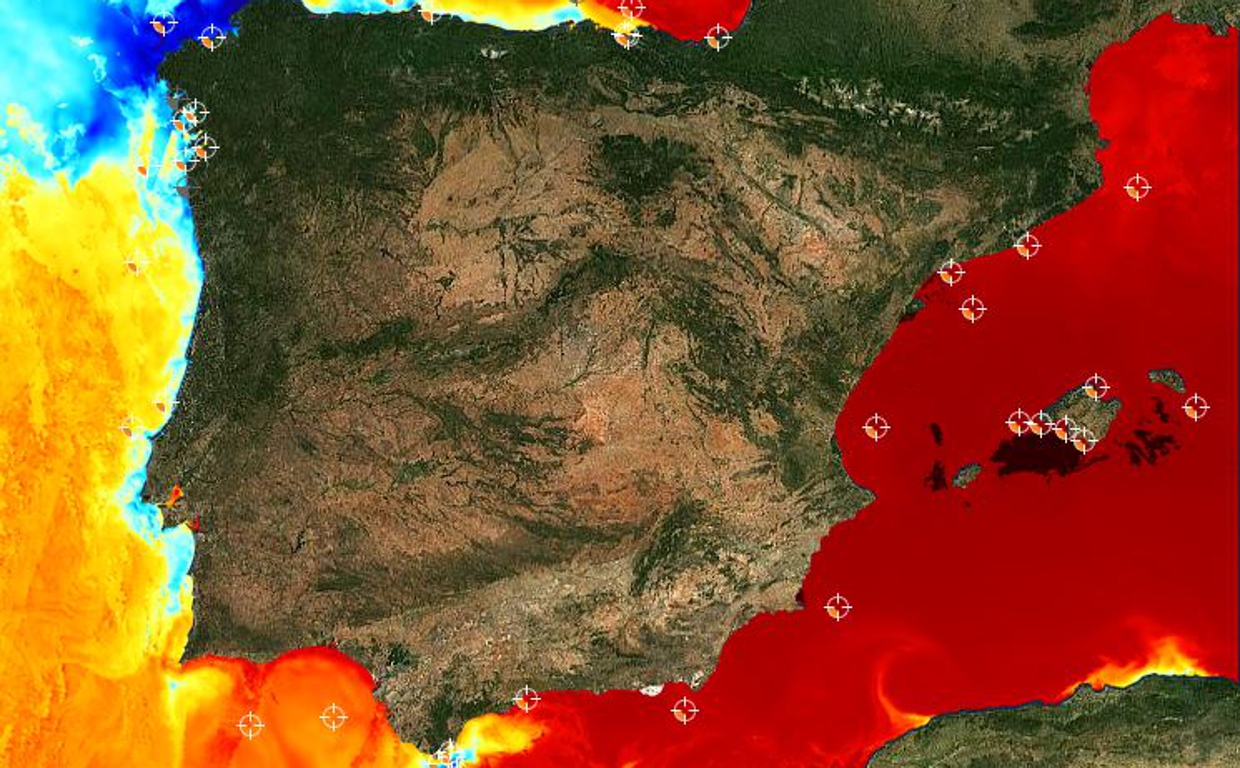
Over the last seven decades, the frequency of planetary wave resonance phenomena has tripled, according to a study published in PNAS. The authors argue that the risk of extreme weather events related to this phenomenon during the northern hemisphere summer could be higher than current model estimates.