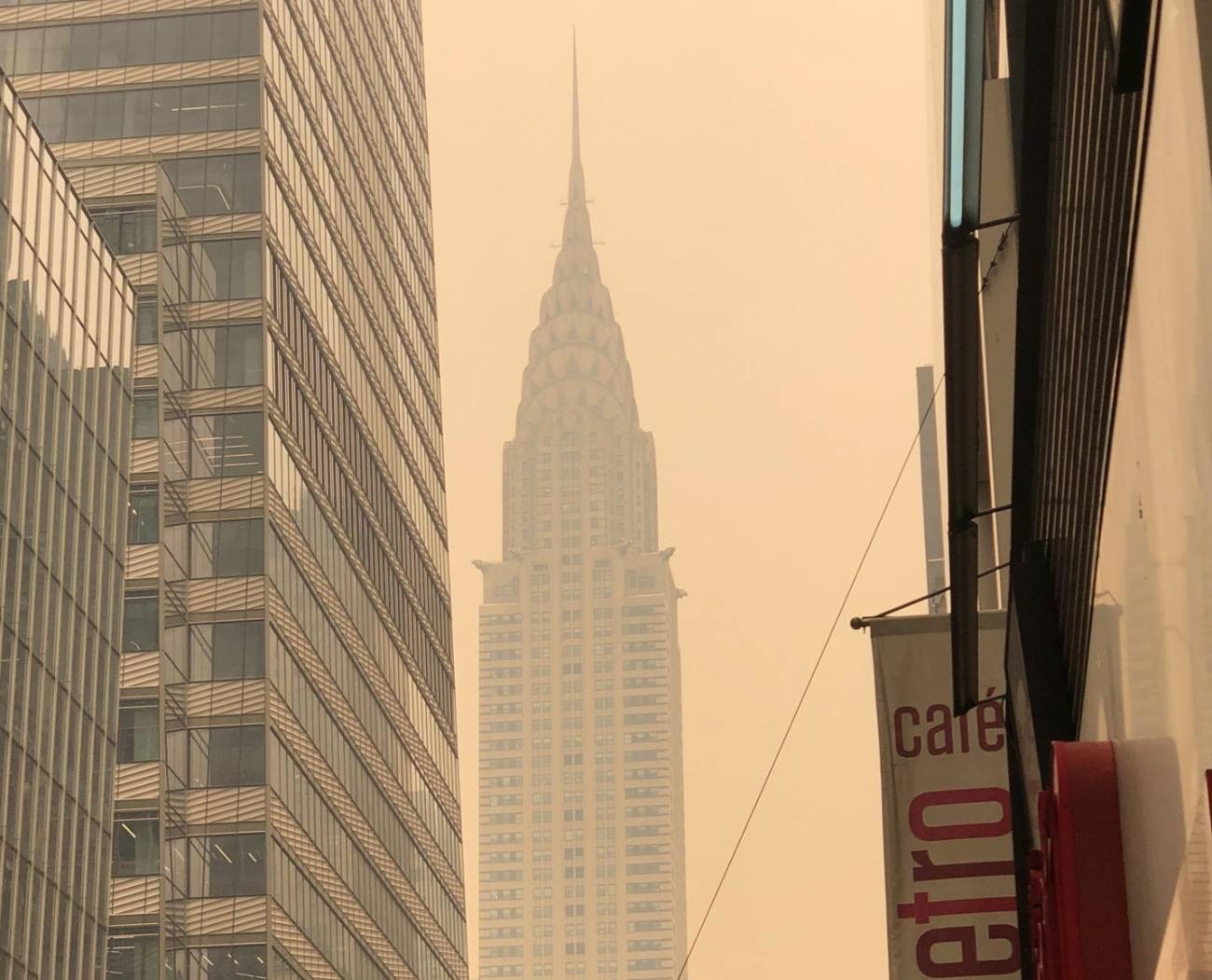
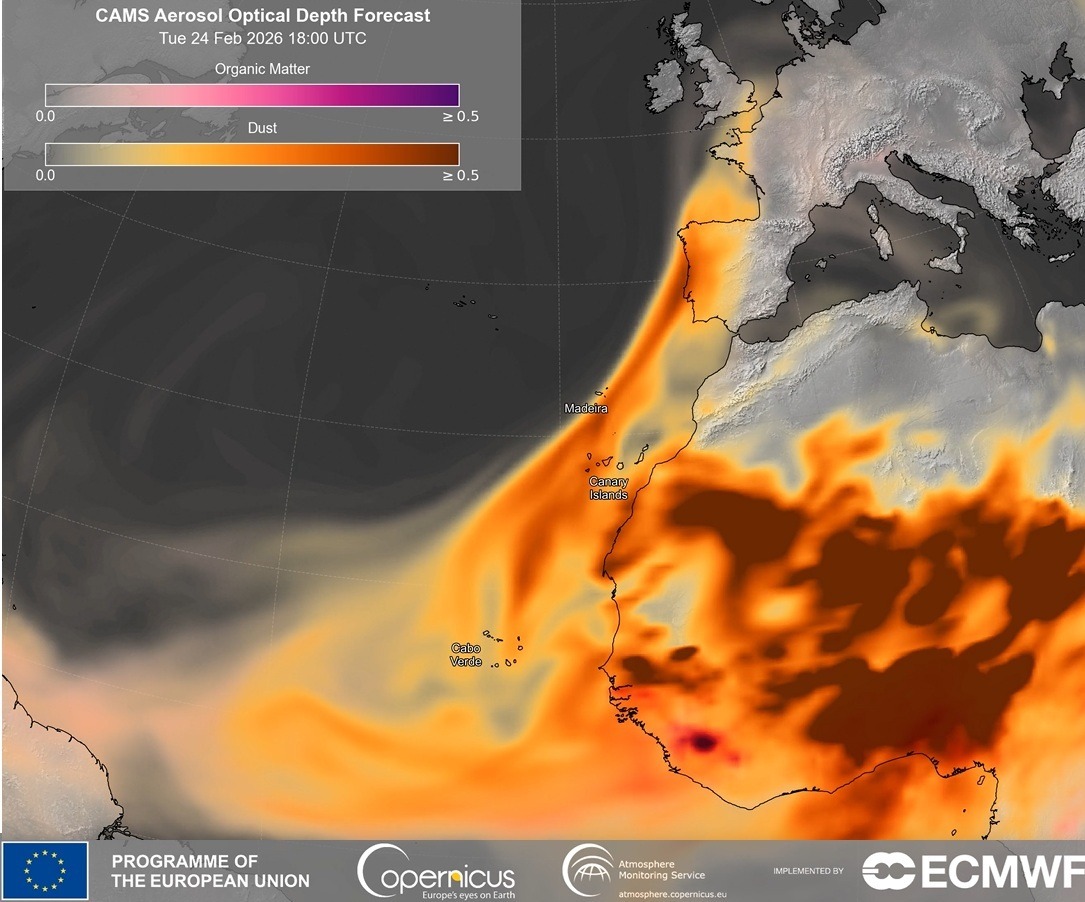
The Iberian Peninsula and the Canary Islands register the arrival of African air masses with dust concentrations
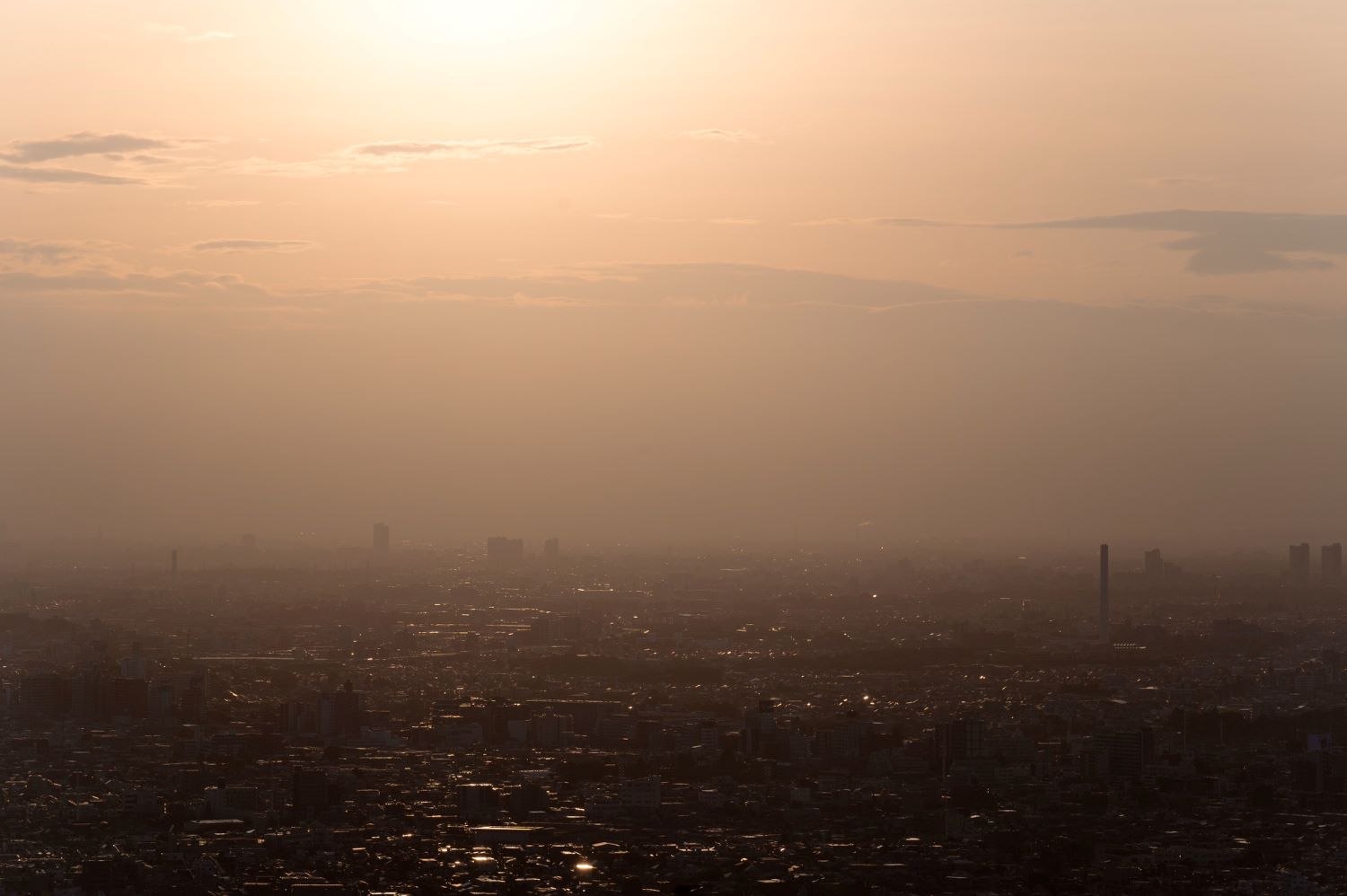
According to the Ministry for Ecological Transition and Demographic Challenge, masses of African air with varying concentrations of surface dust are expected to reach the Canary Islands and the Iberian Peninsula on Wednesday. Health authorities in different provinces have recommended avoiding outdoor physical exercise or activities that require effort, especially for vulnerable groups such as children, pregnant women, the elderly and the sick.