
Synthetic embryos, artificial placentas, genome editing... Advances in biology and medicine keep bringing up thorny ethical questions. Here's an overview of Spain’s many bioethics committees, which can be useful resources for journalists.
Berna Sozen's lab at Yale University has announced a new milestone in the competition to create synthetic embryos: their human pluripotent stem cells self-organise into structures that mimic embryonic development on days 9-14 after fertilisation and include extra-embryonic tissues. Their achievement is published in Nature at the same time as another similar study, that of Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz, who a fortnight ago previewed her stem cell-derived human embryo model to The Guardian, sparking a controversy with Jacob Hanna, author of a preprint showing that she had achieved true synthetic embryos.
The Guardian newspaper reported on Wednesday that Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz's team had announced the generation of synthetic human embryos from stem cells at the annual meeting of the International Society for Stem Cell Research in Boston. The author later denied on Twitter that they were synthetic human embryos and spoke only of models, warning that it was pending publication in a scientific journal. The day after the publication in The Guardian, and as reported in El País, Jacob Hanna and his team published a preprint - a publication that has not been peer-reviewed - in bioRxiv on models of human embryos generated from stem cells without genetic editing. A few hours later, Zernicka-Goetz's team posted their preprint on bioRxiv.
The latest episode of competition between research groups working on the same topic, a very common situation in science, should not distract us from the actual achievement: synthetic human embryos, in the laboratory, made from stem cells, up to a post-implantation stage. Now, we must decide what status or condition we will grant to these synthetic embryos. Once again, science is leaping forward and testing the limits of the laws, posing new ethical challenges for us to solve.

A scientific team has generated synthetic human embryos using stem cells, reports the British newspaper The Guardian. The authors, who announced the breakthrough at the annual meeting of the International Society for Stem Cell Research in Boston (USA), say the model embryos, similar to those found in the early stages of human development, could be crucial for research into genetic disorders and the causes of miscarriages, according to the newspaper. However, the work also raises ethical and legal issues.
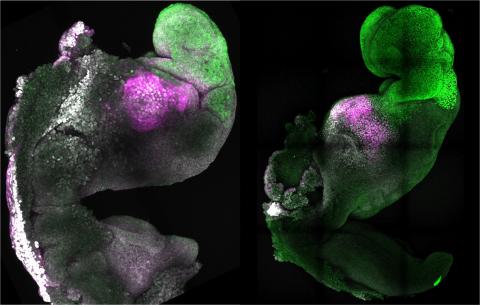
Research published in Nature shows the creation of synthetic mouse embryos derived from stem cells. The embryo model copies the stages of natural rodent embryo development that take place up to day 8.5 after fertilisation and includes regions of the brain, a neural tube and a structure similar to a beating heart.