AlphaGenome, an AI tool from Google, predicts the impact of variations in DNA
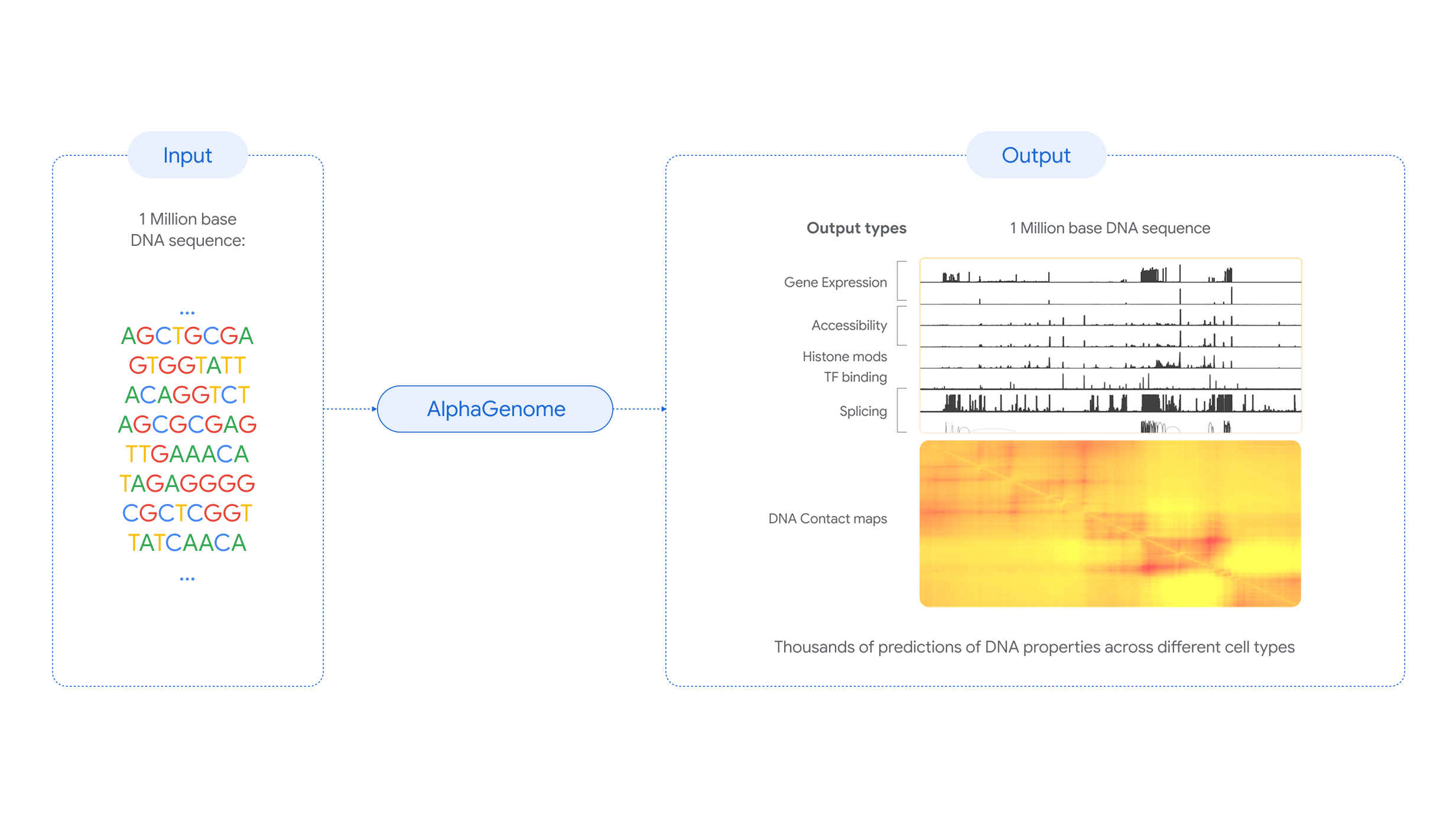
AlphaGenome is a deep learning model developed by Google DeepMind capable of predicting the function of DNA sequences up to one million base pairs long. An evaluation of the tool shows that it matches or improves upon the predictive ability of existing models in 25 of the 26 tests performed. According to the authors, who are part of Google DeepMind itself, AlphaGenome can help scientists "better understand genome function, the biology of diseases, and ultimately drive new biological discoveries and the development of new treatments." The results are published in Nature.