A phase 1 trial is testing a drug to restore the function of p53, the ‘guardian of the genome’, in specific cases
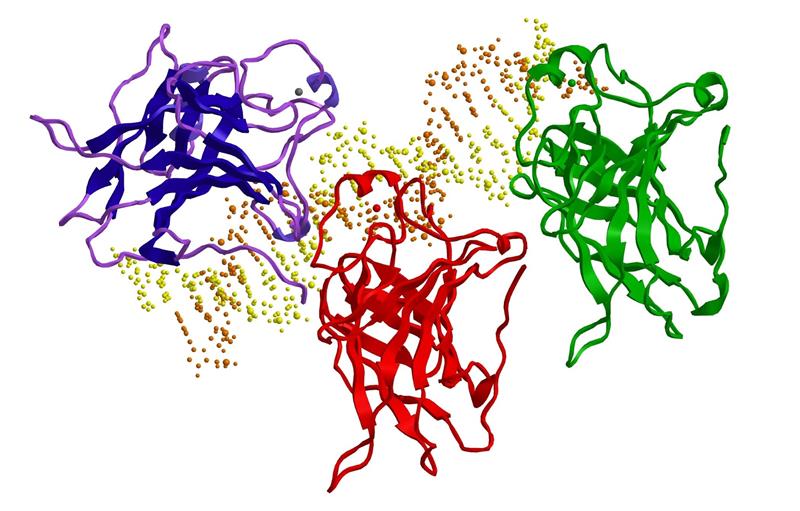
The p53 gene, known as the ‘guardian of the genome’, is a tumor suppressor gene that is mutated in more than half of all solid tumors in humans, affecting the function of the protein it encodes. However, there are no approved treatments capable of reactivating its function. A US team has tested a new drug in a phase 1 clinical trial that is capable of performing this function against a specific mutation, present in approximately 1% of solid tumors. After being administered to 77 people with different types of advanced or metastatic tumors, 20% showed a full or partial response, and the most common adverse effects were nausea or vomiting, according to a report published in NEJM.