Orforglipron is more effective than semaglutide, according to a phase III clinical trial
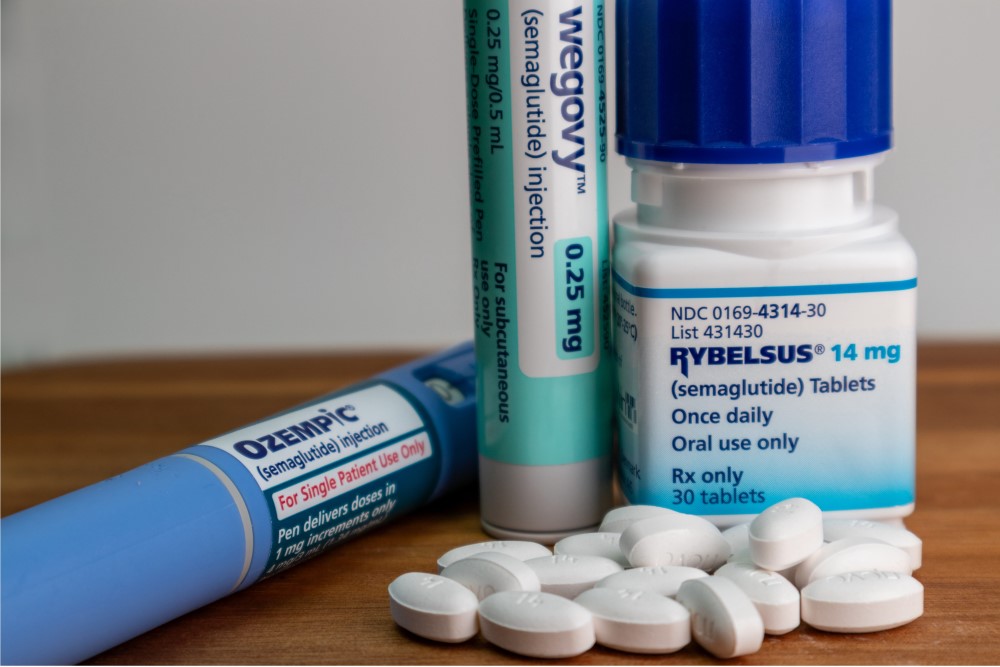
The use of the drug orforglipron reduces blood sugar levels and body weight more than semaglutide, the other available oral GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment, according to a phase III clinical trial. The trial, funded by Eli Lilly, involved 1,500 people with type 2 diabetes who took the drug for one year in five countries, and the results are published in The Lancet.