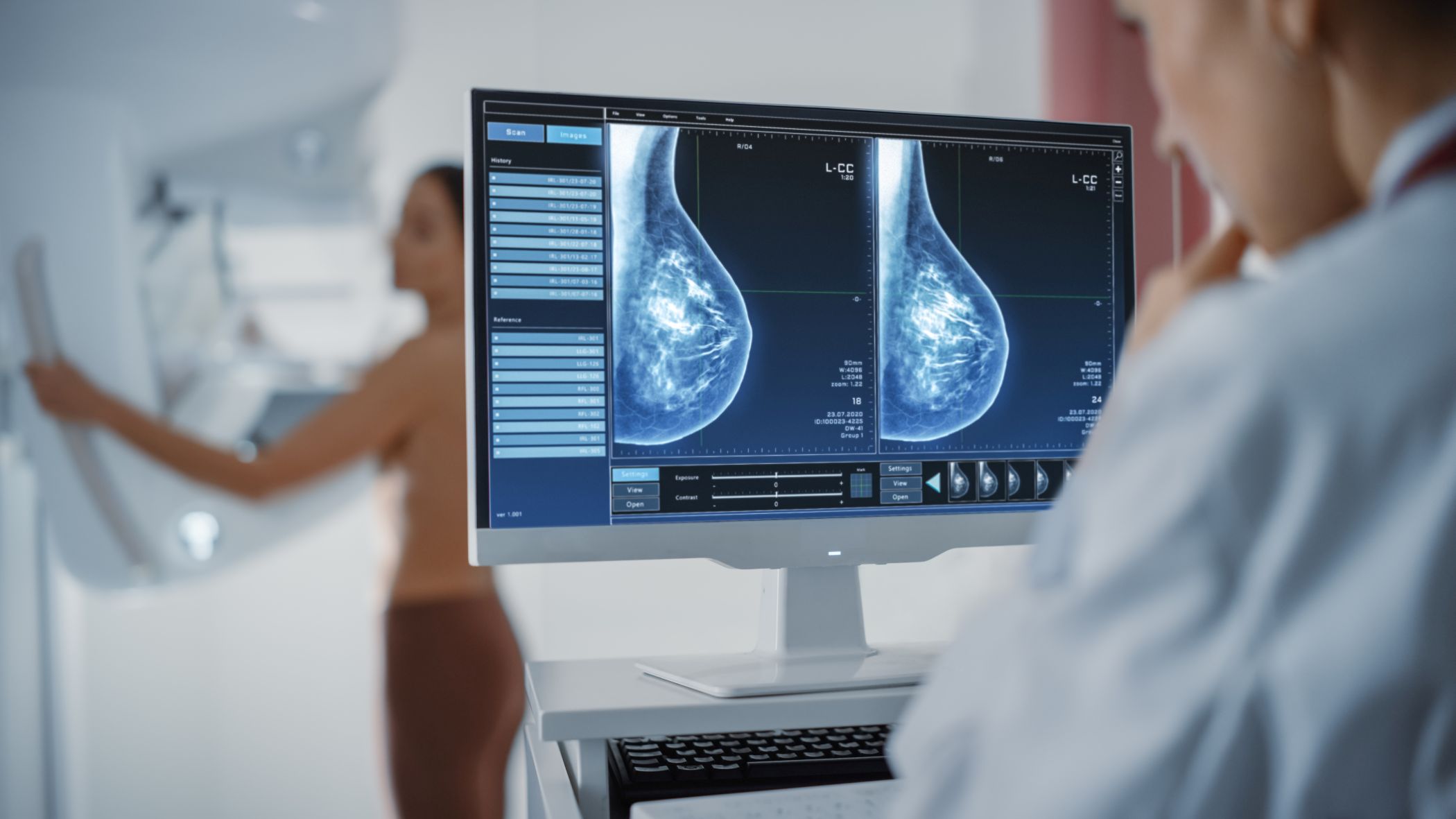
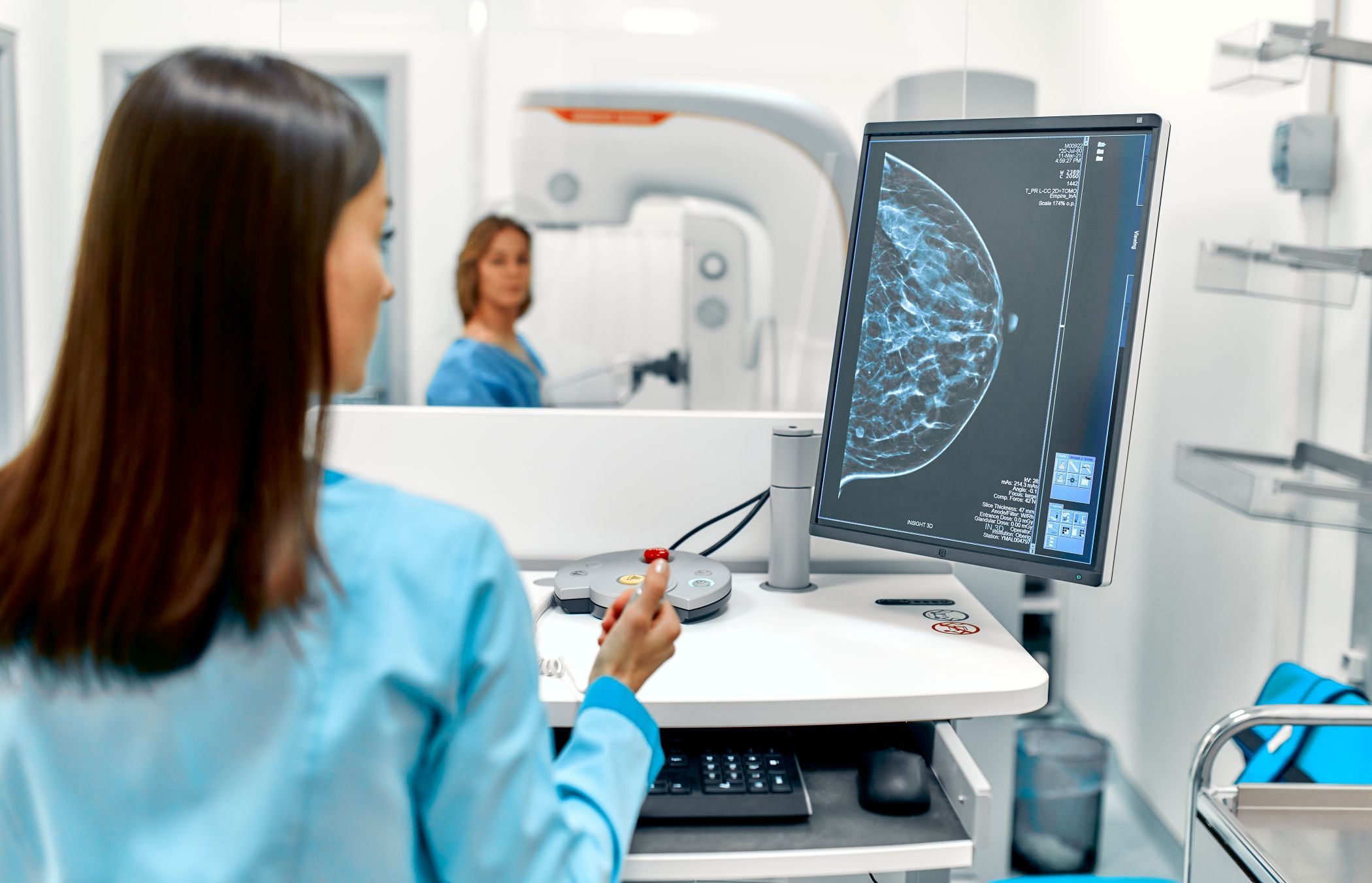
A study shows that an AI-based tool can determine a woman's risk of developing breast cancer in the next four years
An artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm is capable of estimating a woman's risk of developing breast cancer in the next four years, according to a study published in The Lancet Digital Health. The tool identified women at high risk of developing breast cancer, and nearly one in ten of those who scored in the top 2% according to the algorithm were diagnosed within four years, despite having been discharged from hospital. The tool used mammograms from nearly 400,000 women and was then tested with data from nearly 96,000 women in Australia. The results were confirmed in a Swedish population of more than 4,500 women.