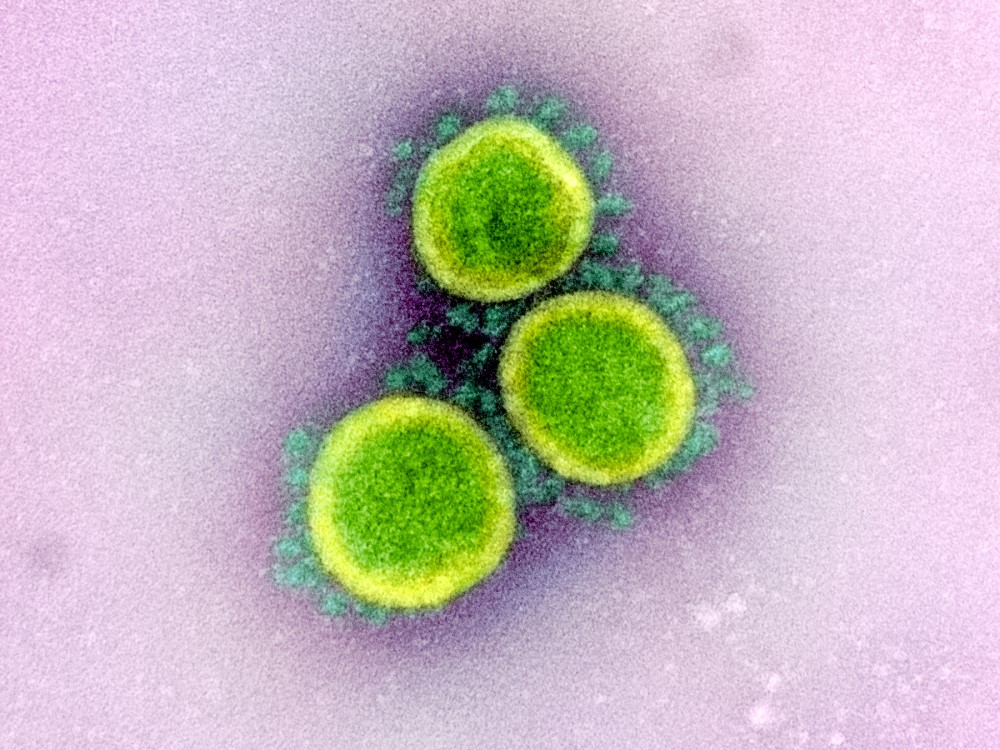
Although tobacco consumption is declining in many parts of the world, there appears to be an increase in the number of lung cancer cases among non-smokers. One of the possible causes of this increase is air pollution. Now, researchers in the US, with Spanish participation, have analysed the genomes of 871 lung tumours in people from various locations who had never smoked. The results, published in the journal Nature, indicate that greater exposure to pollution is linked to an increase in the number of mutations, including those commonly associated with tobacco.