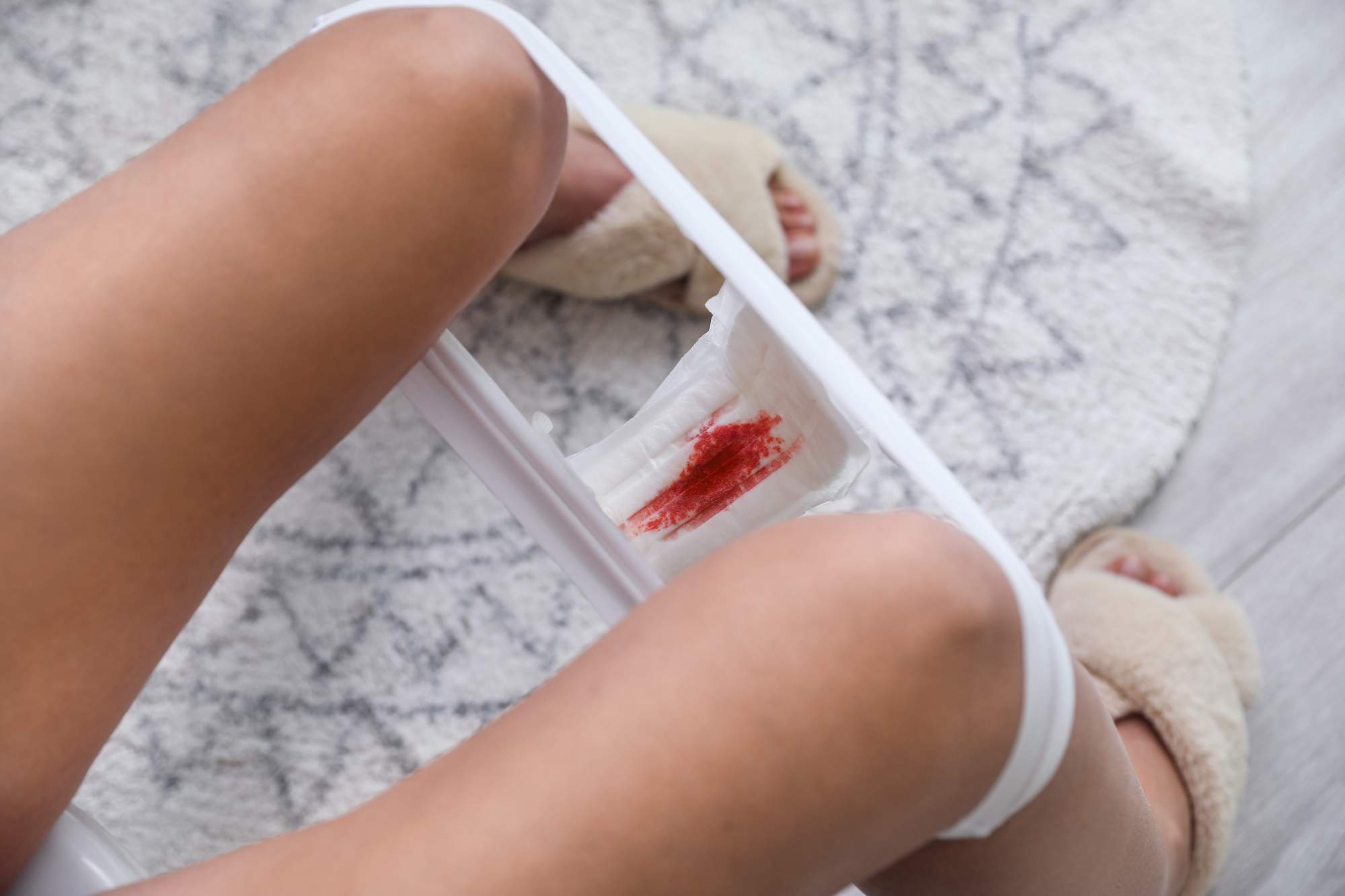
A menstrual blood test detects the human papillomavirus (HPV) and could serve as an alternative in cervical cancer screening
A team in China has studied the ability of a test to detect the human papillomavirus (HPV)—responsible for the vast majority of cervical cancers—in menstrual blood from more than 3,000 women. The results indicate that the test is comparable to current screening performed in medical offices. According to the researchers, “Using menstrual blood for HPV testing is practical and non-invasive, allowing women to collect samples at home and thus potentially offering a practical way to expand access to screening.” The study is published in The BMJ.