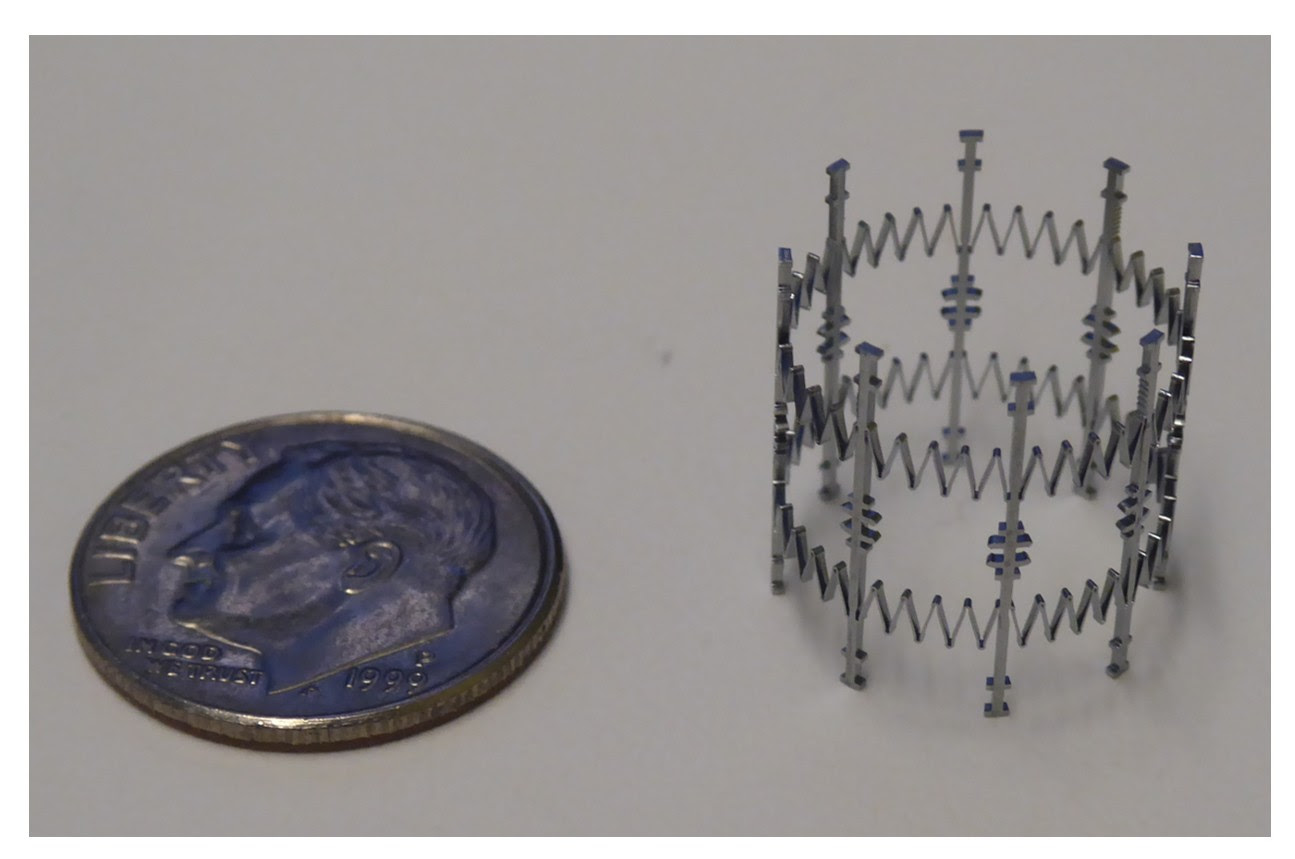
New pediatric cardiac stent grows with the piglet’s heart
A new cardiac valve stent can expand on its own, according to preclinical tests conducted in piglets; the pediatric device doubled in size as the animals matured. As the authors note in their study published in Science Advances, this offers the possibility of adapting to the rapid growth of the hearts of babies and young children with congenital conditions. The stent, which is based on a spring-like expansion mechanism, could eliminate the need for repeated surgeries in pediatric patients.