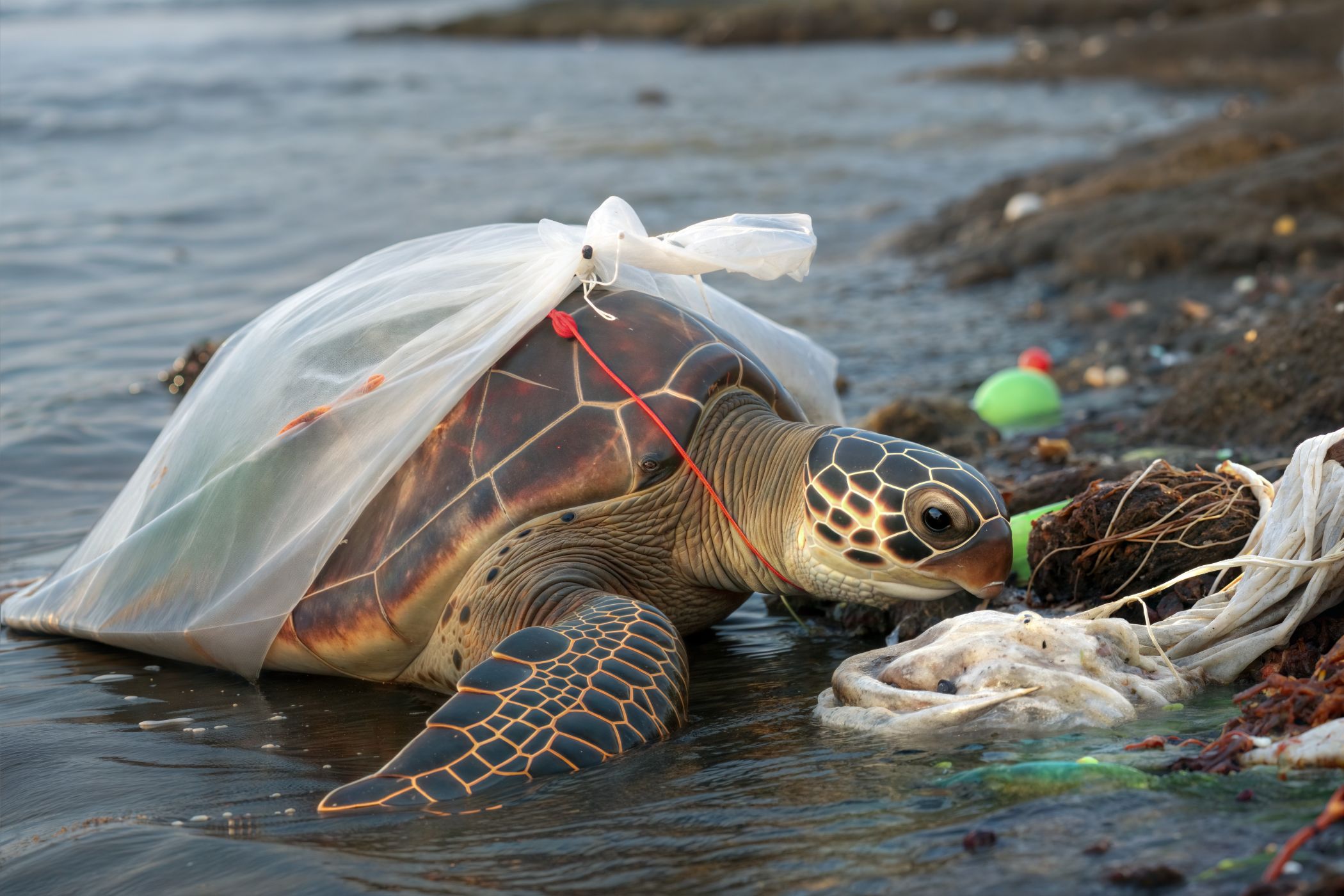
The health impacts related to plastic emissions could double by 2040
A study based on models and data concludes that adverse health effects related to plastic emissions could more than double by 2040 if current practices do not change. The authors note that their model could not assess the potential impacts associated with many chemicals contained in plastics, nor with the microplastics and nanoplastics that form throughout their life cycle, due to a lack of data and “a serious lack of transparency regarding their composition.” The results are published in The Lancet Planetary Health.