A research team with Spanish participation creates an AI model for the diagnosis of rare diseases
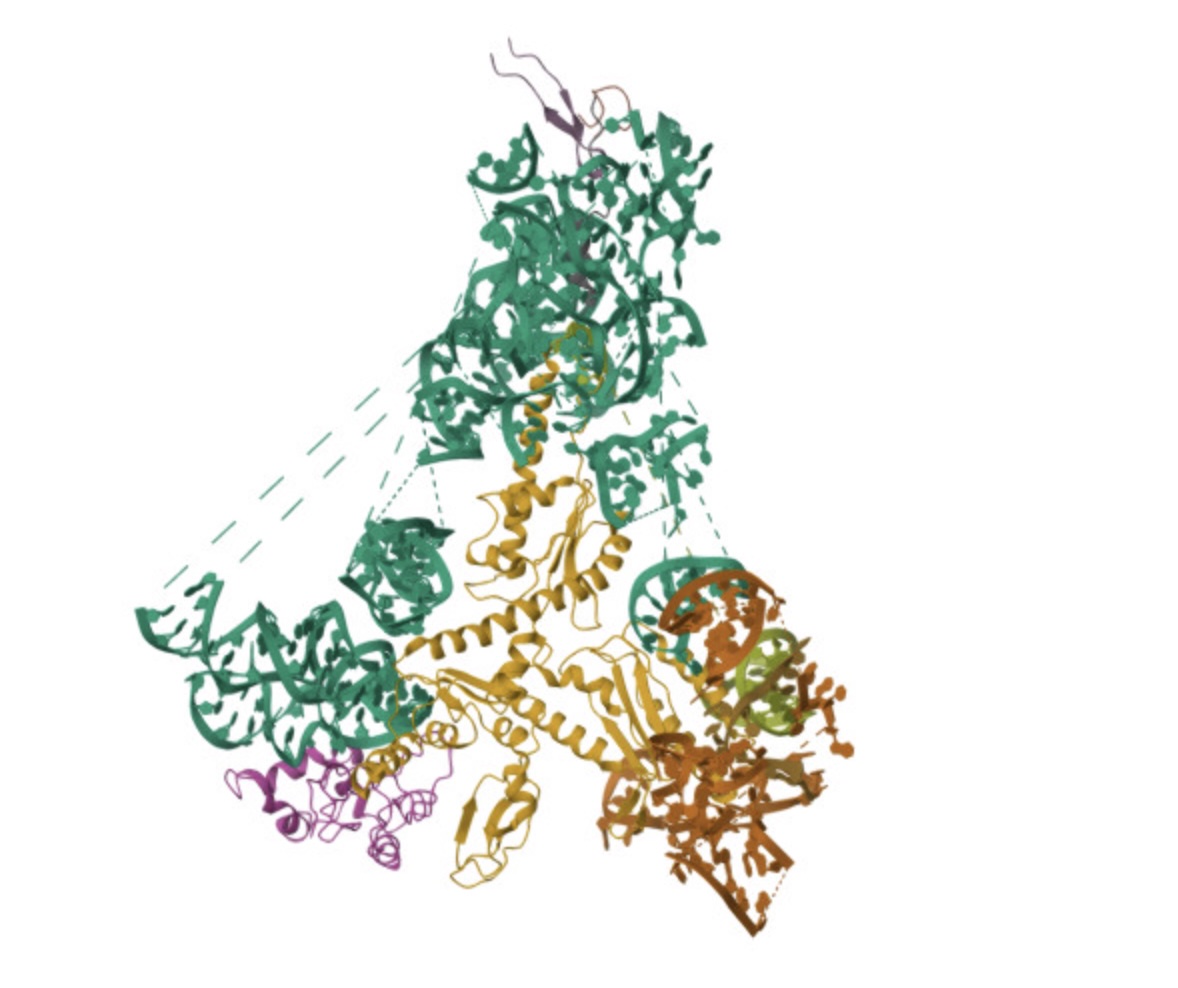
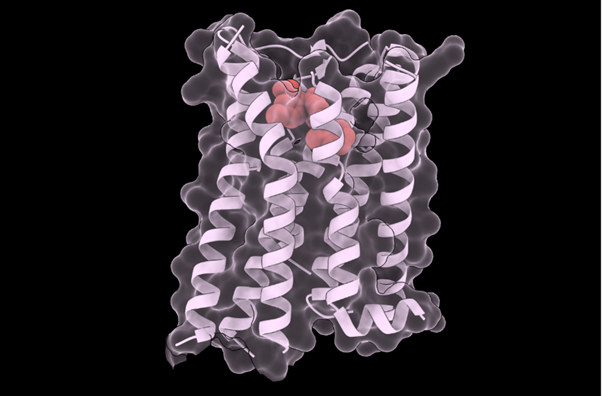
A team from the Center for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona and Harvard Medical School (United States) has created an artificial intelligence (AI) model to support the diagnosis of rare diseases in patients with unique genetic mutations. Called popEVE, the tool performs better than AlphaMissense—another model developed by Google DeepMind—according to an article published in Nature Genetics.