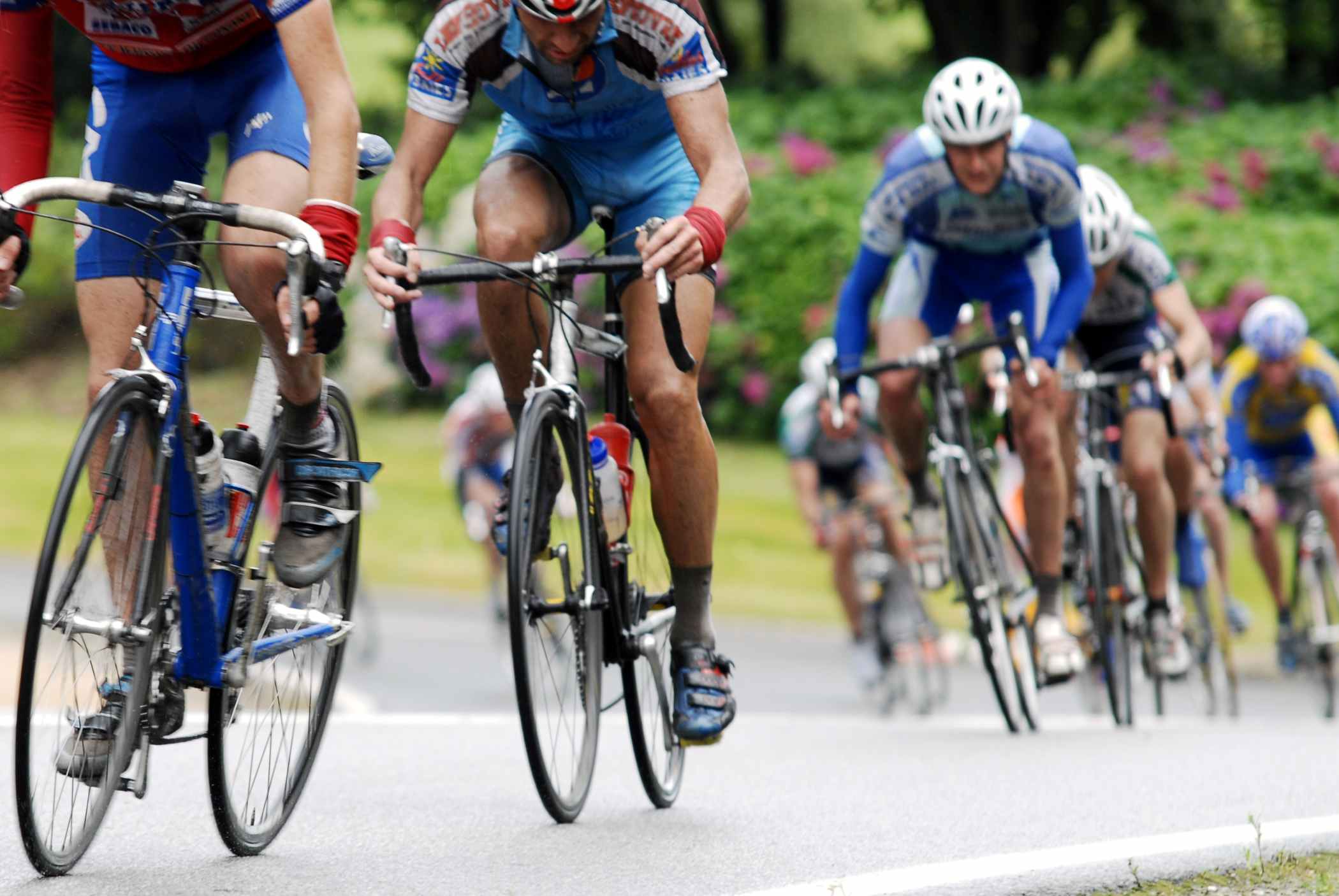
The climate crisis threatens competitions such as the Tour de France, according to a study that analyzed 50 editions of the cycling race
An international team involving ISGlobal has analyzed climate data from 50 editions of the Tour de France between 1974 and 2023. The results show that, during the month of July, the risk of heat stress has increased over the years, with the last decade seeing the highest number of extreme heat episodes. In the locations analyzed, the Tour has so far managed to avoid conditions of maximum risk to health, but according to the researchers, it has been "an extremely fortunate race. With record heat waves becoming more frequent, it seems only a matter of time before the Tour faces days of extreme heat stress that will test current safety protocols. The study, published in Scientific Reports, used the Tour de France as an example of the challenge that rising temperatures associated with climate change pose for the organization of sporting events in the summer.