La Paz University Hospital
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Doctor of Medicine and Psychiatrist at the Carlos III Day Hospital - La Paz University Hospital (Madrid)
Head of the Paediatric Haematology-Oncology Department at the Hospital Universitario La Paz.
Head of Section of the Hospital Paediatrics, Infectious and Tropical Diseases Department of the Hospital Universitario Infantil La Paz (Madrid)
Clinical laboratory geneticist in the Molecular Ophthalmogenetics section of the Institute of Medical Genetics (INGEMM) and Molecular Genetics of the Hospital Universitario La Paz
Head of the Cancer Epigenetics Laboratory at INGEMM and coordinator of Experimental Therapies and Biomarkers in Cancer at IdiPAZ, La Paz University Hospital
Cardiologist at La Paz Hospital and researcher at IdiPAZ (Madrid)
Specialist in Clinical Neurophysiology and coordinator of the Neurological Sleep Disorders Unit at La Paz University Hospital
Cardiologist at the Hospital Universitario La Paz, representative of the Spanish Society of Cardiology in the National Committee for the Prevention of Smoking and member of the Tobacco Expert Group of the World Heart Federation

A few days ago, research published in JAMA Network Open showed that, although the use of melatonin in children is growing, its effectiveness and long-term effects are unknown. It is important to note that there are several types of melatonin, with or without a prescription, and their effects also differ in children and adults.

A meta-analysis published in The Lancet Psychiatry journal concludes that the most effective way to discontinue antidepressant treatment in people with remitting depression is to gradually reduce the dose in combination with psychological therapy. Furthermore, this strategy proved to be just as effective in preventing relapses into depression as continuing medication. The study was based on data from more than 17,000 adults with depression and anxiety in remission, although the evidence for the latter disorder was not as robust.

A large international study has analyzed genomic data from over one million people with 14 different psychiatric disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. According to their analysis, five groups of diseases can be identified that share a significant number of genetic variants. Furthermore, common genetic markers were detected among these 14 disorders. The results are published in the journal Nature.
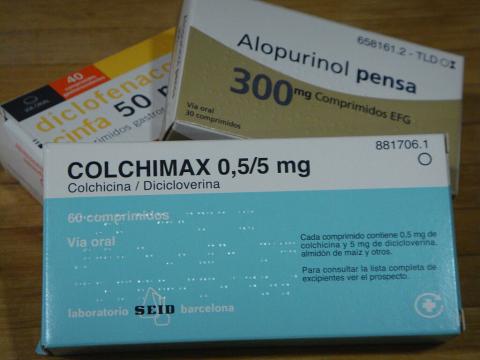
A review conducted by the Cochrane Collaboration analyzed the effects of colchicine—a medication commonly used to treat some rheumatic diseases—on people who had already experienced a cardiovascular event. The review included 12 clinical trials with more than 23,000 patients and concluded that colchicine reduces the risk of stroke or heart attack in these individuals. Overall, for every 1,000 people treated, there were 9 fewer heart attacks and 8 fewer strokes compared to those who did not take the medication, with no apparent serious side effects.

Taking melatonin supplements to treat insomnia for more than a year is associated with an increased risk of heart failure—including an increase in hospitalisations and mortality—within five years of use, according to a study presented at a conference of the American Heart Association. The study compared a group of 65,000 adults diagnosed with insomnia who had a prescription for melatonin with another group who did not have a prescription for this supplement.

An oral formulation of risperidone could be administered weekly instead of daily to treat patients with schizophrenia with the same efficacy, according to a phase III clinical trial published in The Lancet Psychiatry. The study included 83 patients in the United States.

The number of adolescents with anxiety problems seems to be increasing, especially in developed countries. An opinion article published in the journal Science proposes that maternal stress, quality of care and environmental conditions in the early years, together with current social and technological changes, may contribute to explaining this trend.

Large language models—artificial intelligence systems based on deep learning—could be useful in detecting mental health risks such as depression and suicide risk in narrative tests of patients undergoing psychiatric treatment. This is one of the conclusions of research published in JAMA Network Open, which also shows the potential of embeddings — a natural language processing technique that converts human language into mathematical vectors — to achieve the same end.

Narcolepsy type 1 is a sleep disorder characterised by excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy - sudden loss of muscle tone. Existing treatments are based on palliation of symptoms, with moderate success. Now, an international phase 2 clinical trial, involving CEU San Pablo University and other Spanish centres, published in the journal NEJM, shows the results of a new drug targeting the cause of the disorder. Overall, the benefits appear superior and no serious adverse effects were observed. According to the authors, ‘the results are promising’ and represent ‘a very significant impact on the quality of life of these patients’.

An international team has carried out a review of studies and a meta-analysis on the cardiovascular safety of the drugs used to treat ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder). Their conclusions are that most of them, and not just the stimulants, affect the pulse and blood pressure. According to the authors, who publish the results in the journal The Lancet Psychiatry, although the changes are slight, ‘professionals should monitor blood pressure and pulse in patients with ADHD treated with any pharmacological intervention’.