
University of Granada
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Doctor of Ethology, research collaborator in the Department of Zoology
Professor in the Department of Theoretical Physics and the Cosmos at the University of Granada.
Professor at the University of Granada (UGR), lecturer in the Master's Program in Research in Physical Activity and Sport at the UGR and director of the research group "Brain and Human Cognition" at the Mind, Brain and Behavior Research Center (CIMCYC)
Vice-director of FiloLab and professor of Bioethics at the University of Granada
Professor of Pharmacology at the University of Granada and coordinator of the Working Group on Basic Sciences in Pain and Analgesia of the Spanish Pain Society
Full professor and director of the department of Personality, Evaluation and Psychological Treatment at the faculty of psychology of the University of Granada.
Professor of Zoology at the Department of Zoology and coordinator of the Applied Ecology and Agroecosystems research group at the University of Granada
Professor of AI, Director of the DaSCI (Data Science and Computational Intelligence) Research Institute, University of Granada and member of the Royal Academy of Engineering
Professor of Immunology and Director of the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 3 and Immunology at the University of Granada
Permanent professor in the Department of Ecology at the University of Granada

When Neanderthals and modern humans had offspring together, little Neanderthal DNA from the X chromosome entered the human gene pool. A study published in the journal Science traced ancient gene flow and found a relative excess of 62% modern human ancestry on Neanderthal X chromosomes. This suggests that the couples who had children were mostly Neanderthal men and modern human women, although the authors cannot rule out the possibility that demographic processes played a significant role.

High academic pressure during adolescence is linked to increased rates of depressive symptoms and self-harm, which can persist into early adulthood. This finding, published in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health, was observed in a sample of nearly 5,000 young people born in England (UK) in 1991 and 1992. Academic pressure was measured when participants were 15 years old, mental health was assessed repeatedly between ages 16 and 22, and self-harm was tracked up to age 24. While the association with depressive symptoms was observed up to age 22, it was strongest at 16. Regarding self-harm, each one-point increase in academic pressure was associated with an 8 % higher likelihood of engaging in self-injurious behavior.

Various studies have shown that exercise benefits the brain. Now, an international team has studied in mice how physical activity affects the brain and how these changes influence the effects of exercise. The research, published in Neuron, has shown that physical activity causes brain changes in a region of the hypothalamus involved in how the body uses energy and in regulating blood sugar. If these neurons were blocked immediately after exercise, the animals showed no improvement in endurance or metabolism with training. The authors suggest that activating these neurons may help the body recover faster, allowing other parts, such as the muscles, lungs, and heart, to adapt more quickly to more intense workouts.
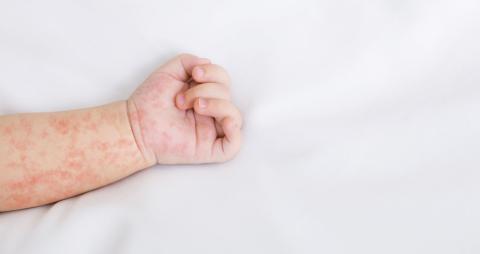
Measles cases in Europe and Central Asia fell in 2025 compared with 2024, according to preliminary data reported by 53 countries in the World Health Organization (WHO) European Region. This decline aligns with the preliminary figures published this week by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). According to the WHO, countries in Europe and Central Asia reported 33,998 measles cases in 2025, representing a decrease of nearly 75 % compared with the 127,412 cases recorded in 2024. In Spain, however, the number of cases has increased, as shown by data from the Carlos III Health Institute. A few weeks ago, the WHO announced that Spain had lost its measles-free status.

The Prime Minister, Pedro Sánchez, announced on Tuesday from Dubai that Spain will ban children under the age of 16 from accessing social media and will adopt other measures to increase control over digital platforms and ensure that their executives are held accountable for violations. Sánchez made this announcement in his speech to the plenary session of the World Government Summit and announced that next week the government will approve a series of measures, including this ban.

An international team has analysed data from more than 700 mammal populations in zoos since 1970 and concludes that there has been an ageing of the animals and a decline in females of reproductive age. According to the authors, this jeopardises the role of zoos in conserving endangered wildlife species and promoting global biodiversity. The findings are published in the journal PNAS.
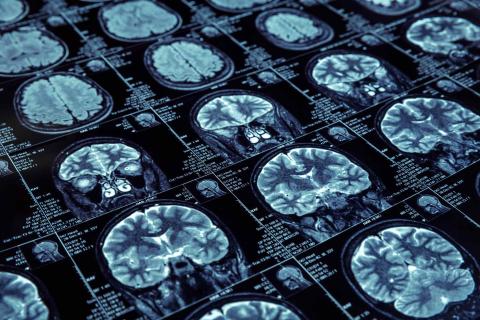
An international team trained 85 people to activate a part of the brain associated with reward and positive expectations, after which they received a hepatitis B vaccine. Overall, those who learned to maintain greater activity in this area showed a greater increase in antibody levels after immunization. According to the authors, the results “suggest that positive thinking could help the brain strengthen the immune system in a non-invasive way.” The work is published in Nature Medicine.

Restrictions on mobility and activity imposed during the covid-19 pandemic had an impact on the beaks of a species of bird, specifically the dark-eyed junco, which lived in urban areas of Los Angeles (USA). This is shown in a study published in the journal PNAS, which reveals how birds born during these lockdowns had beaks similar to their counterparts in the wild. With the return of human activity, the beak returned to its pre-pandemic shape. The authors argue that this change was mainly due to an adaptation to the food available, as the birds no longer had access to human food waste.

A research team led by the British Museum presents evidence in the journal Nature that humans were making fire – deliberately and not just taking advantage of natural fires – 400,000 years ago in Barnham (United Kingdom). The remains analysed, including burnt sediments, heat-damaged flint axes and pieces of pyrite, are much older than those recorded to date, which dated the deliberate use of fire to around 50,000 years ago in northern France.

Gilberto and Tomás are two macaques trained to synchronise their movements with the rhythm of a metronome, who were also able to tap to a musical beat, according to a study published in Science. This result contradicts the vocal learning hypothesis, according to which only species capable of complex vocalisations can perceive and follow a musical rhythm.