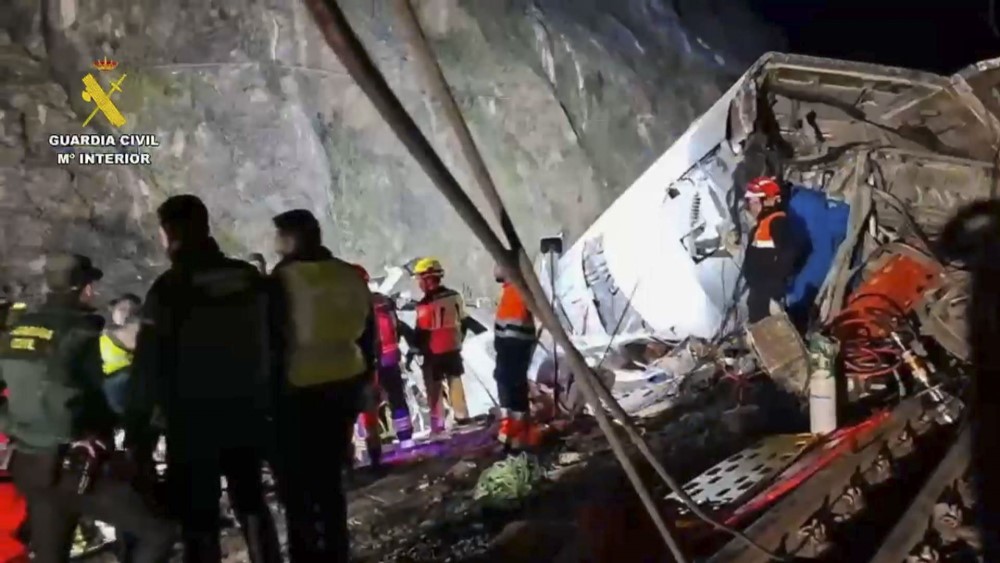
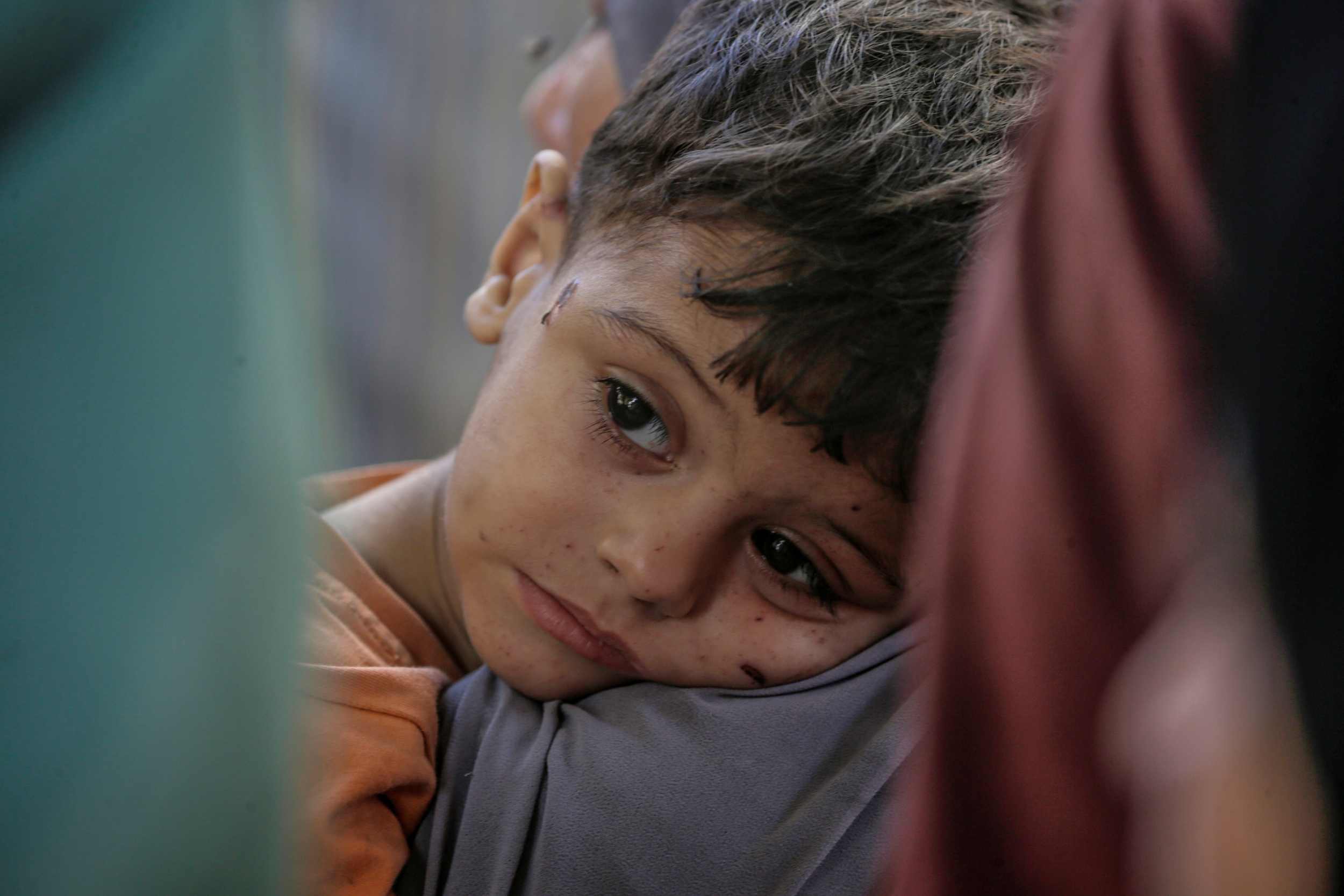
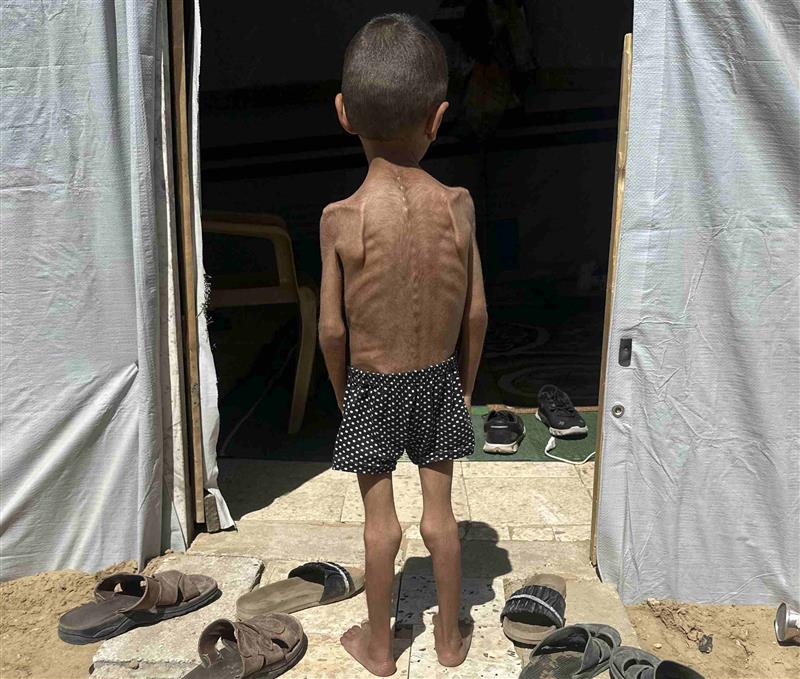
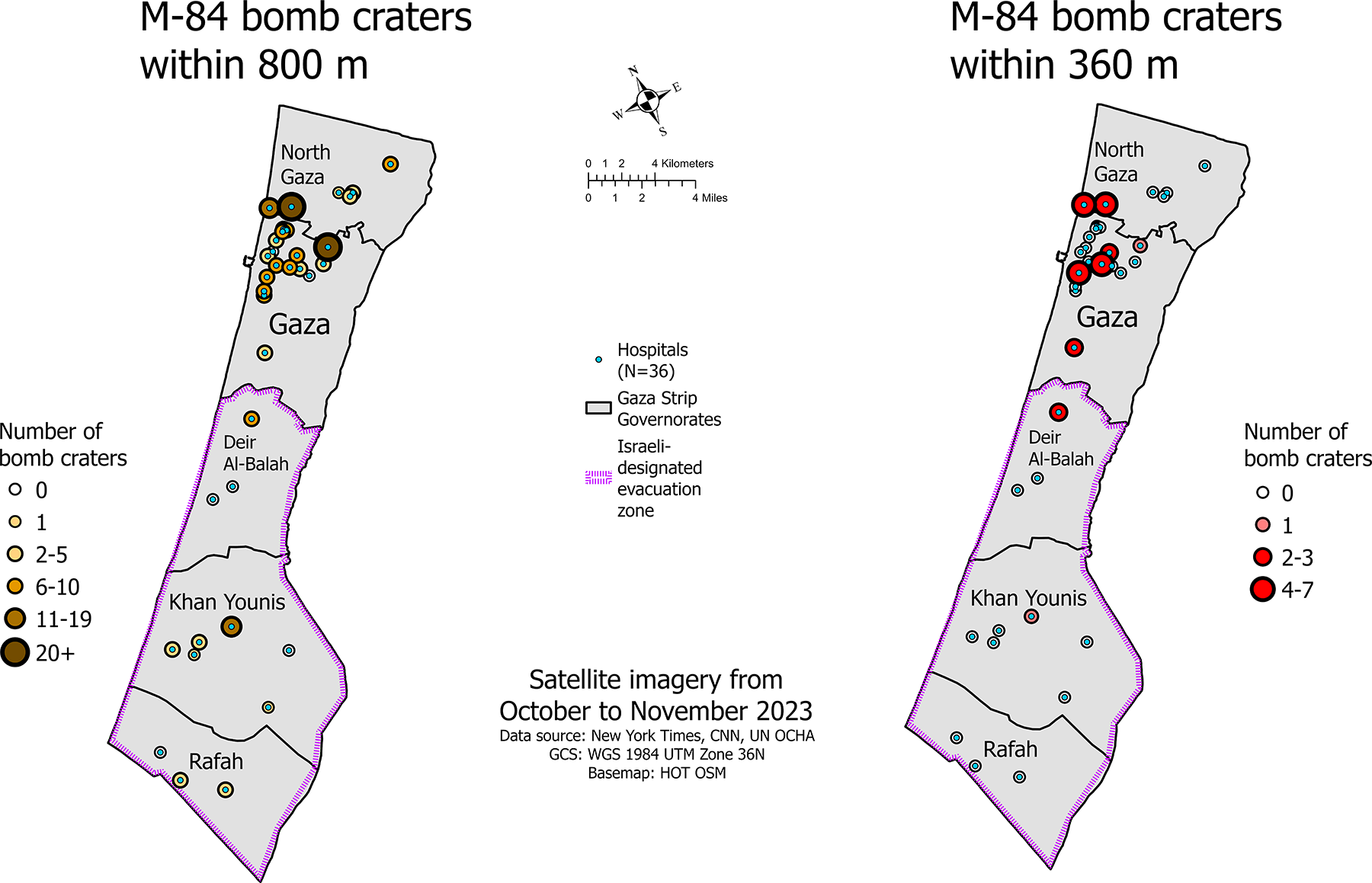
More than 54,600 children under the age of five in Gaza are in need of medical care for acute malnutrition, according to estimates from a study published in The Lancet, which shows that the prevalence of malnutrition decreases during a ceasefire and increases during Israeli blockades of access to food, water, or medicine. For example, after four months of severe aid restrictions—between September 2024 and January 2025—malnutrition increased from 8.8% to 14.3%, with a higher incidence in Rafah and among children between 24 and 59 months of age. The study, conducted by UNRWA, is based on data from more than 219,000 children between the ages of six and 59 months from various locations in the Gaza Strip, collected between January 2024 and August 2025.