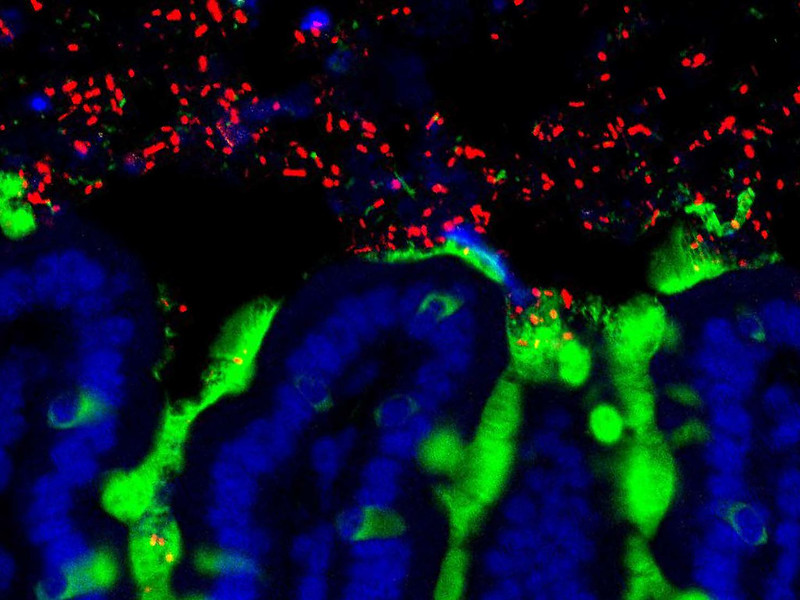
An opinion piece refutes studies linking gut microbiota and autism
There is no solid scientific evidence that alterations in the gut microbiota cause autism, according to an opinion piece published in the scientific journal Neuron. The research supporting this hypothesis—observational studies and clinical trials in humans, as well as mouse models—has both conceptual and methodological shortcomings, the authors write.