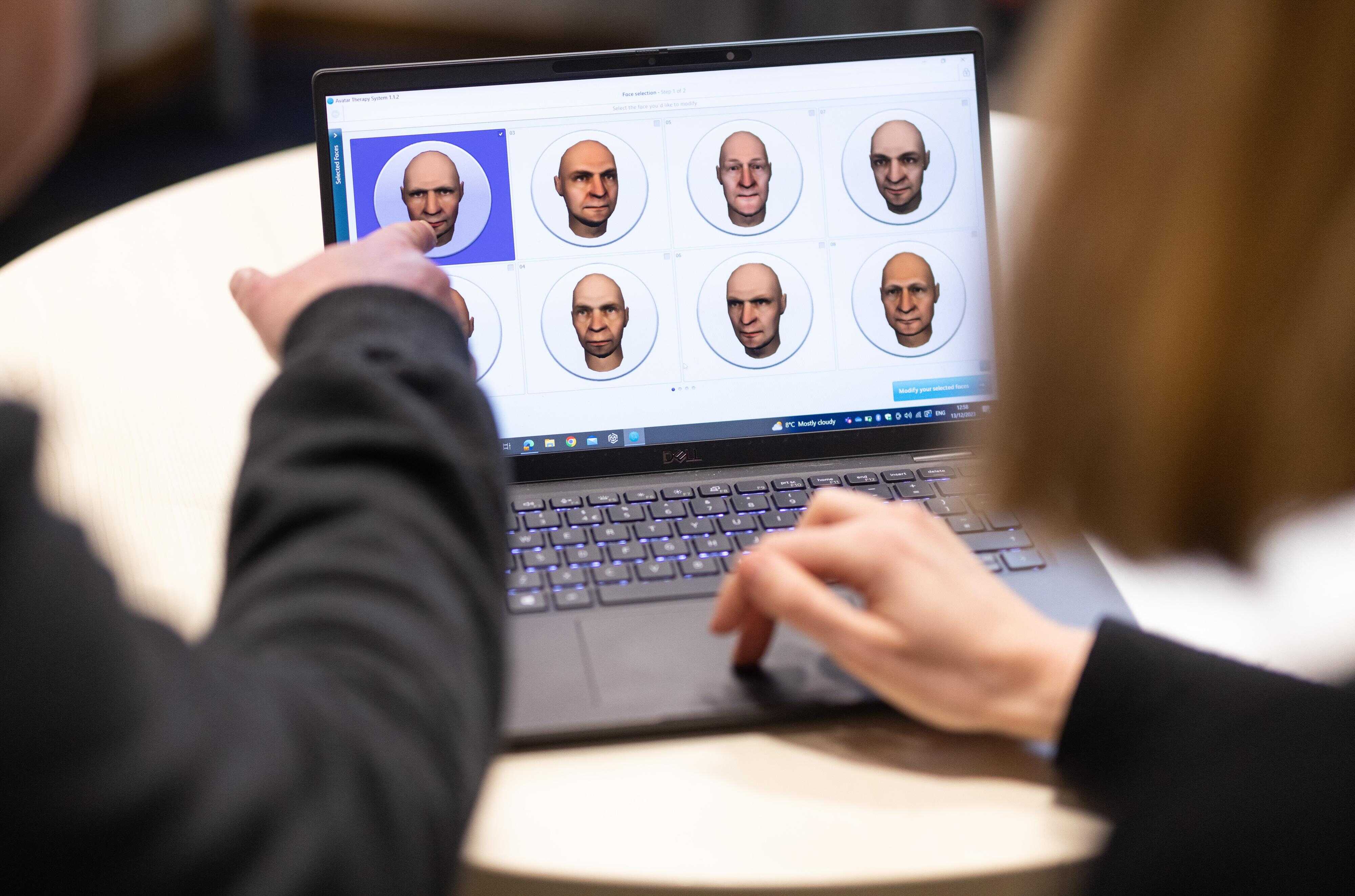
The roadmap for the new DSM, the ‘bible’ of psychiatry, unveiled
The American Psychiatric Association has unveiled the new features of the forthcoming Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) in five articles published in The American Journal of Psychiatry. Among the highlights are the proposed change of name — it will become the Diagnostic and Scientific Manual — and the intention for it to be more dynamic, incorporating biomarkers for diagnosis and integrating the socioeconomic, cultural and environmental determinants of health. According to the authors, the aim is to enable a more personalised and inclusive clinical practice, aligned with scientific rigour. The most recent update was published in 2022 with the DSM-5-TR, and specialists are currently unaware of the date of the next edition, as they reported during a briefing with journalists.