CSIRO Climate Science Centre in Canberra, Australia
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Executive Director of the Global Carbon Project and Senior Research Fellow at the CSIRO Climate Science Centre in Canberra, Australia

Two papers published in Nature Climate Change analyse the possibility of exceeding the Paris Agreement targets of limiting warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial temperatures. Both papers suggest that having exceeded this warming threshold by 2024 could indicate that we have entered a period of several decades with average global warming of 1.5 °C. According to the authors, rigorous climate mitigation efforts are needed to keep the Paris Agreement targets within reach.

Carbon stored globally by plants is shorter-lived and more vulnerable to climate change than previously thought, according to a study published in Science. This has implications for nature's role in climate change mitigation, including the potential for carbon removal projects such as mass tree planting. The research reveals that existing climate models underestimate the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) that vegetation absorbs globally each year, but overestimate how long that carbon stays there.

Global carbon emissions from fossil fuels have increased again in 2023, reaching record levels, reaching 36.8 billion tonnes of CO2. This means they are 1.4% above pre-pandemic CO2 levels. This is one of the forecasts in the Global Carbon Budget 2023 report that researcher Pep Canadell presented at a briefing organised by SMC Spain.

The amount of carbon available to emit without surpassing the 1.5°C limit set by the Paris Agreement, commonly referred to as the carbon budget, could be depleted within the next six years, as suggested by a study published in Nature Climate Change. The findings are based on a reevaluation of existing estimates and indicate that carbon budgets might be lower than previously believed.

A model-based study estimates that there will be ice-free Arctic Septembers about a decade earlier than previously predicted. The possibility of this happening between 2030 and 2050 exists even in low-emissions scenarios, which is a more pessimistic estimate than the last IPCC report. The results are published in the journal Nature Communications.

Almost a decade after the previous edition, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has presented the synthesis report of its sixth assessment cycle (AR6) on Monday in Switzerland. "This synthesis report underlines the urgency of taking more ambitious action and demonstrates that, if we act now, we can still secure a sustainable and liveable future for all," said IPCC chair Hoesung Lee.
The document includes the main findings of the three Working Group reports of 2021 and 2022 (Physical basis, Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability and Mitigation of climate change) and the three special reports of 2018 and 2019 (Global warming of 1.5°C, Climate change and land, Ocean and cryosphere in a changing climate). With this document, which is primarily addressed to policy makers, the IPCC closes its sixth assessment cycle.

Research published in Science assesses for the first time quantitatively the climate projections made by scientists at oil company Exxon and ExxonMobil Corp between 1977 and 2003. According to the study, most of their projections accurately predicted warming consistent with subsequent observations. However, the authors point out that the company's public statements contradicted its own scientific data.
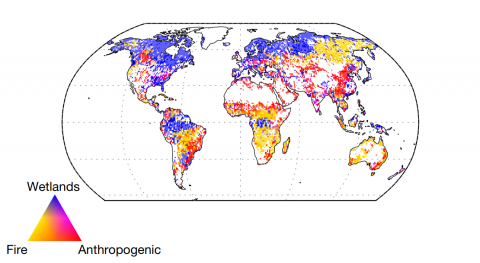
Although in 2020 the covid-19 pandemic caused confinement and economic paralysis in many countries, the rate of methane growth in the atmosphere peaked, reaching the highest level since 1984. Research published in Nature claims that the main source would be the warmer, wetter wetlands of the northern hemisphere.

At current CO2 emission levels, there is a 50 % chance of exceeding 1.5°C warming in nine years. This is one of the conclusions of the Global Carbon Budget 2022 report presented by its coordinator, researcher Pep Canadell, at a briefing organised by SMC Spain.