UR International Group
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Scientific Director of the UR International Group and Coordinator of the Ethics Group of the Spanish Fertility Society
Around 15% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage, and it is estimated that almost half of all conceptions are lost in early stages, without people even realizing it. Now, a team from the United States and Denmark has analyzed data from more than 139,000 embryos from in vitro fertilization of nearly 23,000 couples and has found several genetic variants associated with a higher risk of miscarriage. Many of these are associated with meiosis, a key cell division process in sex cells. The authors, whose study is published in Nature, acknowledge that the new data will not allow for a precise estimation of individual risk, because the most important factors remain age and environmental elements.
An international team has succeeded in generating fertilisable human eggs from skin cells using a novel technique. According to the authors, the study offers a way to address infertility, although they acknowledge that further research is needed to ensure efficacy and safety before future clinical applications. Of the 82 functional oocytes generated and fertilised, only 9% developed to day 6, when the experiment ended. In addition, the embryos had chromosomal abnormalities. The results are published in the journal Nature Communications.

A Canadian team analysed samples from women undergoing in vitro fertilisation and found that higher concentrations of THC metabolites—the main psychoactive substance in cannabis—were associated with a higher rate of oocyte maturation and a lower number of embryos with the correct number of chromosomes. The latter could be replicated at similar concentrations under laboratory conditions. The authors, who published their findings in the journal Nature Communications, acknowledge that the study does not have sufficient statistical power to draw conclusions, but it does warn of possible risks to women's fertility.
In 2015, the United Kingdom became the first country to pass legislation allowing the use of mitochondrial donation technology, pronuclear transfer. The technique is designed to limit, through in vitro fertilization, the transmission of mitochondrial DNA diseases in babies born to women who are at high risk, and for which there is no cure. Two studies published in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) describe the results of the first treatments performed to date, from which eight babies have been born by mitochondrial donation, with reduced risk of disease.
A research team from Murcia has found several types of microplastics in 69% of follicular fluid samples from 29 women and 55% of seminal fluid samples from 22 men, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE), being held from 29 June to 2 July in Paris, France. The most frequent polymer in both types of samples was polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). The abstract of the research is published in the journal Human Reproduction.

The relative risk of being born with a major heart defect is 36% in babies conceived using assisted reproductive techniques, such as in vitro fertilisation, compared to newborns not using these techniques, according to a study published in the European Heart Journal. The absolute risk was 1.84% versus 1.15%. The research, which included more than seven million babies born in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden, also shows that the increased risk is especially associated with multiple births, which are more common in assisted reproduction.

The sperm of men infected with high-risk genotypes of the human papillomavirus (HPV) suffers more damage from oxidative stress and has a weaker immune response, which can lead to reduced fertility. This is one of the conclusions of a study published in the journal Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. The research compared the semen of 20 adults infected with high-risk genotypes, seven infected with low-risk genotypes, and 43 adults without infections.
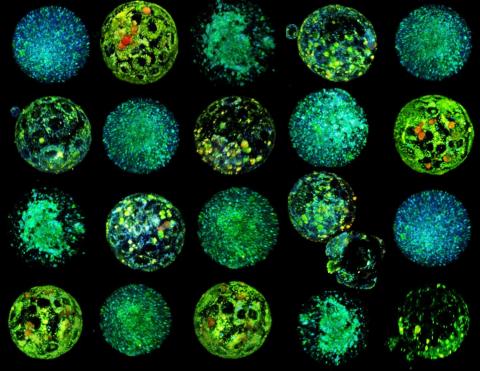
A new technique developed at the Institut de Bioenginyeria de Catalunya (IBEC) has succeeded in assessing the health of mouse oocytes and embryos in a non-invasive way, according to a study published in PNAS. The method generates 3D images to visualise the metabolism of oocytes and embryos obtained by in vitro fertilisation and makes it possible to select those that are most likely to implant and develop, say the authors.
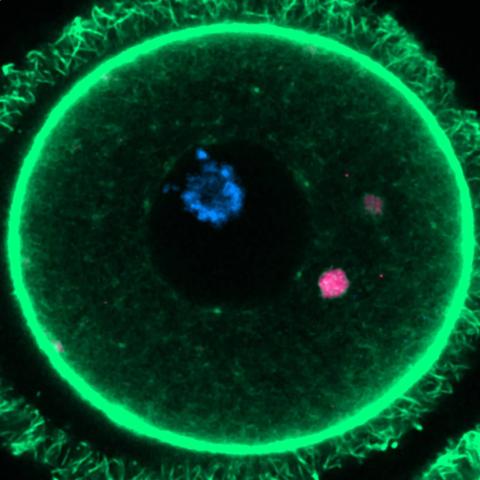
At an informative meeting organized by the Science Media Centre Spain, the coauthor of a paper published this week in the journal Cell discussed his findings with journalists. Although the study was conducted with mice, he is confident in being able to analyze human eggs to see if his conclusions could explain the loss of fertility that occurs in women with age.
An international team, led by a Spanish group, has published the mechanism that allows immature egg reserves (oocytes) to survive for many years, up to almost half a century in the case of humans. The research studies how oocytes are affected by protein aggregates similar to those that damage other cells such as neurons and can cause neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. The finding of how these egg reserves are kept healthy may help to understand some causes of infertility. The results are published in the journal Cell.