A WHO report warns that one in six confirmed bacterial infections in 2023 was resistant to antibiotics
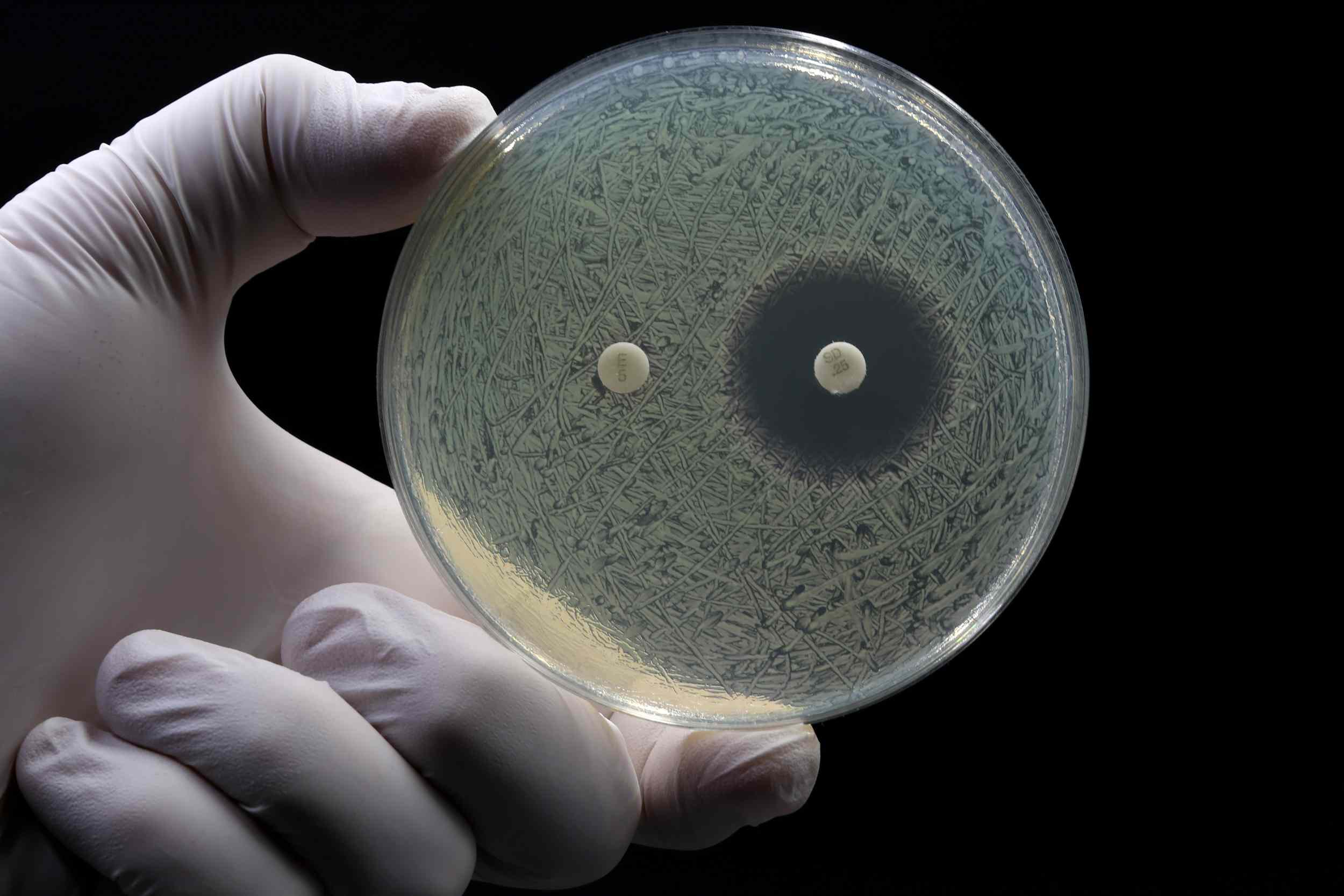
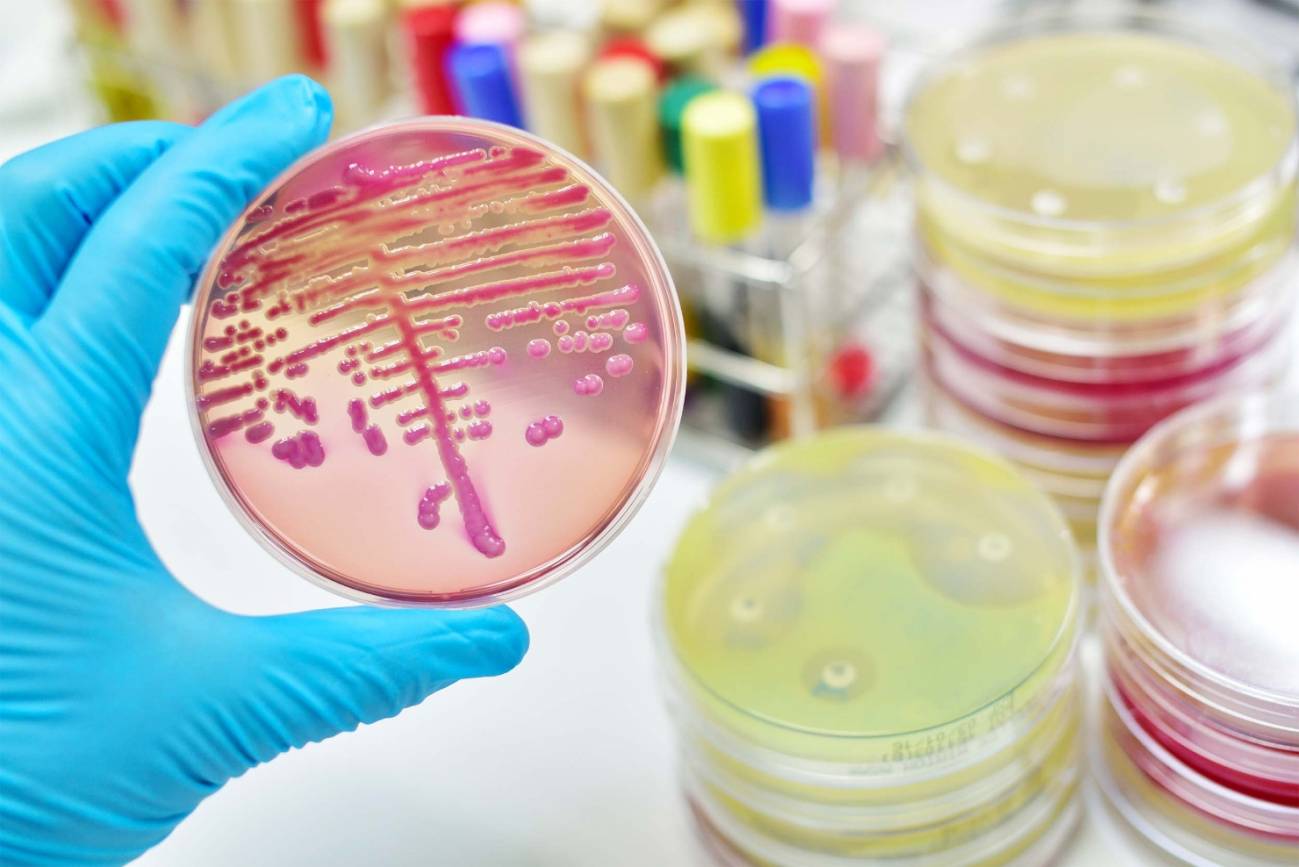
In 2023, one in six laboratory-confirmed bacterial infections were found to be resistant to antimicrobials, according to a report published by the World Health Organisation (WHO). Between 2018 and 2023, resistance increased in more than 40% of monitored antibiotics, which ‘is limiting empirical treatment options and driving a shift from oral to intravenous treatments, including greater reliance on second-line and last-resort antibiotics,’ the report warns. For example, globally, nearly 45% of Escherichia coli bacteria are resistant to third-generation cephalosporins, a proportion that varies from 20% in Europe to more than 70% in Africa.