Institute of Neuroscience (CSIC-UMH)
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Director of the Institute of Neurosciences, a joint centre of the Miguel Hernández University of Elche (UMH) and the CSIC
CSIC Group Leader at the Institute of Neurosciences (CSIC-UMH)
CSIC research professor at the Instituto de Neurociencias de Alicante (CSIC-UMH) and member of the Royal Academy of Sciences of Spain
Research Professor at CSIC at the Institute of Neurosciences (Alicante)
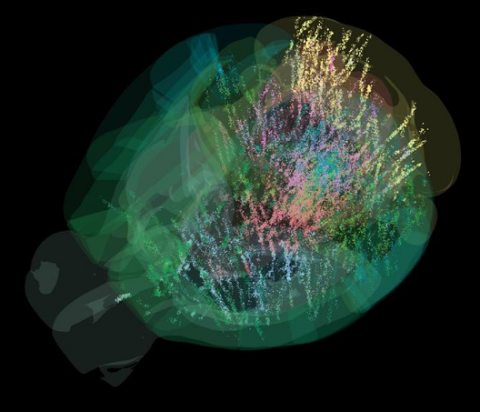
A team of neuroscientists from the International Brain Laboratory has described for the first time a virtually complete map of brain activity in mice during the decision-making process. To do so, they recorded the activity of more than half a million neurons across 12 different laboratories, representing 95% of brain volume. The map contradicts a hierarchical view of information processing and shows that decision-making is distributed in a coordinated manner across multiple brain areas. The results are published in two articles simultaneously in the journal Nature.
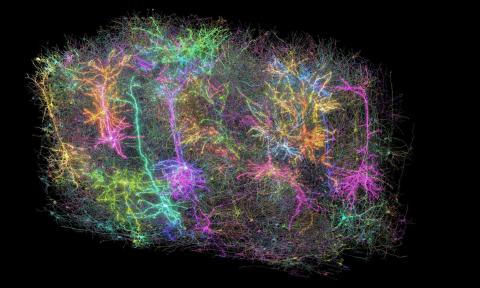
A set of articles published in Nature and Nature Methods draws a high-resolution map of the structure of and connections between the brain cells of mice. The map is based on data from a single cubic millimetre of brain and includes more than 200,000 cells, around 84,000 neurons and 524 million synaptic connections. Although this is a very small part of the mouse brain, it will help us understand how different types of cells work together.
The seventh Annual Report of the COSCE Transparency Agreement, prepared by the European Animal Research Association, which analyses transparency in the use of animals for scientific experimentation in Spain in 2023, was presented today. According to the document, transparency is consolidated among the signatory institutions -168 in 2024- and all of them publish a statement on their websites on the use of animals. Public mention of the number and species used stands at 47%, compared to 38% the previous year.

The Karolinska Institute has awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for the discovery of microRNAs, small RNA fragments that do not contain instructions for making proteins but instead participate in the regulation of gene expression. Their role is fundamental in processes such as cell differentiation, and their alteration can influence diseases like cancer.

The Science group of journals publishes several parts of a high-resolution atlas of human brain cells, the largest 'map' of its kind to date. It is a series of papers from an international mega-project, the Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) Initiative - Cell Census Network (BICCN), launched in 2017 to study brain cell types and their functions in humans, non-human primates and rodents. The data "will now allow researchers to address fundamental scientific questions about the human brain and its genetic organisation," states the introduction to the journal's special issue.

Early-life adversity, such as separation from the mother, can alter the neurological functioning of mice, causing some to experience panic and anxiety later in life. A study shows that these changes can be passed on for at least two generations and that inhalation of a drug, the diuretic amiloride, can reverse them. According to the authors, this treatment could be used in the future to alleviate panic disorders and related conditions in humans. The results are published in the journal Science Advances.

Researchers have presented the first connectome - a diagram of neural connections - of the whole brain of an insect, a vinegar fly larva (Drosophila melanogaster). The work, which the authors say will inspire new studies of neural circuits and machine learning architectures, is published today in Science.

The Karolinska Institute has awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology to Swedish biologist Svante Pääbo, a specialist in evolutionary genetics, for his discoveries on the genomes of extinct hominids and human evolution.
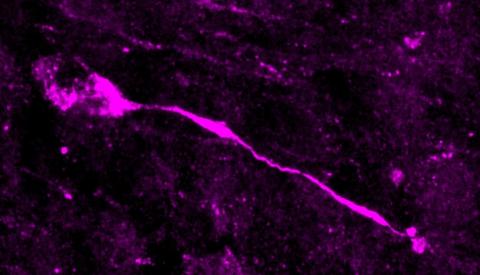
A single amino acid change in a protein (TKTL1) may have given modern humans an advantage over their older contemporaries, such as Neanderthals, by allowing greater neocortical neuronal formation, according to research published in Science.
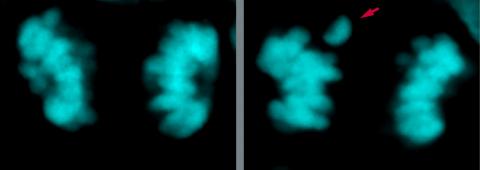
Compared to Neanderthals and apes, modern humans experience fewer chromosomal inheritance errors when their brains develop, according to a new study published in Science Advances.