University of Cantabria
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Full Professor of Prehistory and Director of the EvoAdapta Group at the University of Cantabria
Head of the Neurology Department at the Marqués de Valdecilla-IDIVAL University Hospital and Associate Professor of Medicine in the Department of Medicine and Psychiatry at the University of Cantabria
Professor of the Department of Physiology and Pharmacology at the University of Cantabria.
Professor of Pharmacology at the University of Cantabria and President of the Ibero-American Down21 Foundation
PhD in Physics and tenured scientist at the Institute of Physics of Cantabria (CSIC-UC)
Scientific Director of the Valdecilla Health Research Institute (IDIVAL), Head of the Immunology Department, and Professor of Immunology at the University of Cantabria-Marqués de Valdecilla University Hospital
Associate Professor in the Department of Education at the University of Cantabria
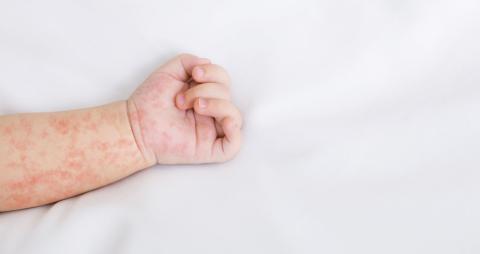
Measles cases in Europe and Central Asia fell in 2025 compared with 2024, according to preliminary data reported by 53 countries in the World Health Organization (WHO) European Region. This decline aligns with the preliminary figures published this week by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). According to the WHO, countries in Europe and Central Asia reported 33,998 measles cases in 2025, representing a decrease of nearly 75 % compared with the 127,412 cases recorded in 2024. In Spain, however, the number of cases has increased, as shown by data from the Carlos III Health Institute. A few weeks ago, the WHO announced that Spain had lost its measles-free status.

Physical inactivity is a risk factor for the onset of Alzheimer's disease. An international team has studied nearly 300 people with preclinical Alzheimer's—without symptoms but with an accumulation of tau and beta-amyloid proteins in the brain—for 14 years to find out whether physical exercise can also influence its progression. The results indicate that even very moderate activity—walking between 3,000 and 5,000 steps per day—was associated with slower deterioration, while the benefits—which appear to be related to lower tau protein deposits—were greater and tended to stabilise with activity involving between 5,000 and 7,500 steps. The results are published in the journal Nature Medicine.

Severe combined immunodeficiency due to ADA enzyme deficiency is a rare disease that, without treatment, usually causes death within the first two years of life. These "bubble children" are currently treated with a bone marrow transplant or with injections that aim to restore, to the extent possible, the function of this enzyme. Now, an international team presents the results of a gene therapy administered to 62 children with the disease between 2012 and 2019. The therapy was effective in 95% of cases and did not cause serious complications, according to the authors, whose work is published in the journal NEJM.

The Karolinska Institute has awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology to Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell and Shimon Sakaguchi for describing how the immune system is regulated so as not to harm us. His groundbreaking discoveries on peripheral immune tolerance have spurred the development of new treatments for cancer and autoimmune diseases.
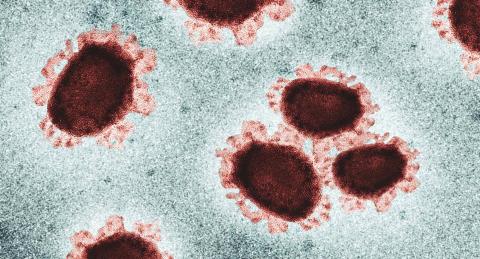
A US team has analysed the presence of beta-amyloid deposits – which are linked to Alzheimer's disease – in the post-mortem retinas of four people with covid-19 and found that they were larger than in four people without covid. In complementary experiments, the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in retinal organoids produced an increase in deposits, while the use of a drug that blocks the virus from binding to neurons reduced their accumulation. The results are published in the journal Science Advances.
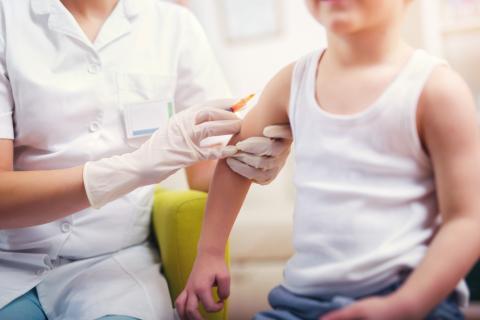
If immunisation rates continue to decline over an extended period, measles and even other eradicated diseases—such as rubella and polio—could re-emerge in the United States at endemic levels, according to a new study published today in the journal JAMA.
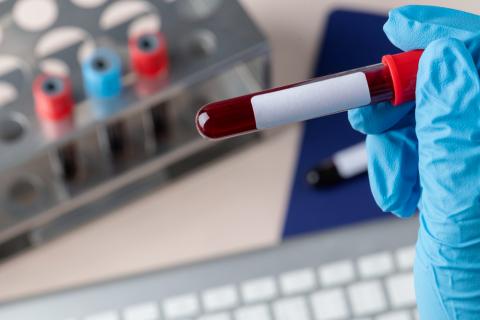
An international team with Spanish participation has analysed the usefulness of a blood biomarker - the p-tau217 protein - for detecting Alzheimer's disease in 1,767 patients. According to the authors, who publish the results in the journal Nature Medicine, the test has detected the disease with high reliability in four hospital cohorts, as well as in a primary care cohort. They add that it is an assay that can be easily implemented in clinical laboratories and is already routinely used in some centres in Spain.
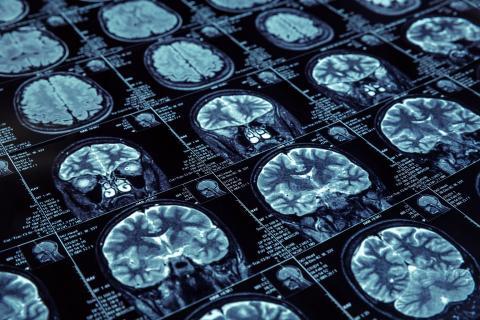
The DIAN-TU platform is an initiative to test Alzheimer's disease treatments early, by recruiting people with a mutation that leads to developing the disease in the future. One of the trials with the anti-amyloid drug gantenerumab ended without reaching the targets. However, a continuation of the study in 73 patients suggests - for the first time, according to the authors - that long-term, high-dose treatment given some time before symptoms develop could delay the onset of the disease. The results are published in the journal The Lancet Neurology.

Patients receiving organ transplants often need to be treated with long-term immunosuppressants to reduce the likelihood of rejection, which has numerous side effects. An international team has shown in crab macaque monkeys that, in the case of heart transplantation, the use of these drugs could be avoided if combined with a kidney transplant from the same donor. The results are published in the journal Science Translational Medicine.

A team of researchers has analyzed more than 300 human genomes from the last 50,000 years and has concluded that most of the gene flow we received from Neanderthals is attributable to a single period, which probably occurred between 50,500 and 43,500 years ago. In addition, Neanderthal inheritance underwent rapid natural selection in subsequent generations, especially on the X chromosome, according to a study published in Science.