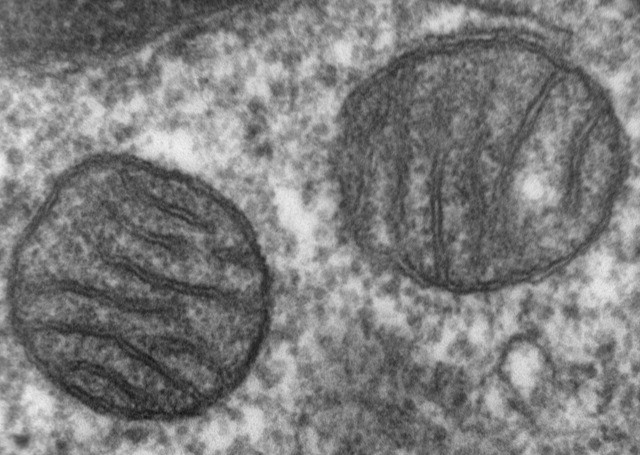
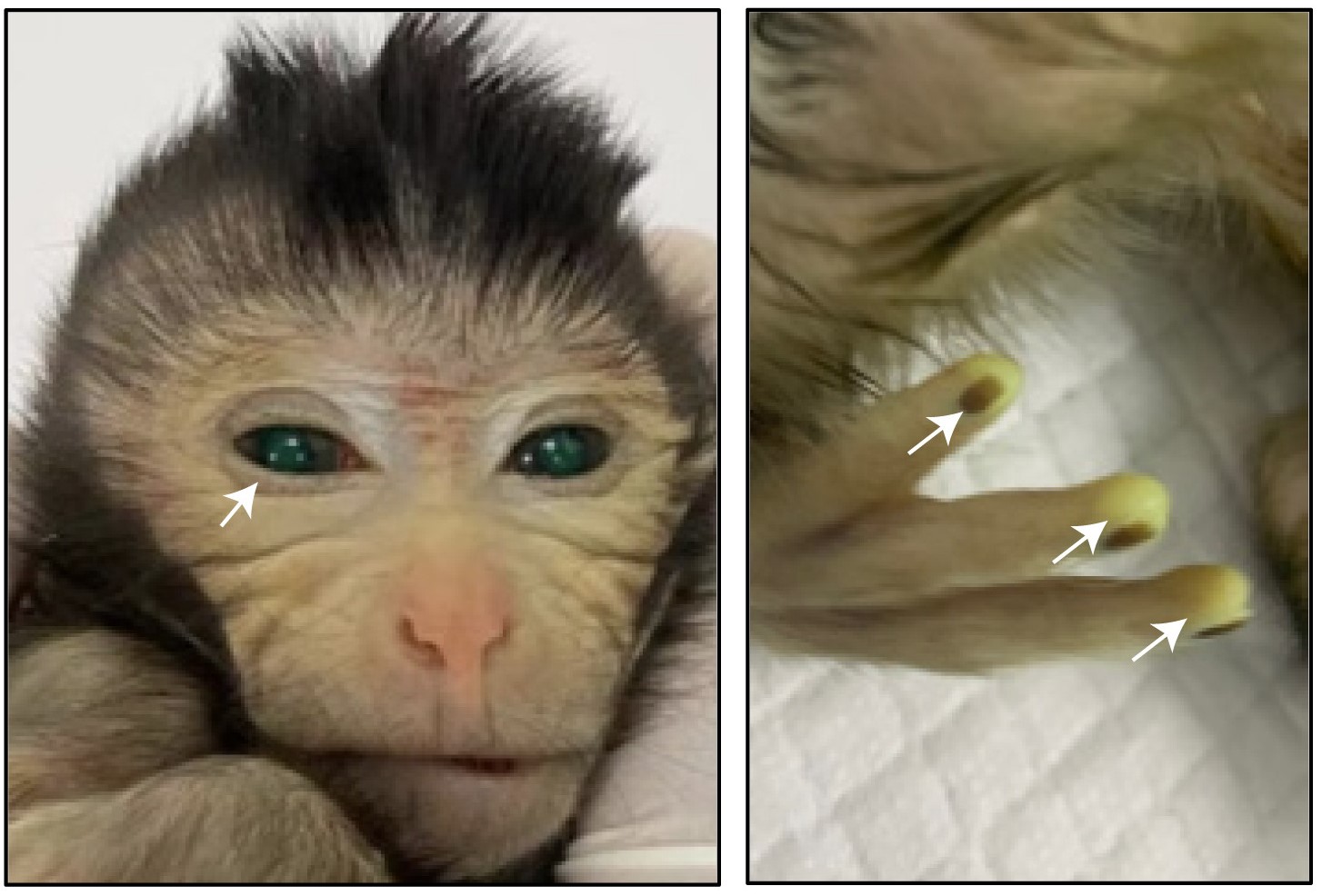
Regions in our DNA that control genes related to hibernation have been identified
At least some of the genes that enable hibernation in certain animals are also found in our DNA, but they are regulated differently. Now, researchers at the University of Utah (United States) have analyzed the human genome and identified specific regions and changes that affect this regulation, which could be useful in the future to take advantage of some of its benefits. According to the researchers, who share their findings in two papers published simultaneously in the journal Science, "there is a possibility that, by understanding these mechanisms, we may find strategies to intervene and help with age-related diseases and improve our own health".