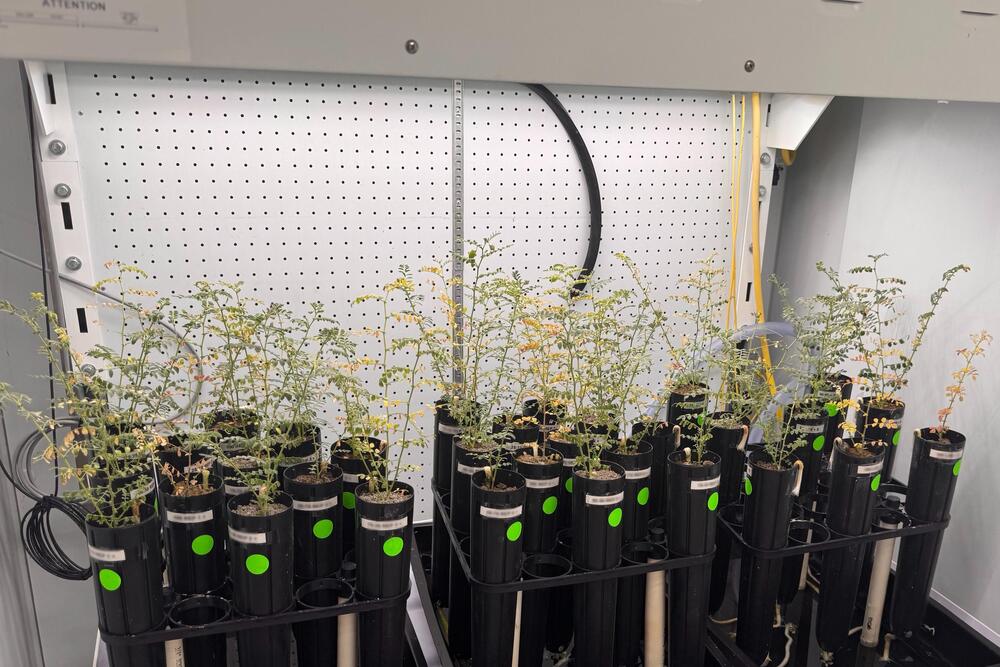
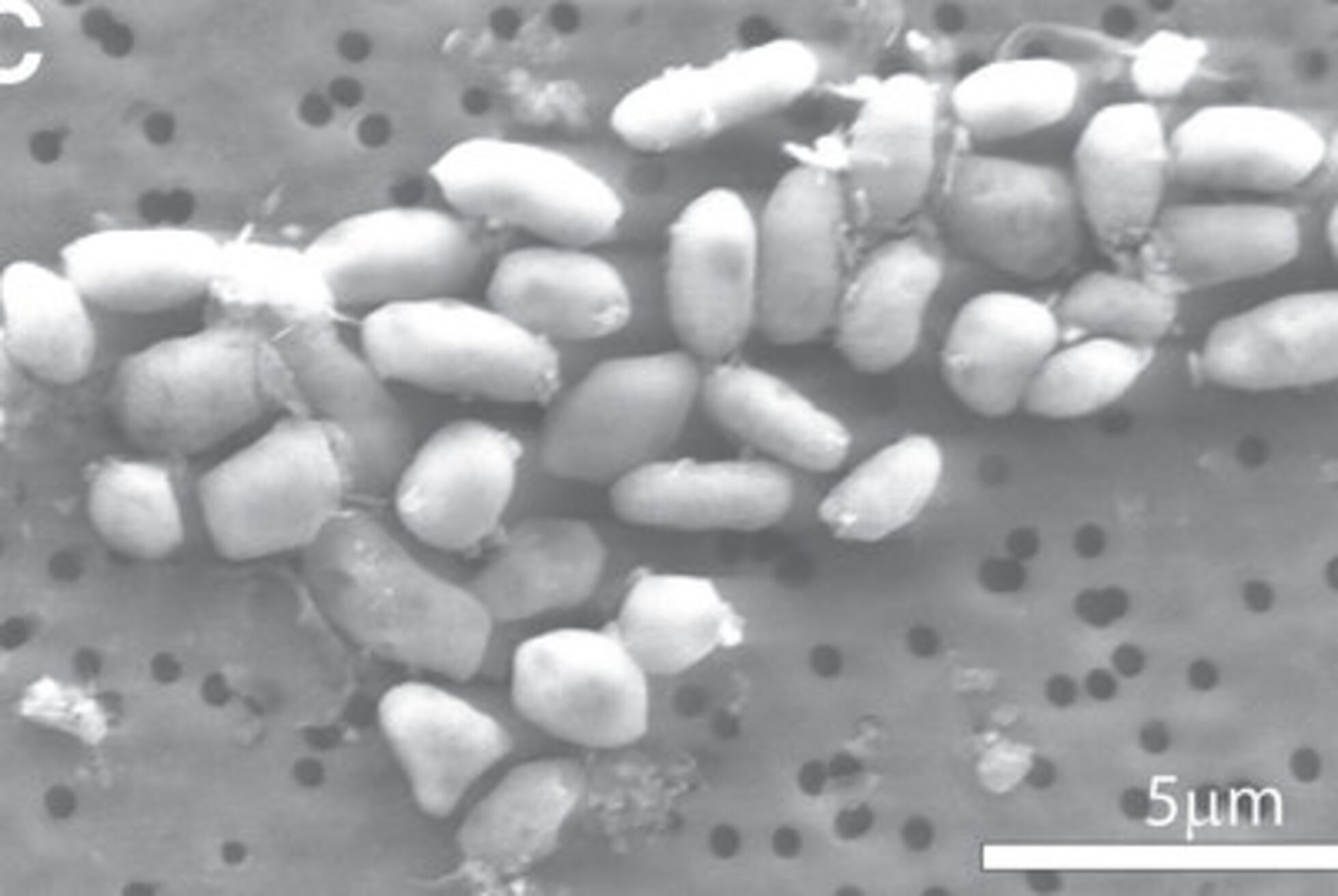
Chickpea plants and microorganisms survive on Earth in lunar and Martian soil simulants
Two articles published in the journal Scientific Reports explore the survival capacity of microorganisms and plants in imitations of lunar and Martian soils. In the first, the team succeeded in cultivating chickpea plants in a lunar soil simulant — lunar regolith — treated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and worm compost. In the second article, microbial growth was investigated in a Martian soil simulant with different water proportions and under pressure and temperature conditions similar to those on Earth. At a water level comparable to that on Mars, an atmospheric humidity of 34 %, microbial mass increased, although it fell back to zero after 60 days. “These findings extend the known physicochemical limits of life in solid substrates and provide new insight into the potential habitability of hyper-arid extraterrestrial environments,” the authors say.