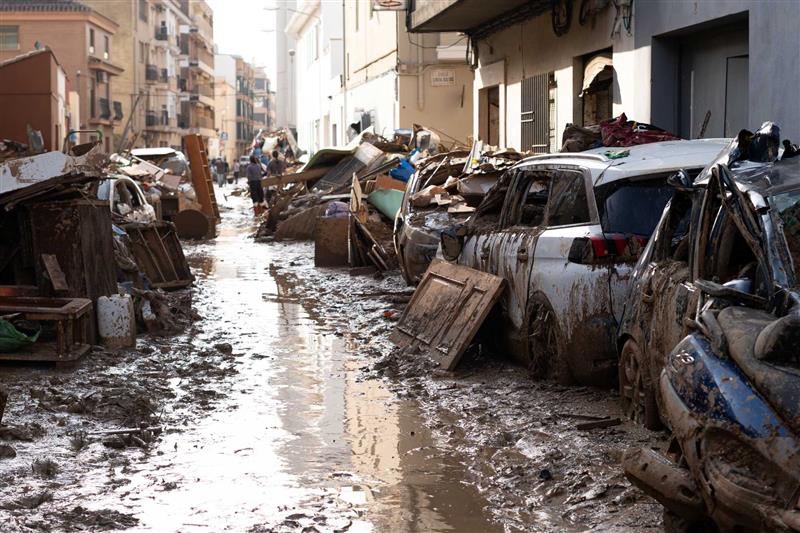
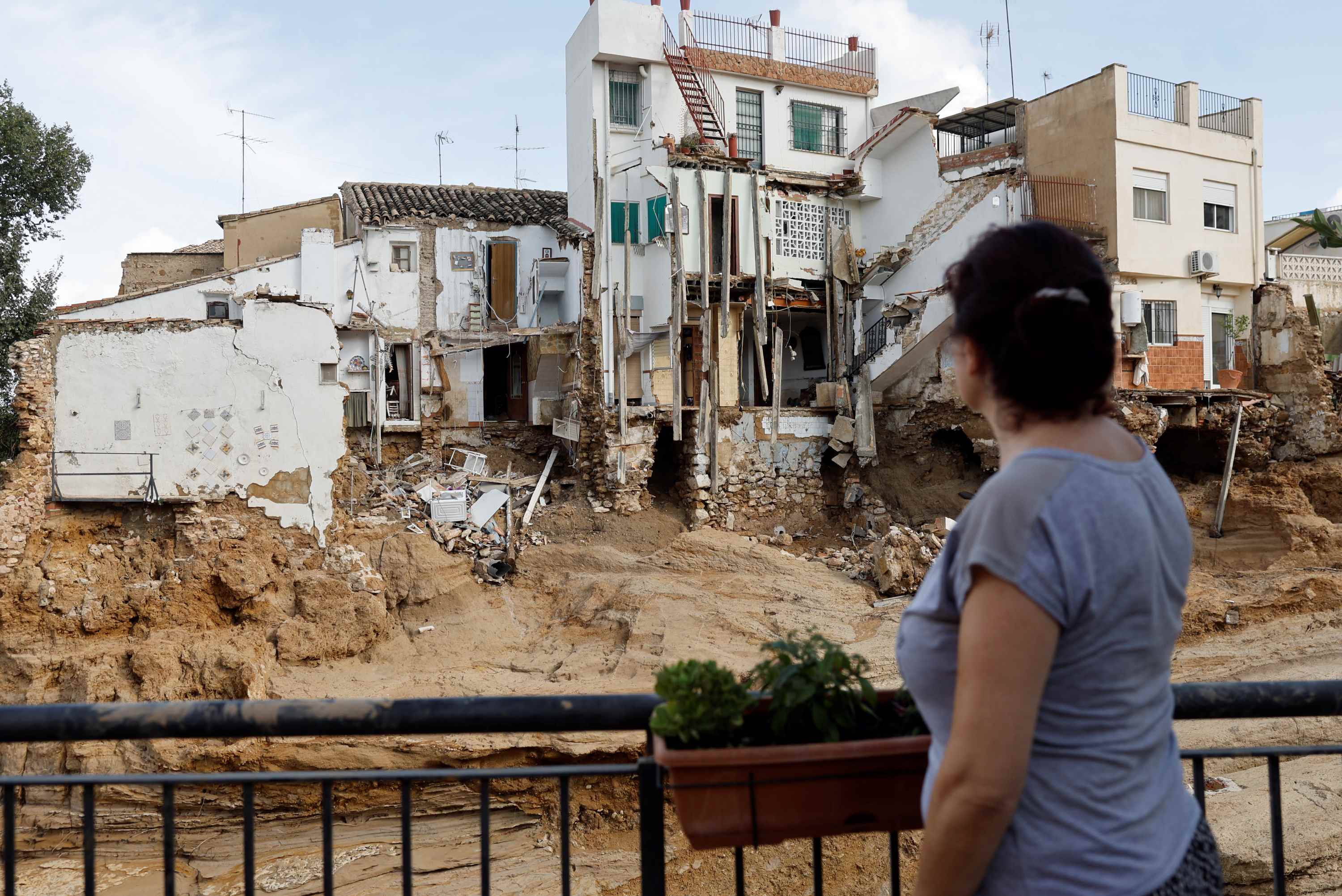
A new study concludes that climate change intensified the flooding caused by the dana in Valencia in 2024
Human-induced climate change amplified the intensity and extent of the rainfall that affected Valencia during the October 2024 dana, according to a new attribution study involving several Spanish research centres. Using climate simulations, the study, published in Nature Communications, shows that present-day global warming conditions increased precipitation intensity by 21 %, expanded the area receiving more than 180 millimetres of rain by 56 %, and raised the total rainfall volume in the Júcar River basin by 19 % compared to a pre-industrial scenario. The authors highlight “the urgent need for effective adaptation strategies and improved urban planning to reduce the growing risks associated with extreme hydrometeorological events in a rapidly warming world.”