U.S. malaria initiative would save more than 100,000 lives in Africa this year if continued
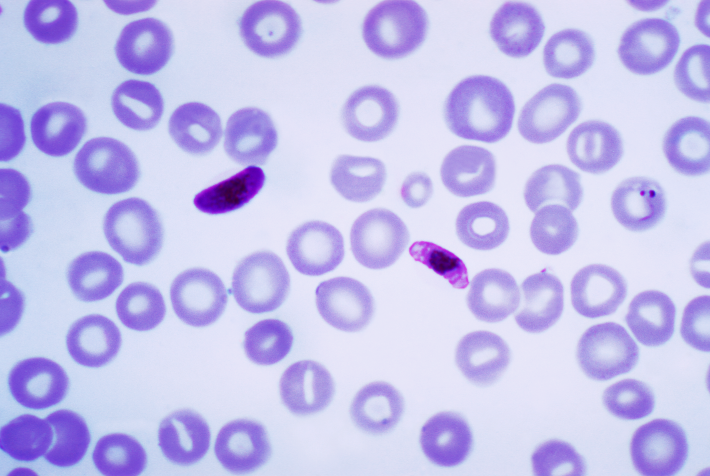
The U.S. Presidential Malaria Initiative is a project that has been in place since 2005 to reduce malaria cases and deaths in Africa. The Donald Trump administration has halted some of its services and questioned its continuity. Now, a team has analyzed the possible consequences in 27 of the most affected countries on the continent. According to their estimates, some 104,000 deaths and around 13.6 million cases would be avoided if full funding were maintained. The results are published in The Lancet.