
CSIC Delegation in the Region of Valencia
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Director of the Institute of Neurosciences, a joint centre of the Miguel Hernández University of Elche (UMH) and the CSIC
Researcher at the Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology of Plants (UPV-CSIC)
Professor of Theoretical Physics at the Institute of Corpuscular Physics (IFIC), University of Valencia - CSIC
Researcher at the Climate, Atmosphere and Oceans Laboratory (Climatoc-Lab) at the Desertification Research Centre (CIDE, CSIC-UV-GVA)
Senior Scientist in Social Sciences at INGENIO (CSIC-UPV)
CIDEGENT Distinguished Researcher
Researcher, Instituto de Física Corpuscular
Professor of the Department of Theoretical Physics & IFIC of the University of Valencia - CSIC
Coordinator of the CSIC Global Health Platform and researcher at the Instituto de Biomedicina de Valencia (IBV-CSIC)
CSIC Group Leader at the Institute of Neurosciences (CSIC-UMH)
CAR-T cells, T lymphocytes modified in the laboratory to attack tumor cells, have shown promise against certain types of cancer. Now, a US team has followed the same concept and introduced artificial receptors into astrocytes, a type of nerve cell, with the aim of reducing the amyloid plaques characteristic of Alzheimer's disease. The experiments, conducted in mice, showed a significant reduction in amyloid, although no changes in the animals' behavior were observed. The results are published in Science.

Science journal has published a global map showing exposure to perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) through the consumption of fish products. PFAS are substances that are difficult to break down, meaning they can accumulate in the body, and some are linked to health problems. The authors collected data over 20 years from PFAS measurements in the marine environment and fisheries, and mapped the concentrations of these compounds in more than 200 species of marine fish. The study shows that international fish trade redistributes the risk of PFAS exposure from highly polluted regions to less exposed areas, with European trade playing a key role in increasing the risk of exposure to these substances.

A team from the United States has used data from health studies to analyze the extent to which prestigious journals capture or ignore science considered influential. Their findings indicate that most of the most cited articles—thus considered most influential—are published in journals not ranked among the most prestigious. According to the study, approximately half of all researchers never publish in a journal with an impact factor above 15, which, according to certain evaluation systems, could exclude them from opportunities. However, overall, traditional journal-based measures may only recognize between 10% and 20% of influential work. The results are published in Plos Biology.

Consuming up to four cups of coffee a day is associated with an increase in telomere length in people with severe mental disorders, such as schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Telomere length is an indicator of cellular ageing and is shorter in people with these disorders, although the causes are not clearly understood. According to the study, published in BMJ Mental Health, the effect shown is comparable to ‘a biological age five years younger’ in coffee drinkers.
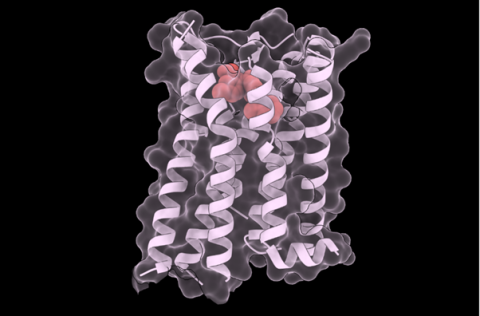
Most rare diseases are caused by mutations in DNA, but the same gene can mutate in different ways, which complicates treatment. Now, a team from the CRG in Barcelona has shown that an already approved drug is capable of stabilising almost all mutated versions of a human protein—specifically, the vasopressin V2 receptor, which is linked to a rare disease called nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. According to the researchers, who published their findings in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, the study is the first proof of concept demonstrating that a drug can act as a ‘near-universal’ treatment, which could accelerate the development of therapies.

Cosmological models suggest that matter and antimatter were created in equal amounts in the Big Bang, but in the current universe matter seems to predominate over antimatter. This imbalance is believed to be due to differences in the behaviour of the two, a violation of symmetry known as CP violation. This effect was predicted by the Standard Model of Physics and observed experimentally in mesons more than 60 years ago. Now, the LHCb collaboration at CERN, which includes significant Spanish participation, has observed this phenomenon for the first time in the decay of baryons, particles that make up most of the matter in the observable universe. The study is published in Nature.

The KATRIN (Karlsruhe Tritium Neutrino Experiment) team has published the most accurate measurement to date of the upper limit of the neutrino mass in the journal Science, establishing it at 0.45 electronvolts (eV), less than a millionth of the mass of an electron. The KATRIN experiment, launched in 2018 in Germany, will finalise its neutrino mass measurement campaign this year, having reached 1,000 days of data acquisition.

While some studies have suggested that having a mother with Alzheimer's may increase the risk of developing the disease, a new study reveals that having a father with the disease may be related to a greater spread of tau protein in the brain, which is a sign of the disease. The study, published in Neurology, does not prove that having a father with Alzheimer's causes these brain changes; it only shows an association.
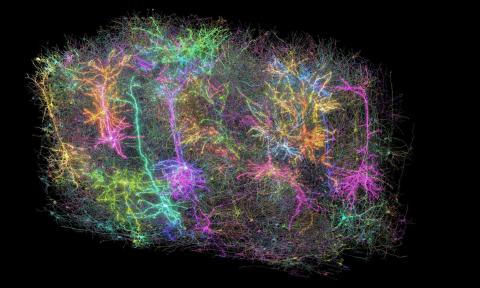
A set of articles published in Nature and Nature Methods draws a high-resolution map of the structure of and connections between the brain cells of mice. The map is based on data from a single cubic millimetre of brain and includes more than 200,000 cells, around 84,000 neurons and 524 million synaptic connections. Although this is a very small part of the mouse brain, it will help us understand how different types of cells work together.
An international team with Spanish participation has analysed the usefulness of a blood biomarker - the p-tau217 protein - for detecting Alzheimer's disease in 1,767 patients. According to the authors, who publish the results in the journal Nature Medicine, the test has detected the disease with high reliability in four hospital cohorts, as well as in a primary care cohort. They add that it is an assay that can be easily implemented in clinical laboratories and is already routinely used in some centres in Spain.