Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Neurologist in charge of the “Central Autoimmune Neurology Unit” at the Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau in Barcelona
Director of the Prenatal Screening Unit and attending physician in the Obstetrics service of the Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau (Barcelona)
Psychologist and doctor of pharmacology at the Hospital de Sant Pau in Barcelona, president of the Spanish Society for Psychedelic Medicine (SEMPsi) and coordinator of the Psychedelicare initiative in Spain
Specialist doctor at the Clinical Epidemiology and Public Health Service of the Hospital de Sant Pau in Barcelona and Patient Safety Expert
Director of the Internal Medicine Department and head of the Fibromyalgia and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Functional Unit at the Hospital Sant Pau in Barcelona
Clinical Head of the Thoracic Surgery Department at the Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau in Barcelona, co-coordinator of the CASSANDRA lung cancer screening project and director of Integrated Research Projects in Thoracic Oncology at the Spanish Society of Pneumology and Thoracic Surgery (SEPAR)
Director of the Memory Unit of the Neurology Service of the Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau and director of the Alzheimer's Unit at the Fundació Catalana Sindrome de Down
Director of the Dermatology Department of the Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau and professor at the Autonomous University of Barcelona
Neurologist in the Neuromuscular Diseases Unit - Autoimmune Neurology - Neuromuscular Lab
Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau & Institut de Recerca Biomèdica Sant Pau, Barcelona
Specialist in Immunology at the Hospital de Sant Pau in Barcelona and secretary of the Spanish Society of Immunology

The study of psychedelic drugs in pharmacological treatments had its eureka moment with chemist Albert Hofmann's famous bike ride under the influence of LSD in 1938 and then developed over decades, but with Richard Nixon it was shelved. In recent years, it has resurfaced in hospitals and laboratories around the world. Last week, the Congress of Deputies hosted a conference on these substances. We explain what they are, what they are used for, the current state of research, and their risks, with the help of expert sources.

Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is responsible for the psychedelic effects of ayahuasca. According to the results of a phase IIa clinical trial published in Nature Medicine, this molecule improved depressive symptoms in adults with depression after one dose. The trial included 34 people, 17 of whom received intravenous DMT. This second group showed greater improvements in depressive symptoms than the control group. After two weeks, in the second part of the trial, DMT was administered to all participants and the antidepressant effects lasted for three months. Adverse effects were mainly pain at the injection site, nausea and transient anxiety.

The American Psychiatric Association has unveiled the new features of the forthcoming Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) in five articles published in The American Journal of Psychiatry. Among the highlights are the proposed change of name — it will become the Diagnostic and Scientific Manual — and the intention for it to be more dynamic, incorporating biomarkers for diagnosis and integrating the socioeconomic, cultural and environmental determinants of health. According to the authors, the aim is to enable a more personalised and inclusive clinical practice, aligned with scientific rigour. The most recent update was published in 2022 with the DSM-5-TR, and specialists are currently unaware of the date of the next edition, as they reported during a briefing with journalists.
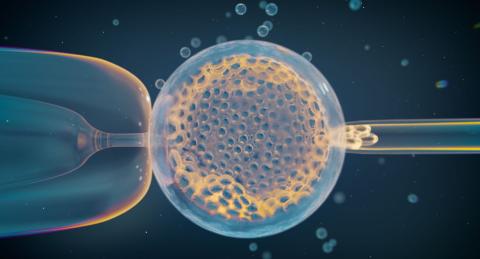
Around 15% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage, and it is estimated that almost half of all conceptions are lost in early stages, without people even realizing it. Now, a team from the United States and Denmark has analyzed data from more than 139,000 embryos from in vitro fertilization of nearly 23,000 couples and has found several genetic variants associated with a higher risk of miscarriage. Many of these are associated with meiosis, a key cell division process in sex cells. The authors, whose study is published in Nature, acknowledge that the new data will not allow for a precise estimation of individual risk, because the most important factors remain age and environmental elements.
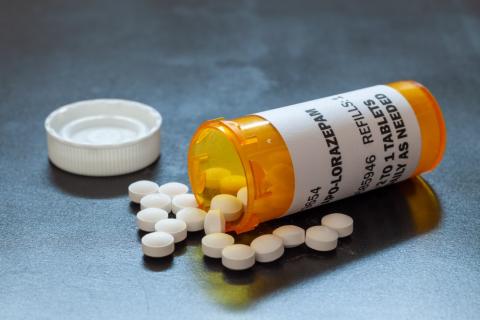
According to a study published in the journal JAMA Health Forum, the use of the benzodiazepine lorazepam by the character Victoria Ratliff in the series The White Lotus was associated in the United States with an increase in Google searches for this medication, including queries about how to obtain it online. The series generated 1.6 million more searches than usual over a 12-week period. Although the study reflects searches for information and not actual consumption, the abuse of anti-anxiety drugs is a fact: illegal sales of benzodiazepines have increased in the United States, and Spain leads the rankings in terms of consumption.

Severe combined immunodeficiency due to ADA enzyme deficiency is a rare disease that, without treatment, usually causes death within the first two years of life. These "bubble children" are currently treated with a bone marrow transplant or with injections that aim to restore, to the extent possible, the function of this enzyme. Now, an international team presents the results of a gene therapy administered to 62 children with the disease between 2012 and 2019. The therapy was effective in 95% of cases and did not cause serious complications, according to the authors, whose work is published in the journal NEJM.

Prenatal exposure to triptans—alone or in combination with other migraine medications—does not increase the risk of developmental disorders in children up to age 14, according to research published in Neurology. The study is based on data from more than 26,000 pregnancies in a national registry in Norway and includes autism spectrum disorders, language disorders, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, among other diagnoses.

EMA’s human medicines committee has recommended not authorising the marketing of Kisunla (donanemab), a drug intended for the treatment of early-stage Alzheimer's disease. The committee considered that the benefits of this drug were not great enough to outweigh the risk of potentially fatal events. In recent years, several patients have died due to microbleeds in the brain.
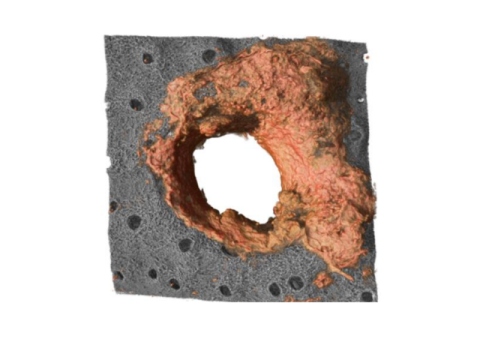
A CNIC research team has identified a population of skin neutrophils that reinforce the physical protection of the tissue against infection. These immune cells are known for their microbicidal role, and the study published in Nature reveals that they also produce an extracellular matrix that reinforces the physical barrier of the skin.

Less than four months after the European Medicines Agency recommended in July not to grant marketing authorisation for Leqembi™ (lecanemab) for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, the EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has reassessed the available evidence to conclude that the benefits outweigh the risks.