First clinical trial of stem cell use to treat spina bifida during pregnancy
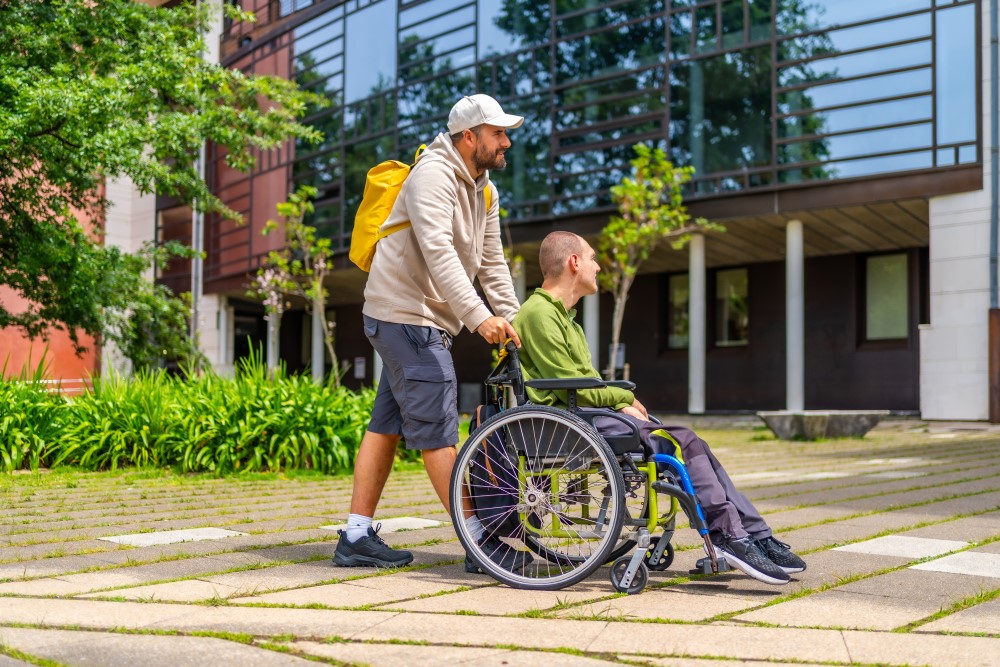
Spina bifida is a congenital malformation in which the spinal column does not close completely. A team in California (USA) has completed a phase 1 clinical trial testing, for the first time, a stem cell treatment combined with standard foetal surgery. The trial was conducted on six pregnant women with foetuses diagnosed with myelomeningocele, the most severe form of spina bifida. The six babies, born between 2021 and 2022, maintained the repair intact and had no serious adverse effects. The team will follow up carefully to ensure that the treatment remains safe and improves the children's quality of life. The results are published in The Lancet.