
Polytechnic University of Valencia
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Full Professor at the Universitat Politècnica de València, where he carries out his teaching and research activity related to propulsive systems in means of transport.
Researcher at the Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology of Plants (UPV-CSIC)
Senior Scientist in Social Sciences at INGENIO (CSIC-UPV)
Lecturer at the Polytechnic University of Valencia and former Deputy Director-General of the FAO
Full professor at the Polytechnic University of Valencia and member of the Evaluation and Monitoring Committee of the ANECA state accreditation system
Director of the ETSI of Telecommunications of the Polytechnic University of Valencia
Researcher on the evaluation of science at Leiden University (Netherlands) and at the Ingenio Institute (CSIC-UPV)
Head of the Department of Architectural Constructions at the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV)
Professor and researcher at the Valencian University Institute for Research in Artificial Intelligence at the Universitat Politècnica de València.
Professor of Optical Communications Systems and Networks at the Polytechnic University of Valencia (UPV)

Human-induced climate change amplified the intensity and extent of the rainfall that affected Valencia during the October 2024 dana, according to a new attribution study involving several Spanish research centres. Using climate simulations, the study, published in Nature Communications, shows that present-day global warming conditions increased precipitation intensity by 21 %, expanded the area receiving more than 180 millimetres of rain by 56 %, and raised the total rainfall volume in the Júcar River basin by 19 % compared to a pre-industrial scenario. The authors highlight “the urgent need for effective adaptation strategies and improved urban planning to reduce the growing risks associated with extreme hydrometeorological events in a rapidly warming world.”

A team from the United States has used data from health studies to analyze the extent to which prestigious journals capture or ignore science considered influential. Their findings indicate that most of the most cited articles—thus considered most influential—are published in journals not ranked among the most prestigious. According to the study, approximately half of all researchers never publish in a journal with an impact factor above 15, which, according to certain evaluation systems, could exclude them from opportunities. However, overall, traditional journal-based measures may only recognize between 10% and 20% of influential work. The results are published in Plos Biology.

The frequency of fire-related disasters increased significantly from 2015 onwards, according to a study analysing data from reinsurance companies between 1980 and 2023. Forty-three per cent of the 200 most damaging events, in terms of both human and economic damage, occurred in the last decade, the authors estimate in the journal Science. The risks were highest in the Mediterranean and in temperate coniferous biomes, and their frequency coincides with increasingly extreme weather conditions, they add.

Climate change has made the hot, dry and windy weather conditions that spread fires across the Iberian Peninsula 40 times more frequent and 30% more intense than in the pre-industrial climate, according to a rapid study by World Weather Attribution. The ten-day heatwave was also 200 times more likely and 3°C hotter due to climate change. The study, which analysed weather observations rather than climate models, warns that fires in Europe are overwhelming firefighting resources and highlights the importance of controlling vegetation in affected areas.

Four people have died in the fires that began last weekend on the Iberian Peninsula and have spread to different areas of Galicia, Castile and León, Andalusia, Castile-La Mancha, Extremadura and Madrid. The heatwave that continues to grip the country, strong gusts of wind and their changing direction, and the thermal drought are hampering firefighting efforts. The government declared on Tuesday a pre-emergency phase and thousands of people have had to be evacuated.

Forests cover approximately 40% of Europe's land area. Between 1990 and 2022, they absorbed around 10% of the continent's emissions from human activity, but this process is slowing down. An international team, including CREAF and CSIC, analyzes this decline and its causes in an article and proposes possible solutions. The work is published in the journal Nature.

Power shortages left millions of people in the Iberian peninsula and parts of southern France without electricity on Monday. The situation was exacerbated by the failure of telecommunications, which were vulnerable to the power failure.

The power outage that occurred after midday on Monday has left millions of people in the Iberian peninsula and some parts of southern France without electricity. According to Red Eléctrica, at 11:15 (peninsular time) on Tuesday, the peninsular electricity system was back to normal. ‘After surpassing the morning peak demand at 8:35 am with 28,677 MW, the night peak is expected at 21:10 pm with 31,200 MW’, they indicate.
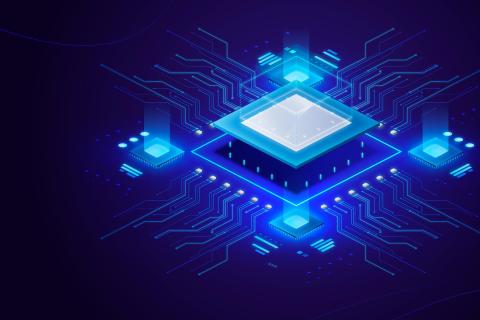
Two independent teams have developed photonic computing chips - which use photons instead of electrons - that could help cope with the increased energy demanded by AI-based technologies. The work is published in two papers in the journal Nature. ‘Photonic computing has been decades in the making, but these demonstrations could mean that we can finally harness the power of light to build more powerful and energy-efficient systems,’ notes a piece accompanying the research in the same journal.

According to a modelling study published in Nature Cities, the frequency of some types of fires in cities is expected to increase in the coming decades as a result of climate change. This increase would be seen in vehicle fires and in those that occur outdoors. The conclusions are based on data from more than 2,800 cities in 20 countries and could be useful for future urban planning and emergency response strategies.