University Clinical Hospital of Santiago
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Member of SEEDO and Head of Epigenomics in the Endocrinology and Nutrition Group of the Epigenomics Unit at the Santiago Health Research Institute (IDIS), Santiago University Hospital Complex (CHUS)
Head of the Paediatrics Department of the Hospital Clínico Universitario de Santiago. Coordinator of the WHO Collaborating Centre for Vaccine Safety in Santiago de Compostela and member of the WHO-Europe Vaccine Advisory Committee.
Head of the Immunology Department at the Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Santiago de Compostela (CHUS), Servicio Gallego de Salud (SERGAS)

A meta-analysis published in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews concludes that intermittent fasting is not particularly effective for weight loss in adults who are obese or overweight, who showed moderate weight loss. This strategy also does not differ significantly from standard dietary advice or improvement in quality of life. The review included 22 studies with nearly 2,000 participants and evaluated various forms of intermittent fasting, including restricting food intake for most of the day and fasting every other day.
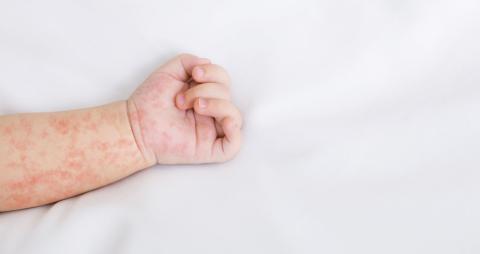
Measles cases in Europe and Central Asia fell in 2025 compared with 2024, according to preliminary data reported by 53 countries in the World Health Organization (WHO) European Region. This decline aligns with the preliminary figures published this week by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). According to the WHO, countries in Europe and Central Asia reported 33,998 measles cases in 2025, representing a decrease of nearly 75 % compared with the 127,412 cases recorded in 2024. In Spain, however, the number of cases has increased, as shown by data from the Carlos III Health Institute. A few weeks ago, the WHO announced that Spain had lost its measles-free status.
A clinical trial funded by Pfizer has tested a new influenza vaccine based on messenger RNA (mRNA). The phase 3 trial included more than 18,000 people aged 18 to 64, half of whom received the new compound and the other half a conventional vaccine. The results indicate that the mRNA vaccine was more effective, but it also caused more adverse reactions: for example, 5.6% of the volunteers who received it developed a fever, compared to 1.7% of those who received the conventional vaccine. The study is published in the journal NEJM.

The Karolinska Institute has awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology to Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell and Shimon Sakaguchi for describing how the immune system is regulated so as not to harm us. His groundbreaking discoveries on peripheral immune tolerance have spurred the development of new treatments for cancer and autoimmune diseases.

In recent decades, the rate of pollen allergies has increased worldwide. One of the reasons being considered is the increase in atmospheric nitrogen pollutants. Now, a study published in the journal The Lancet Planetary Health estimates that grasslands fertilised with nitrogen release six times more pollen and that this pollen is five times more allergenic than that from unfertilised fields.

According to a new study published in Science, a machine learning-based artificial intelligence (AI) system - called Mal-ID - can decipher an individual's history of infections and diseases in the immune system. The authors say this provides a powerful tool with the potential to accurately diagnose autoimmune disorders, viral infections and vaccine responses.
A team led by the CEU San Pablo University has analysed the role of vaccination against influenza on the risk of infection and mortality. The meta-analysis, published in European Respiratory Review, includes 192 articles from different countries over the last 20 years and includes data from more than 6.5 million patients. The results show that the level of protection varies according to age group and influenza subtype. Although it does not reduce the risk of infection for influenza A H3N2 in those over 65 years of age, nor does it show a reduction in mortality for influenza B - which is less associated with mortality than influenza A - overall, vaccination is shown to be effective in both preventing infection and reducing mortality.

An analysis of the gut microbiota of children growing up on farms or with pets shows that early establishment of anaerobic commensal bacteria is associated with lower rates of allergy later in life. The study, which used data from 65 children aged between three days and 18 months, is published in the journal PLOS ONE.
Antimicrobial resistance caused around 5 million deaths worldwide in 2019. The use of vaccines has the potential to reduce these deaths - 515,000 fewer deaths per year - according to a report published by the WHO. The work focused on 24 pathogens and 44 vaccines, licensed by regulatory agencies, in clinical development or in development. By counting existing vaccines alone, antibiotic use could be reduced by 142 million daily doses per year.

Toledo and Alicante are suffering the first outbreaks of measles recorded in Spain since the pandemic, El País reported today. In total, 15 cases have been confirmed since 1 January, of which seven are imported and eight autochthonous.