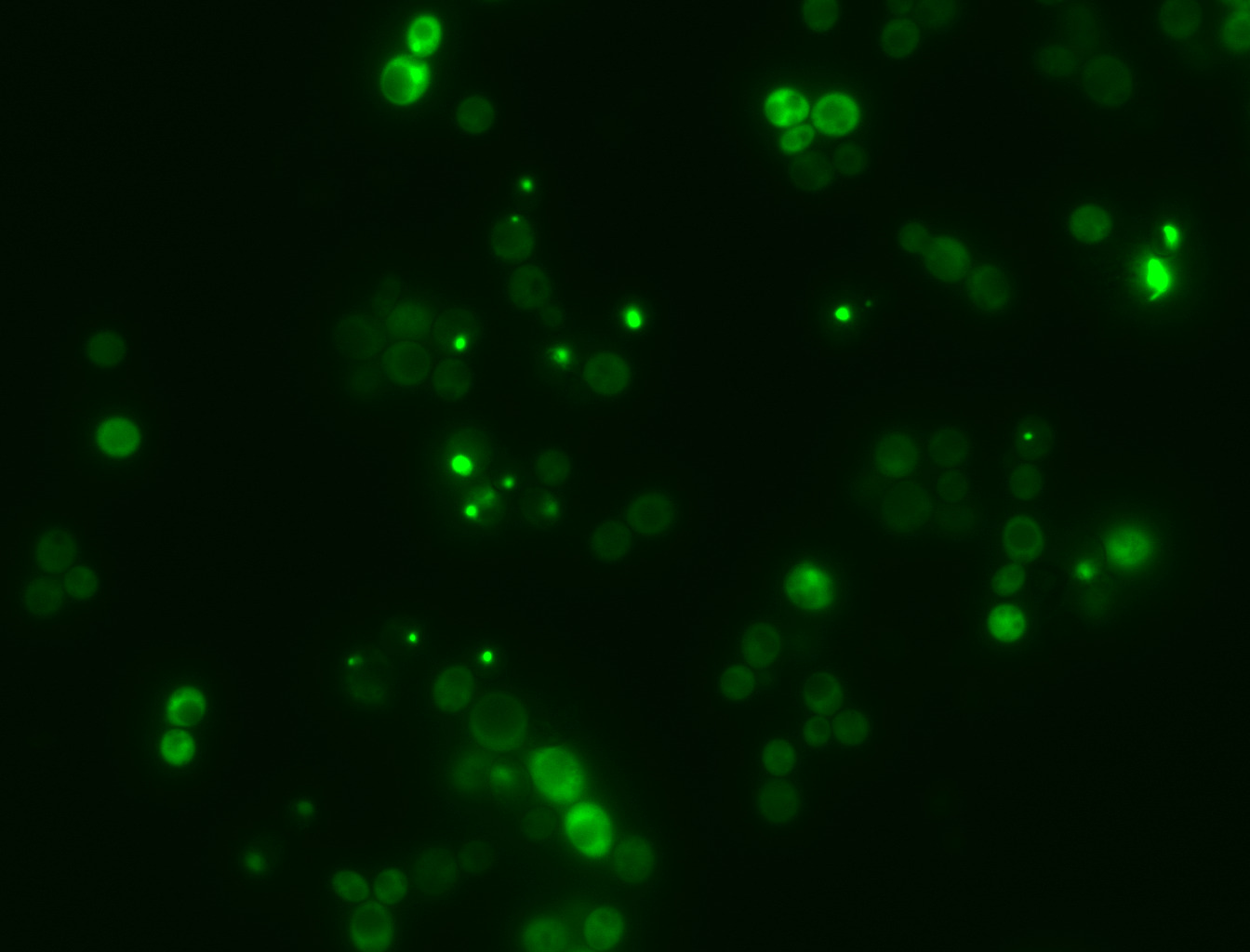
Spanish project develops an AI to predict protein aggregation
A team led by the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona and the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) has developed and used a new artificial intelligence (AI) tool called CANYA, together with a large volume of data, to predict when and why protein aggregation takes place. The resource could be used to advance research into neurodegenerative diseases and drug production, according to the joint press release. The results are published in the journal Science Advances.