First Arctic ice-free day could happen before 2030
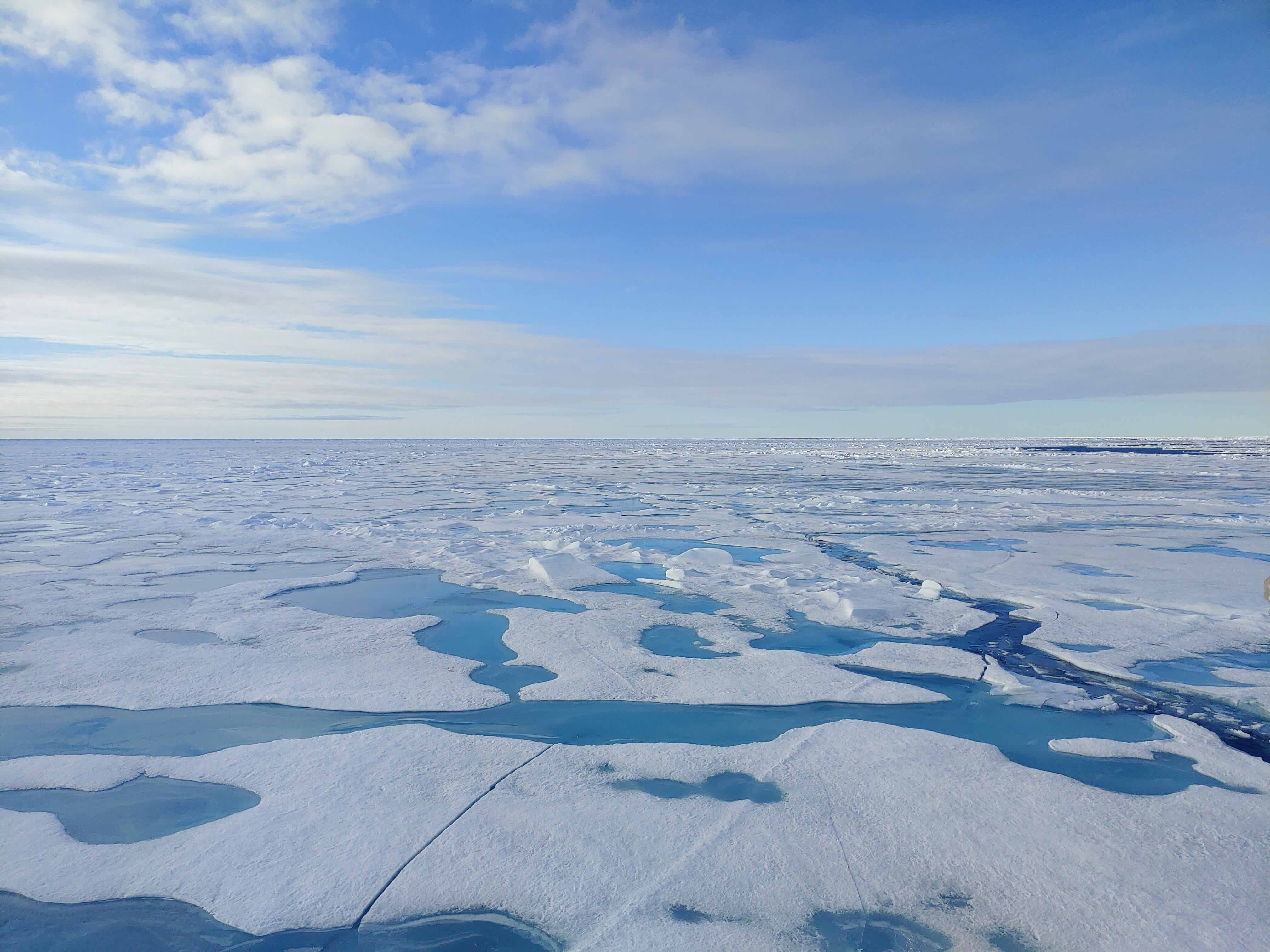
In three to six years, the first ice-free day in the Arctic could occur if a series of extreme weather events - such as an unusually warm autumn, winter and spring in the region - occur, according to a study comparing various models and scenarios in Nature Communications. An ice-free day refers to a day with Arctic Ocean ice coverage of less than 1 million square kilometres; the average coverage was 6.85 million square kilometres between 1979 and 1992.