Gregorio Marañón University Hospital
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Neurologist at the Centro de Ictus of the Gregorio Marañón General University Hospital
Head of the Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Director of the Institute of Psychiatry and Mental Health of the Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón
Endocrinology Specialist at the Endocrinology and Nutrition Service of the Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón and Director of the SEEN-University of Barcelona-Editorial Panamericana University Expert Course in Transgender Medicine
Doctor at the Paediatrics Department of the Gregorio Marañón University Hospital and coordinator of the PedGAS-net Project -a national network for the study of invasive S. pyogenes infections-
President of the Colegio de Médicos de Madrid, Professor of Medicine and Head of the Cardiology Department at Gregorio Marañón Hospital
Head of the Medical Oncology Department of the Gregorio Marañón Hospital and president of GEICAM
Specialist in Clinical Neurophysiology, founder and head of the Sleep Disorders and Epilepsy Unit of the Clinical Neurophysiology Service of the Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón, currently retired
A meta-analysis concludes that the use of beta-blockers is not necessary in patients who have suffered a heart attack but have normal cardiac function. The research, coordinated in Spain by the CNIC, brings together data from five clinical trials and 17,801 patients. One of these trials, REBOOT, already showed that patients who did not have reduced cardiac function after a heart attack did not benefit from treatment with beta blockers. According to this recent meta-analysis, published in the New England Journal of Medicine and presented at the American Heart Association Congress in New Orleans (USA), the use of these drugs does not reduce mortality, reinfarction or heart failure in this group of patients.

Narcolepsy type 1 is a sleep disorder characterised by excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy - sudden loss of muscle tone. Existing treatments are based on palliation of symptoms, with moderate success. Now, an international phase 2 clinical trial, involving CEU San Pablo University and other Spanish centres, published in the journal NEJM, shows the results of a new drug targeting the cause of the disorder. Overall, the benefits appear superior and no serious adverse effects were observed. According to the authors, ‘the results are promising’ and represent ‘a very significant impact on the quality of life of these patients’.

An international team has analysed data on the incidence and mortality of breast cancer in 185 countries. In 2022, 2.3 million new cases and 670,000 deaths were recorded and, with this trend, it is predicted that by 2050 these figures will increase by 38% and 68% respectively, particularly affecting low-income countries. Although the mortality rate fell in 30 of the 46 countries studied over the last ten years, only seven of them met the WHO targets of reducing it by at least 2.5% each year. The results are published in the journal Nature Medicine.

World Cancer Day is celebrated on 4 February. Behind the cases of this disease there are people who, although they have overcome it, bear the burden of the diagnosis years after the end of their treatment. Survivors demand the right to be forgotten so as not to suffer financial, employment and social discrimination.

A team of researchers from the United Kingdom has conducted a phase 2/3 clinical trial in people with a psychotic disorder to study the efficacy of interaction with a digital avatar in alleviating the discomfort generated by hearing voices. After analyzing it in 345 people, they conclude that it can reduce the frequency of occurrence at 16 and 28 weeks. The discomfort provoked is reduced at 16 weeks, but not at 28 weeks. The team publishes the results in the journal Nature Medicine.

The U.S. FDA has approved a new drug—called Cobenfy—to treat the symptoms of schizophrenia. Unlike traditional treatments, which are based on blocking the effects of dopamine, its mechanism of action simulates the effects of another neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. It is the first drug to be approved with a different mechanism of action in over 70 years.

The number of people who suffer a stroke, die from it or live with a subsequent disability has risen sharply worldwide between 1990 and 2021, according to a study published in The Lancet Neurology. The contribution of high temperatures to ill health and premature death from stroke has increased by 72% since 1990. For the first time, the study reveals the high contribution (on par with smoking) of particulate air pollution to subarachnoid haemorrhage (fatal brain haemorrhage).
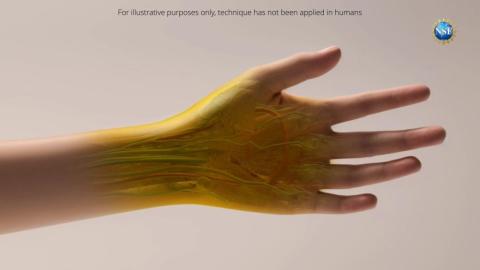
A team of researchers at Stanford University (USA) has developed a technique that makes animal tissues transparent in vivo and reversibly. Based on a food dye, they have tested it topically on mice. According to the authors, who publish their research in the journal Science, “this technology could make veins more visible for blood collection or help in the early detection and treatment of cancer”.

The mental health of young people has deteriorated over the last two decades and is entering a dangerous phase, according to a new Commission by The Lancet Psychiatry. Several global factors are involved, including inaction on climate change, intergenerational inequality, and adversity linked to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Although breast cancer mortality has reduced by more than 40% in most high-income countries, a Lancet commission warns that one million people will die from the disease by 2040, especially in low- and middle-income countries. The authors highlight some of the knowledge gaps that persist about the disease, such as the lack of knowledge about the number of patients living with metastatic breast cancer and their needs, or the costs associated with breast cancer - including physical, psychological, social and economic costs - which, according to the authors, are immense but underestimated, and not adequately reflected in global health indicators.