
Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute
If you are the contact person for this centre and you wish to make any changes, please contact us.
Head of the Stem Cell and Cancer Research Group at the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM)
Professor of Public Health in the Department of Medicine and Life Sciences (MELIS) at Pompeu Fabra University, researcher at the Centre for Occupational Health Research (CISAL) at IMIM-PSMar, and scientific director of the Ibero-American Observatory on Occupational Safety and Health
Coordinator of the Research Group on Molecular Mechanisms of Cancer and Stem Cells at IMIM-Hospital del Mar
Researcher at the Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute (IMIM), professor of public health at the Autonomous University of Barcelona and author of the book Vive más y mejor
Research director
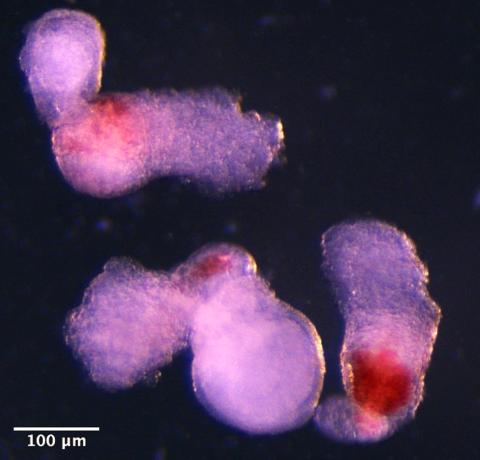
A team led by the University of Cambridge (UK) has used human stem cells to produce three-dimensional embryo-like structures that replicate certain aspects of early development, including, they say, the production of blood stem cells. They have called these structures “hematoids” and, according to the university press release, “they offer great potential for better understanding blood formation during the earliest stages of human development, for simulating disorders such as leukemia, and for producing long-lived blood stem cells for transplantation.” The results are published in the journal Cell Reports.

The frequency and intensity of extreme heat events have increased in recent years, heightening the risks for those who work outdoors and indoors. Health risks include heatstroke, dehydration, kidney dysfunction and neurological disorders. These are some of the conclusions of a joint report by the World Health Organisation (WHO) and the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO), which estimates that worker productivity falls by between 2% and 3% for every degree above 20°C. The document proposes measures for governments, businesses and health authorities to mitigate the risks of extreme heat for these people.

Less than four months after the European Medicines Agency recommended in July not to grant marketing authorisation for Leqembi™ (lecanemab) for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, the EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has reassessed the available evidence to conclude that the benefits outweigh the risks.

An international team of researchers has analyzed various data sources and scientific literature and identified 3,601 chemical substances in human samples such as blood, urine or breast milk that are known to be in contact with food, for example, because they are used in packaging. According to the authors of the study, “this work shows that food contact materials are not completely safe, even if they comply with regulations, because they transfer known substances to food". The research is published in the Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology.
A study describes changes in a woman's brain during and after pregnancy, including a ‘pronounced’ decrease in grey matter volume and cortical thickness, and an increase in ventricular volume and cerebrospinal fluid. Some of the changes are maintained in the postpartum period; others reverse within months. The team performed 26 MRI scans and blood tests on one mother, from pre-conception until two years postpartum, and publish the results in Nature Neurology.
Research published a few days ago in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) found a considerable and hitherto unknown degree of micro- and nanoplastic contamination in human arteries. It was a bit of a surprise that NEJM accepted the paper, as it usually publishes little on the environmental causes of human disease. The good thing is that the publication makes visible, legitimises, stirs up and will encourage other similar work.

Klotho is a protein whose concentrations tend to decline with age and which has been linked to ageing processes. Now, researchers have found that administration of the protein improves cognitive function in aged rhesus macaques, including benefits in spatial and working memory. According to the authors, who publish the results in the journal Nature Aging, its use "may be therapeutic in humans".

Swedish research involving more than 6,000 male footballers in the country's top division (between 1924 and 2019) indicates that they were 1.5 times more likely to develop a neurodegenerative disease compared to the population analysed who were not involved in professional football. Unlike outfield players, goalkeepers did not have this increased risk, which, according to the authors, supports the hypothesis that impacts to the head when striking the ball could explain the increased risk. The study is published in The Lancet Public Health.

A study published in the journal Neurology claims to have confirmed the usefulness of a biomarker in blood to diagnose Alzheimer's disease without the need for other tests.
A few weeks ago, a press release from the Biogen and Eisai companies reported significant results from their lecanemab antibody for the treatment of early-stage Alzheimer's. The data from the phase 3 trial are now published in the New England Journal of Medicine, coinciding with the CTAD conference on Alzheimer's disease clinical trials in San Francisco. Data from the phase 3 clinical trial are now published in the New England Journal of Medicine, coinciding with the 15th CTAD Alzheimer's disease clinical trials conference in San Francisco.