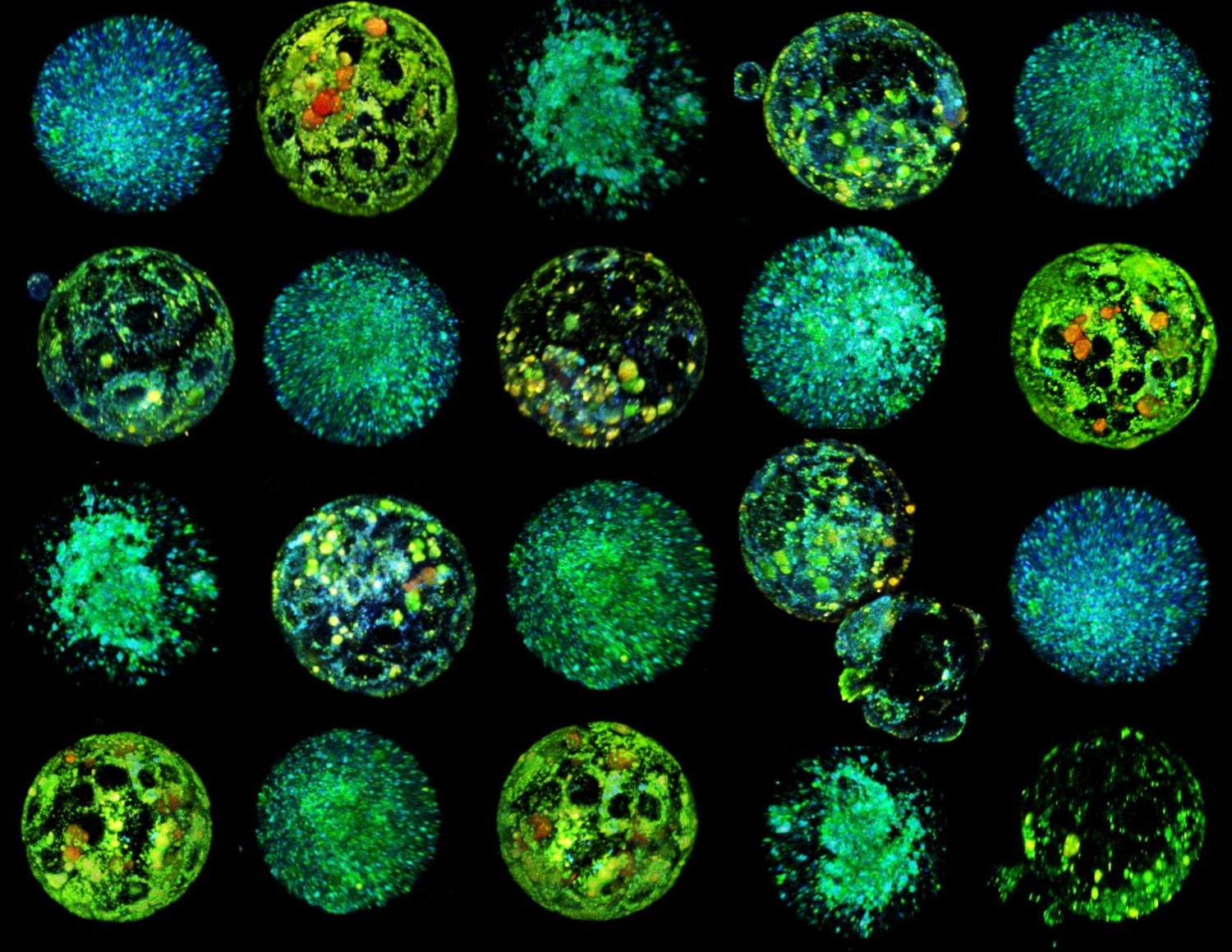
Non-invasive method assesses the quality of mouse oocytes and embryos
A new technique developed at the Institut de Bioenginyeria de Catalunya (IBEC) has succeeded in assessing the health of mouse oocytes and embryos in a non-invasive way, according to a study published in PNAS. The method generates 3D images to visualise the metabolism of oocytes and embryos obtained by in vitro fertilisation and makes it possible to select those that are most likely to implant and develop, say the authors.