The p53 gene, known as the ‘guardian of the genome’, is a tumor suppressor gene that is mutated in more than half of all solid tumors in humans, affecting the function of the protein it encodes. However, there are no approved treatments capable of reactivating its function. A US team has tested a new drug in a phase 1 clinical trial that is capable of performing this function against a specific mutation, present in approximately 1% of solid tumors. After being administered to 77 people with different types of advanced or metastatic tumors, 20% showed a full or partial response, and the most common adverse effects were nausea or vomiting, according to a report published in NEJM.

A study conducted in South Korea collected data from more than 410,000 smokers over an average of nine years. The analyses indicate that the risk of developing Parkinson's disease in those who quit smoking during that period was about 60% higher than in those who continued to smoke; however, their risk of death was lower. According to the researchers, who emphasise that the study does not prove that smoking prevents Parkinson's disease, smoking ‘remains one of the leading causes of preventable death and contributes to the development of heart disease, cancer and chronic lung disease. The health benefits of quitting smoking remain substantial and clear.’ The results are published in Neurology.

The combination of the antiretrovirals bictegravir and lenacapavir in a single tablet allows HIV treatment —previously based on multiple daily medications— to be simplified, according to the results of a new phase 3 clinical trial published in The Lancet. The trial, which included over 550 people living with HIV from 15 countries with a median age of 60, showed that the new treatment was just as effective at maintaining viral suppression as multi-drug regimens. Most participants were taking between two and eleven tablets daily, and around 40 % were on antiretrovirals more than once a day. The results were presented at the 2026 Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) in Denver, USA.

In the ephemeral pools along the coasts of the Caribbean island of Curaçao lives Choanoeca flexa, a tiny unicellular aquatic organism belonging to the choanoflagellates, important for being close relatives of animals. As the pools evaporate and refill, C. flexa can switch between unicellular and multicellular forms in three different ways: by division, by aggregation, or by combining both, mechanisms that were previously thought to be mutually exclusive. The discovery, published today in Nature, may challenge current understanding of the origins of multicellular life.

Speaking to the media in Barcelona, the Minister for Social Rights, Consumer Affairs and the 2030 Agenda, Pablo Bustinduy, announced that the ministry will ban the sale of energy drinks to minors under the age of 16 in Spain. The regulation will also apply to minors under the age of 18 when the drinks contain more than 32 milligrams of caffeine per 100 millilitres.

New research analysing more than 33,000 fish populations in the northern hemisphere between 1993 and 2021 reveals that chronic ocean warming is driving a long-term decline in biomass of up to 19.8% per year for species in the Mediterranean, North Atlantic and North-East Pacific. At the same time, in the short term, more fish are thriving in cold areas due to the heat, but these increases are temporary and the authors warn that relying on them would lead to unsustainable exploitation. The study, by the National Museum of Natural Sciences (MNCN-CSIC) and the National University of Colombia, is published in Nature Ecology & Evolution.
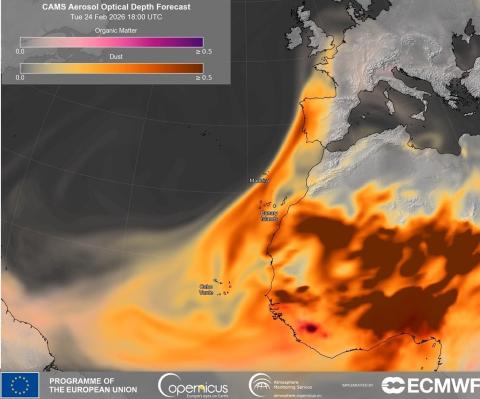
According to the Ministry for Ecological Transition and Demographic Challenge, masses of African air with varying concentrations of surface dust are expected to reach the Canary Islands and the Iberian Peninsula on Wednesday. Health authorities in different provinces have recommended avoiding outdoor physical exercise or activities that require effort, especially for vulnerable groups such as children, pregnant women, the elderly and the sick.

Sequencing the genomes of nearly 38,000 smokers in Mexico revealed that variants in a nicotine receptor gene were associated with a lower likelihood of heavy smoking, according to a study published in Nature Communications. The variant occurs in the CHRNB3 gene, which encodes the β3 subunit that binds nicotine and mediates its rewarding effects in the brain. Compared with individuals carrying the more common version of the gene, those with one or two copies of the identified variant smoked 21% and 78% fewer cigarettes, respectively. The findings were validated in populations of Asian and European ancestry.

An international team involving ISGlobal has analyzed climate data from 50 editions of the Tour de France between 1974 and 2023. The results show that, during the month of July, the risk of heat stress has increased over the years, with the last decade seeing the highest number of extreme heat episodes. In the locations analyzed, the Tour has so far managed to avoid conditions of maximum risk to health, but according to the researchers, it has been "an extremely fortunate race. With record heat waves becoming more frequent, it seems only a matter of time before the Tour faces days of extreme heat stress that will test current safety protocols. The study, published in Scientific Reports, used the Tour de France as an example of the challenge that rising temperatures associated with climate change pose for the organization of sporting events in the summer.

A study published in PNAS reveals the effects of large-scale wildfire smoke and aerosols from major volcanic eruptions on global atmospheric temperatures. Using satellite observations, the team estimated the temperature disturbances associated with the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines, the 2019–2020 Australian wildfires, and the 2022 eruption of the submarine Hunga Tonga volcano in Tonga. All three events had measurable impacts on global atmospheric temperatures. Sulfate particles from Pinatubo caused cooling in the troposphere and warming in the stratosphere, confirming previous measurements. Aerosols from the Australian wildfires —though only about 5 % of the aerosol mass emitted by Pinatubo— also produced both effects, while water vapor from Hunga Tonga led to tropospheric cooling.