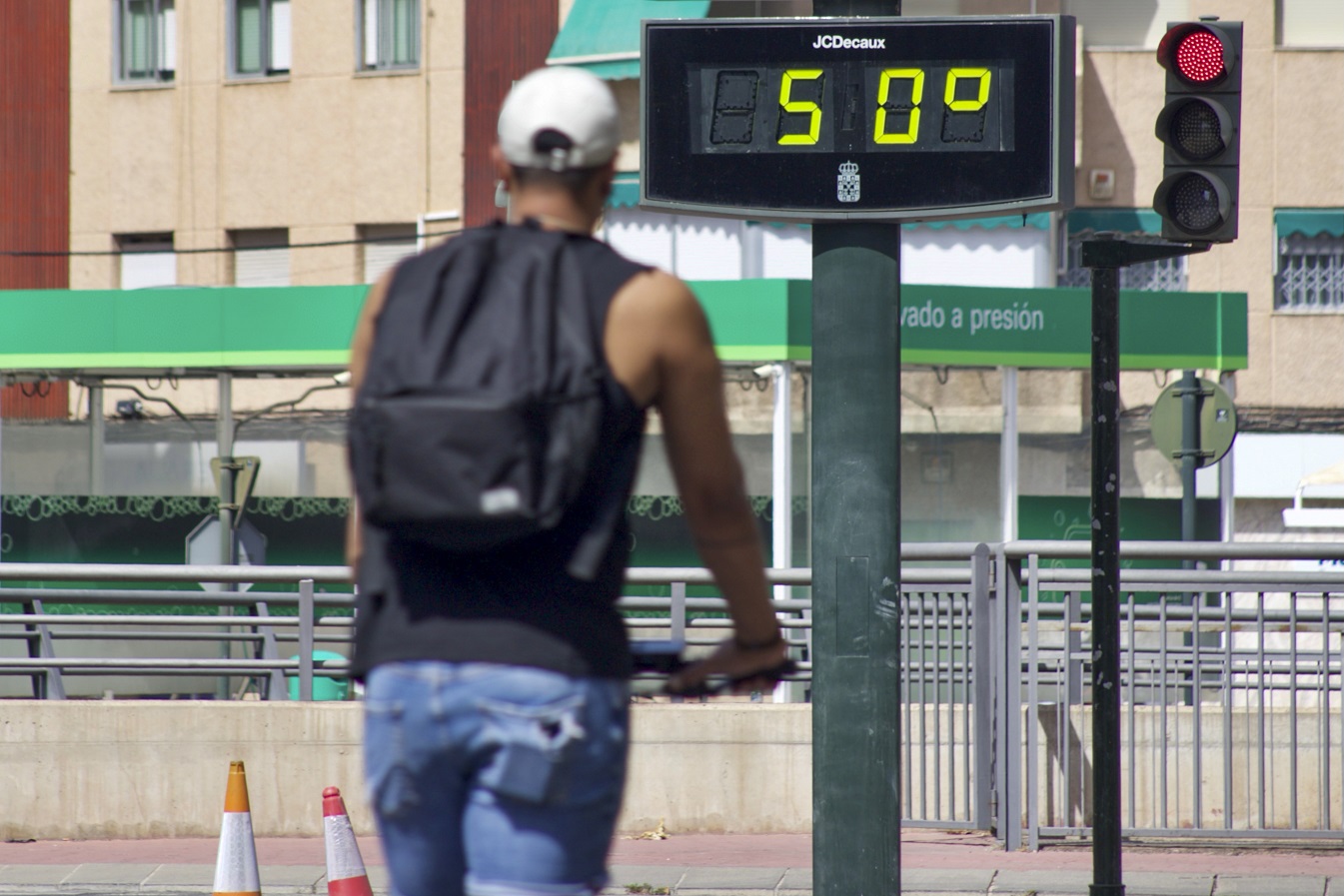
The summer of 2023 the warmest in 2,000 years in the northern hemisphere, according to a study
An international group of researchers analyzed multiple data sets with current measurements and historical reconstructions. Their research concludes that, in the extratropical regions of the Northern Hemisphere (including Europe), the summer of 2023 was the warmest in 2,000 years. The authors published the results in the journal Nature.