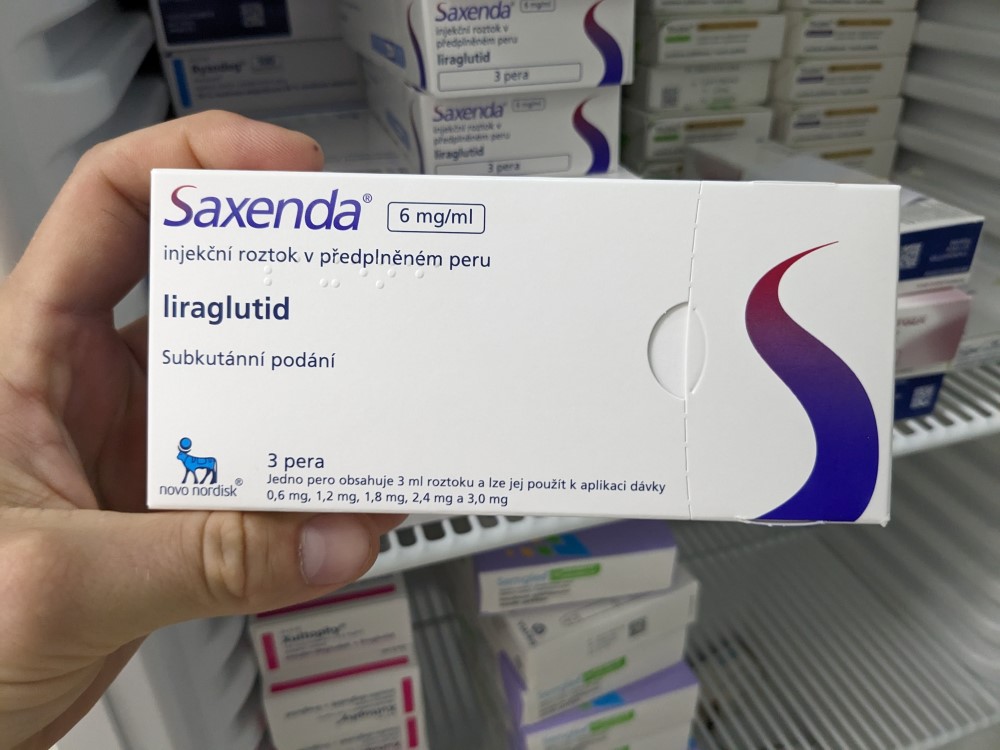
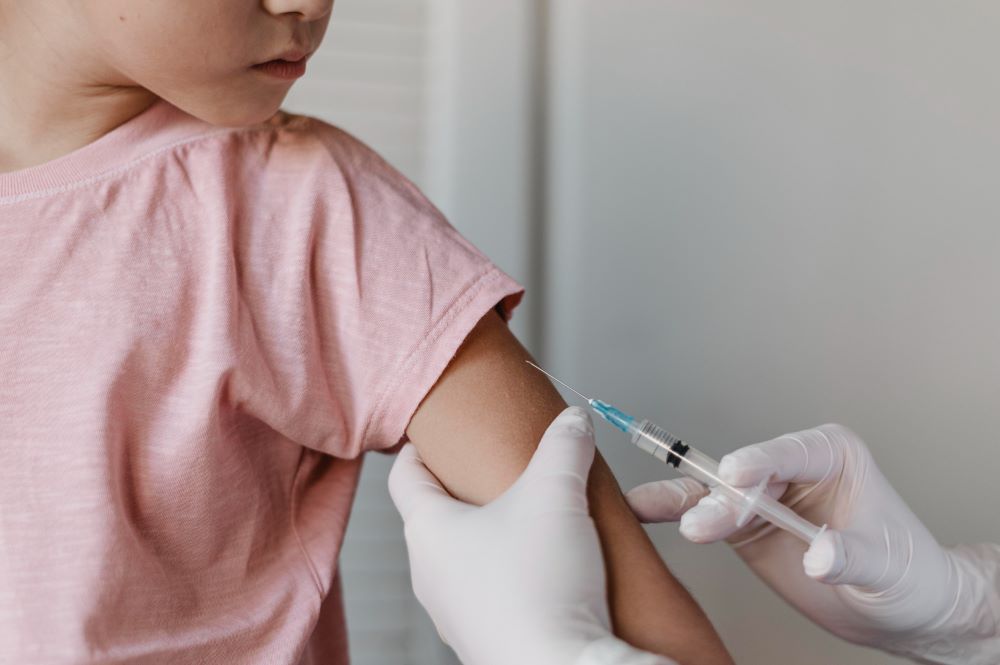
Slimming drug liraglutide is safe and effective in children under 12 years of age
A new study presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), being held in Madrid from September 9-13, and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), has revealed that liraglutide, an anti-obesity drug, is safe and effective in children aged 6-12 years.