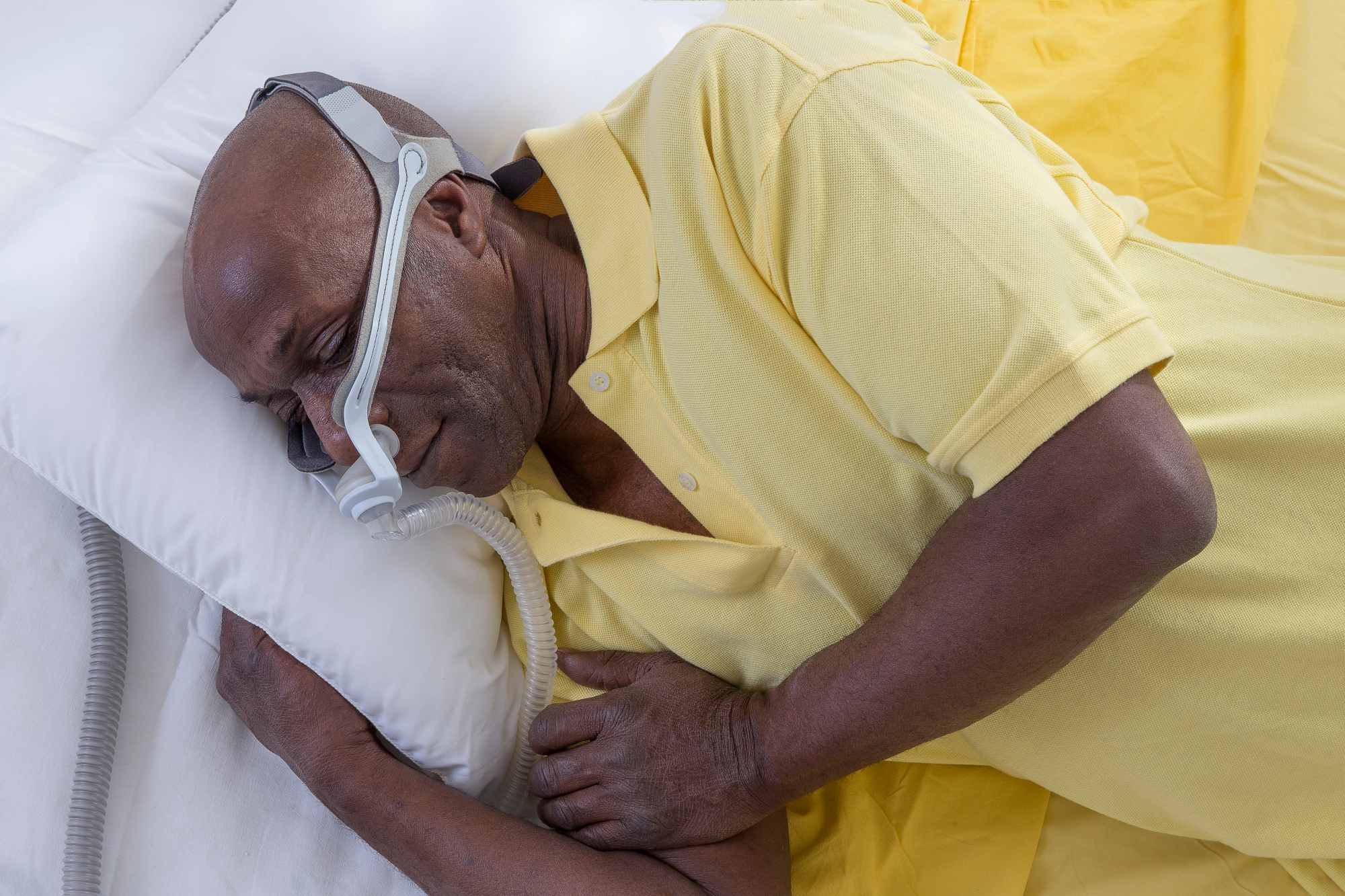
Untreated sleep apnoea is associated with an increased risk of Parkinson's disease, according to data from US war veterans
An investigation published in JAMA Neurology concludes that obstructive sleep apnoea is associated with an increased risk of Parkinson's disease, according to the medical records of more than 11 million American war veterans, mainly men. The article also indicates that this risk can be reduced by early treatment with continuous positive airway pressure, suggesting intervention in sleep-disordered breathing as a strategy for preventing neurological diseases.