Laboratory embryo models developed that produce blood cells
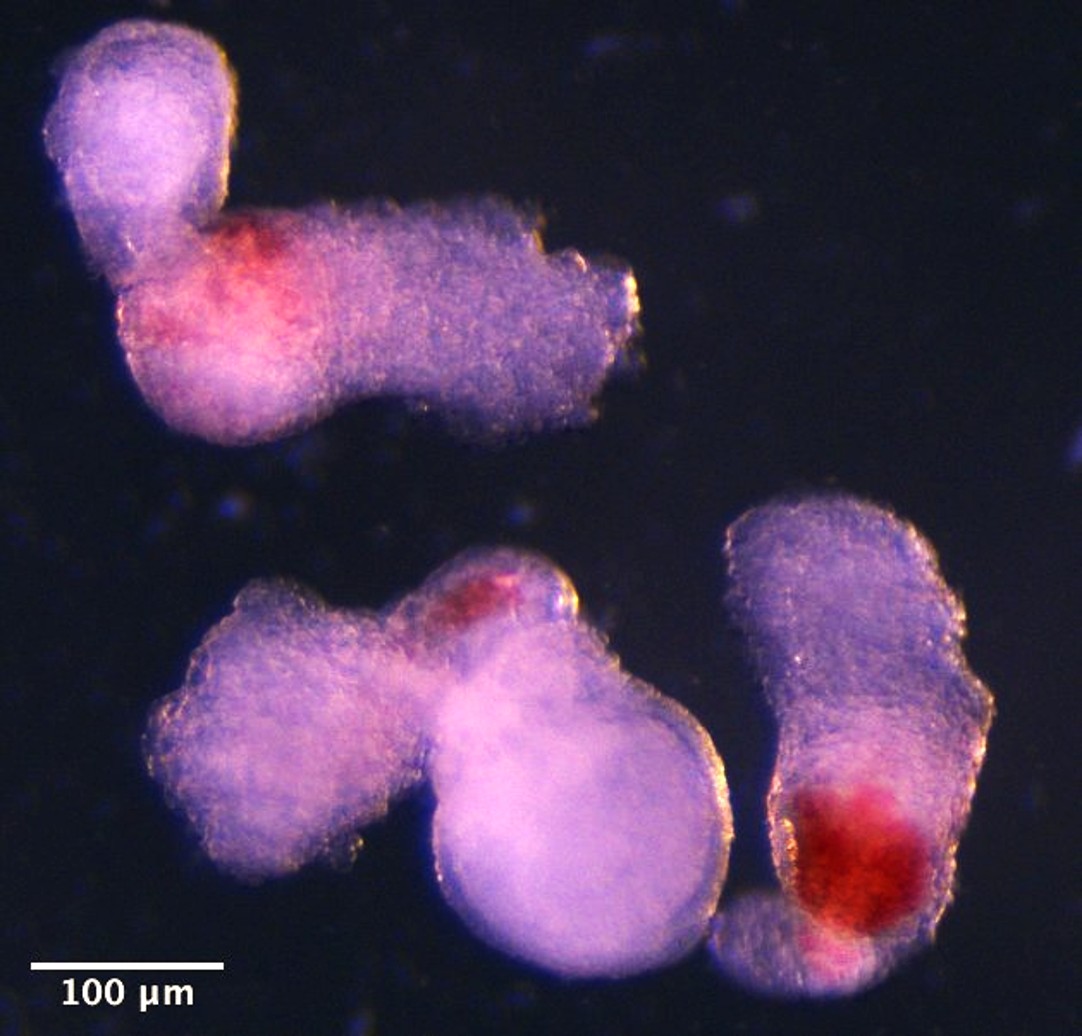
A team led by the University of Cambridge (UK) has used human stem cells to produce three-dimensional embryo-like structures that replicate certain aspects of early development, including, they say, the production of blood stem cells. They have called these structures “hematoids” and, according to the university press release, “they offer great potential for better understanding blood formation during the earliest stages of human development, for simulating disorders such as leukemia, and for producing long-lived blood stem cells for transplantation.” The results are published in the journal Cell Reports.